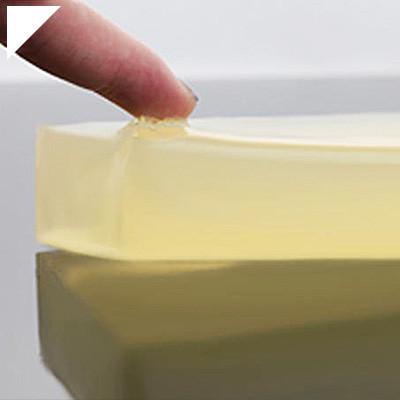
Optical Bonding Adhesive

Optical bonding adhesives have emerged as a remarkable innovation in display technologies, offering a range of captivating features that enhance visual experiences across various electronic devices. These adhesives possess unique characteristics that make them indispensable in manufacturing high-performance displays. Their primary function is attaching a protective layer to a display panel, eliminating the air gap between surfaces. This bonding process minimizes light’s reflection and refraction and significantly enhances optical clarity and visibility, even in challenging lighting conditions.
Optical bonding adhesives are used across diverse industries, from consumer electronics to automotive displays and medical devices. In consumer electronics, these adhesives have paved the way for thinner and sleeker designs while improving sunlight readability and touch sensitivity. Automotive shows integrated with optical bonding enjoy reduced glare and enhanced ruggedness, ensuring safety and comfort for drivers. Additionally, the medical field benefits from enhanced visualization in surgical displays, allowing for precise and accurate procedures. The versatility of optical bonding extends further to outdoor digital signage, avionics, and marine displays, where optimal visibility in harsh environments is essential.
What is Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Optical bonding adhesive is a type of adhesive material used in the manufacturing and assembly of electronic devices with display panels, such as smartphones, tablets, monitors, and other touchscreen devices. The primary purpose of optical bonding is to enhance the optical properties and durability of the display by eliminating the air gap between the display panel and the protective cover, often made of glass or other transparent materials.
The optical bonding process involves applying a specialized adhesive material between the display panel and the cover glass. This adhesive is designed to have excellent optical clarity and refractive index matching properties, which means it minimizes the reflection and refraction of light as it passes through the various layers. By eliminating the air gap and using an adhesive with these optical properties, several benefits are achieved:
- Reduced Reflection:Air gaps between layers can cause reflections and distortions, which degrade the display’s visibility, especially in bright lighting conditions. Optical bonding reduces these reflections, improving readability and image quality.
- Improved Contrast:Minimizing the air gap can enhance the perceived contrast of the display, making images and text appear sharper and more vibrant.
- Durability and Impact Resistance:Optical bonding strengthens the structure of the device by creating a more solid and rigid assembly. This can make the display more resistant to impacts and damage.
- Moisture and Dust Resistance:By sealing the display and cover together, optical bonding can help prevent the ingress of moisture and dust, enhancing the device’s overall durability.
- Touch Sensitivity:Optical bonding can improve touch sensitivity by reducing the distance between the touch sensor and the display, resulting in a more accurate and responsive touch experience.
The choice of adhesive material is critical in optical bonding, as it must provide excellent optical properties and strong bonding characteristics. The adhesive should be transparent, resistant to yellowing over time, and capable of adhering well to glass and display panel substrates. Manufacturers typically use UV-cured or optically clear adhesives (OCAs).
Optical bonding adhesive is crucial in enhancing the visual quality, durability, and functionality of modern electronic devices with displays, contributing to a better user experience.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Work?
Optical bonding adhesive is a specialized type of adhesive used in the manufacturing of electronic devices, especially those with display screens, to improve the visual performance and durability of the device. It is commonly used to bond a protective cover (usually glass or plastic) to the display panel. The primary purpose of optical bonding is to eliminate or reduce the air gap between the surface and the display, thereby enhancing optical properties such as clarity, contrast, and outdoor visibility and improving mechanical robustness.
Here’s how optical bonding adhesive works:
- Preparation: The surfaces to be bonded, which are typically the display panel and the protective cover, are thoroughly cleaned and prepared. Any contaminants or particles that could affect the bonding process are removed.
- Selection of Adhesive: Optical bonding adhesives are chosen based on their optical properties, thermal characteristics, and bonding strength. These adhesives are often optically clear and possess properties that allow them to transmit light effectively without causing distortion or reducing image quality.
- Dispensing: The adhesive is dispensed onto one of the surfaces, either the display panel or the protective cover. The amount of glue used and the dispensing pattern can affect the overall quality of the bonding, including the elimination of air pockets and even the distribution of the adhesive.
- Lamination: The protective cover is carefully placed over the display panel with the adhesive in between. This process requires precision to avoid trapping air bubbles. Some manufacturing setups may use special equipment like vacuum chambers or rollers to ensure proper adhesion and minimize the chances of air entrapment.
- Curing: Optical bonding adhesives are usually designed to be cured, meaning they undergo a chemical or physical change to solidify and reach their full bonding strength. Curing methods can include exposure to UV light, heat, or both, depending on the specific adhesive’s properties.
- Optical Enhancement: As the adhesive solidifies and bonds the cover and the display panel, air gaps that could cause reflections or distortions in the transmitted light are eliminated. This improves optical properties such as reduced glare, increased contrast, and enhanced visibility, especially in bright outdoor environments.
- Mechanical Strength: The adhesive enhances optical performance and increases the mechanical strength of the device. The bond created is capable of withstanding external forces, protecting the display panel from damage due to impacts, vibrations, and other mechanical stresses.
When Should Optical Bonding Adhesive Be Used?
Optical bonding adhesive is used to enhance the performance and durability of visual displays, typically in applications such as touchscreen devices, industrial displays, medical devices, outdoor displays, and more. Optical bonding involves attaching a protective layer, often made of glass or plastic, directly to the display panel using a specialized adhesive. This process offers several benefits, including improved visibility, reduced glare, increased ruggedness, and enhanced optical properties.
Optical bonding adhesive should be used in the following situations:
- Improved Optical Performance: Optical bonding reduces the air gap between the display panel and the protective layer. This minimizes internal reflections and increases the display’s contrast and readability, making it ideal for environments with varying lighting conditions.
- Enhanced Durability and Impact Resistance: The adhesive layer provides extra protection to the display against scratches, impacts, and dust. This is crucial for applications that are exposed to harsh or demanding environments.
- Reduced Glare and Reflection: The air gap between layers minimizes the reflection and glare, making the display more readable even in bright sunlight or high-glare conditions.
- Improved Touch Performance: In touchscreen devices, optical bonding can improve touch accuracy and responsiveness by minimizing the parallax effect caused by the air gap between the display and the touch sensor.
- Water and Dust Resistance: Optical bonding seals the edges of the display, preventing the ingress of water, dust, and other contaminants that could compromise the device’s functionality.
- Vibration and Shock Resistance: In industrial or automotive applications where devices are subject to vibrations and shocks, optical bonding helps prevent delamination and improves the overall durability of the display.
- Thermal Performance: Optical bonding can enhance the display’s ability to dissipate heat, preventing overheating in devices that generate a significant amount of heat.
- Outdoor Applications: Displays used in outdoor environments benefit from optical bonding as they enhance visibility in direct sunlight and protect the display from environmental elements.
- Medical and Healthcare Devices: Optical bonding can be helpful in medical equipment where cleanliness, durability, and visibility are critical factors.
- Aesthetic Improvements: Optical bonding can improve the overall appearance of a display by reducing the visible air gap and providing a sleek, seamless look.
It’s important to note that optical bonding is a specialized process that requires specific equipment, expertise, and controlled conditions. Additionally, the choice of adhesive and materials depends on the application requirements. Before using optical bonding adhesive, it’s recommended to consult with experienced professionals to ensure the best results for your specific application.
Where is Optical Bonding Adhesive Applied?
Optical bonding adhesive is typically applied in the manufacturing process of visual displays, touchscreens, and other similar devices to improve their performance and visibility. Optical bonding involves using a transparent adhesive material between different layers of a display assembly, such as the cover glass, touch sensor, and LCD panel. This process aims to eliminate or reduce the air gap between these layers, which can improve optical characteristics such as contrast, brightness, and outdoor readability. Here are the common layers where optical bonding adhesive is applied:
- Cover Glass: The top layer of the display assembly is often made of durable and scratch-resistant glass. Optical bonding adhesive is applied to the underside of the cover glass before it is attached to the other layers.
- Touch Sensor: Beneath the cover glass, a touch-sensitive layer usually detects user input. The optical bonding adhesive is applied over the touch sensor to bond it to the cover glass.
- LCD Panel: The liquid crystal display (LCD) panel produces the visual content. The LCD panel is positioned beneath the touch sensor, and the optical bonding adhesive attaches it to the other layers.
The optical bonding adhesive fills the gaps between these layers, reducing reflections and improving light transmission. This can enhance display readability, improve outdoor performance, and provide a more seamless appearance.
Optical bonding requires precision to avoid defects such as air bubbles, dust particles, or uneven bonding. It’s commonly used in applications like smartphones, tablets, industrial displays, medical devices, and automotive displays, where display quality and visibility are crucial.
Why is Optical Bonding Adhesive Important for Displays?
Optical bonding adhesive is crucial for displays because it enhances the visual performance and durability of the show in various ways. Optical bonding is a process in which a layer of adhesive material is applied between the display panel (such as an LCD or OLED screen) and the protective cover glass or touch panel. This adhesive layer eliminates the air gap between these components, leading to several significant benefits:
- Improved Optical Clarity: The adhesive used in optical bonding has optical properties that are carefully selected to match those of the display panel and cover glass. By eliminating the air gap and reducing reflections at the interfaces, optical bonding minimizes light loss due to internal thoughts. It increases the display’s brightness, contrast, and visibility in various lighting conditions.
- Reduced Reflectance and Glare: Air gaps between display layers can cause light to reflect off different interfaces, leading to unwanted glare and reduced readability in bright environments. Optical bonding reduces these reflections, resulting in a display with improved readability and reduced glare.
- Enhanced Durability: The adhesive layer adds structural integrity to the display assembly, making it more resistant to physical impacts and environmental stressors. This can prevent the formation of cracks or delamination in the display layers and improve the overall lifespan of the device.
- Improved Touch Sensitivity: Optical bonding can improve touch sensitivity in devices with touch panels by reducing the distance between the touch sensor and the display panel. This can lead to a more responsive touch experience.
- Prevention of Moisture and Dust Ingress: Optical bonding helps seal the display components, preventing moisture, dust, and other particles from infiltrating the space between layers. This enhances the display’s reliability and longevity, especially in challenging environments.
- Enhanced Ruggedness: Devices equipped with optical bonding are more rugged and capable of withstanding harsh conditions, making them suitable for outdoor applications, industrial settings, and other demanding environments.
- Increased Aesthetic Appeal: Optical bonding eliminates the visual artifacts caused by the air gap, such as the “Newton’s rings” effect, which can appear as colorful interference patterns. This results in a more visually appealing display.
- Touch Panel Alignment: When a touch panel is optically bonded, it is precisely aligned with the display panel. This alignment improves touch input accuracy and reduces parallax errors, where the touch point doesn’t align perfectly with the displayed content.
What Are the Advantages of Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Optical bonding adhesive offers several advantages in various applications, particularly in the display and electronics industries. Optical bonding involves adhering a protective glass or plastic layer directly to the surface of a display panel or other optical components. Here are some of the critical advantages of optical bonding adhesive:
1.Improved Optical Performance: Optical bonding eliminates the air gap between the display panel and the protective layer, reducing the reflection and refraction of light at the air-to-glass interface. This results in enhanced contrast, reduced glare, improved readability, and better visual clarity.
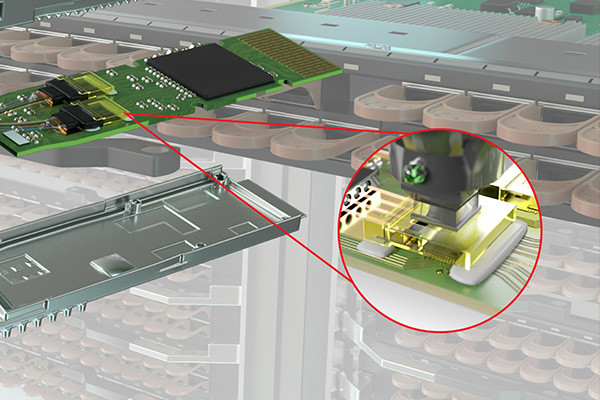
2.Enhanced Durability and Impact Resistance: The adhesive layer provides an additional protective barrier that helps shield the display from external factors such as dust, moisture, and physical impacts. This makes the bonded display more durable and resistant to damage, improving its lifespan in rugged environments.
3.Reduced Parallax Effect: Parallax occurs when the apparent position of an object varies depending on the viewing angle. Optical bonding reduces or eliminates the parallax effect, ensuring that the displayed content maintains its accuracy and alignment, even when viewed from oblique angles.
4.Better Touch Performance: Optical bonding adhesive can improve touch accuracy and responsiveness when used in touch-sensitive displays. This is because reducing the air gap between the touch sensor and the display surface minimizes the distance a touch input needs to travel.
5.Vibration and Shock Resistance: In applications where displays or optical components are subject to vibrations or shocks, optical bonding can help prevent delamination or separation of layers. This is crucial in automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment industries.
6.Improved Thermal Conductivity: Some optical bonding adhesives have good thermal conductivity properties, which can help dissipate heat generated by the display or other components. This prevents overheating and ensures consistent performance, especially in high-demand applications.
7.Enhanced Outdoor Visibility: Displays bonded with optical adhesive are better suited for outdoor environments where direct sunlight or bright ambient light can make screens difficult to read. In contrast, the reduction of reflections and the overall improvement contribute to better visibility under challenging lighting conditions.
8.Sealing Against Environmental Factors: Optical bonding can create a seal that protects the internal components of a device from moisture, dust, and other contaminants. This is especially important in outdoor or industrial applications.
9.Customization and Aesthetics: Optical bonding can combine multiple layers, such as a touch sensor, display panel, and cover glass, into a single unit. This can lead to sleeker and more aesthetically pleasing designs while maintaining functionality.
10.High-Quality User Experience: Reduced reflections, improved readability, and enhanced touch responsiveness contribute to a better user experience, making products more engaging and user-friendly.
It’s worth noting that while optical bonding offers these advantages, it also requires specialized equipment and expertise for proper implementation. The choice of adhesive and bonding process should be carefully considered based on the application’s specific requirements.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Enhance Display Clarity?
Optical bonding adhesive is a technology used to enhance the clarity and performance of displays, particularly in applications like touchscreen devices, outdoor displays, and industrial equipment. It involves applying a specialized adhesive layer between the display panel and the protective cover glass or touchscreen surface. This adhesive layer helps improve the overall display quality in several ways:
- Reduction of Reflections:When light passes through different mediums with varying refractive indices (how much light bends when transitioning from one medium to another), some light gets reflected at the interface between these mediums. This reflection can cause glare and reduce display visibility, especially in bright environments. Optical bonding reduces the number of interfaces that light has to pass through, minimizing reflections and enhancing visibility.
- Elimination of Air Gap:Without optical bonding, there is typically an air gap between the display panel and the cover glass or touchscreen surface. This air gap can cause two main problems: First, it can cause a phenomenon known as “parallax,” where the displayed image appears displaced from where the user touches the screen. Second, the air gap can cause internal reflections that reduce display clarity. Optical bonding eliminates this air gap, improving touch accuracy and display clarity.
- Reduction of Internal Reflections:In displays without optical bonding, light can bounce between the display panel, the cover glass, and any air gaps. This bouncing of light, or internal reflections, can lead to a washed-out appearance and reduced contrast. Optical bonding minimizes these internal reflections, improving color vibrancy and contrast.
- Enhanced Durability:The adhesive used in optical bonding serves visual purposes and acts as a protective layer for the display. It helps prevent dust, moisture, and other contaminants from entering the gap between the production and the cover glass. This improves the durability and longevity of the display assembly, especially in rugged environments.
- Improved Impact Resistance:The adhesive layer in optical bonding can add an extra layer of structural integrity to the display assembly, making it more resistant to impacts and mechanical stress. This is particularly important in applications where the display might be subject to physical abuse or vibrations.
- Better Thermal Performance:Optical bonding can help dissipate heat more effectively. Without air gaps, heat generated by the display is conducted more efficiently through the materials, reducing the risk of overheating and maintaining consistent performance.
What Are the Different Types of Optical Bonding Adhesives?
Optical bonding adhesives attach optical components, such as displays, touchscreens, and protective glass, to various devices while minimizing air gaps and improving visual performance. Several types of optical bonding adhesives are available, each with specific characteristics suited for different applications. Here are some common types:
- Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive (LOCA):LOCA is an adhesive that is applied in liquid form and then cured to form a transparent, solid layer between the optical components. It is widely used in touchscreen displays and smartphones. LOCA adhesives are UV-curable and offer good optical properties like clarity and transparency.
- Dry Film Adhesives:Dry film adhesives are pre-cured adhesive sheets placed between optical components and bonded using heat and pressure. They are easy to handle and can provide good bonding with minimal mess. Dry film adhesives are commonly used in display bonding applications.
- Optical Clear Resin (OCR):Optical clear resins are UV-curable materials that provide strong bonding and excellent optical properties. They are often used in applications where high optical clarity and durability are required, such as outdoor displays or ruggedized devices.
- Optically Clear Silicone (OCA):Optically clear silicone adhesives offer flexibility and durability, making them suitable for curved displays or applications where the components might experience mechanical stress. They are also known for their resistance to yellowing over time.
- Dual-Cure Adhesives:These adhesives combine both UV curing and chemical curing mechanisms. They can offer faster curing times and better adhesion compared to UV-curing alone. Dual-cure adhesives are used in applications where speed and performance are required.
- Acrylic Adhesives:Acrylic adhesives are known for their fast curing times and strong adhesion properties. They are used in applications where optical clarity is less critical and rapid assembly is necessary.
- Epoxy Resins:Epoxy adhesives provide excellent bonding strength and durability. They are often used in applications where high mechanical stability and resistance to environmental factors are essential.
- Thermal Cure Adhesives:These adhesives cure at elevated temperatures and are often used in industrial applications where heat can aid the curing process. They offer good bonding strength and reliability.
- Conductive Adhesives:In some cases, optical bonding may also require electrical conductivity. Conductive adhesives are used when components must be optically bonded and electrically connected.
When selecting an optical bonding adhesive, factors such as the optical properties (transparency, clarity, refractive index matching), mechanical properties (flexibility, rigidity), curing method (UV, heat, chemical), and intended application environment should be considered, it’s essential to choose an adhesive that best meets the specific requirements of your application to achieve optimal performance and longevity.
How to Choose the Right Optical Bonding Adhesive for a Specific Application?
Choosing the suitable optical bonding adhesive for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and durability. Optical bonding is adhering a protective cover glass or touch panel to a display to improve readability, reduce glare, enhance ruggedness, and improve the overall user experience. Here are the key steps to help you select the appropriate optical bonding adhesive:
- Application Requirements:Identify the specific requirements of your application, such as display type, environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, exposure to UV light, etc.), expected operating lifespan, optical clarity, and bonding strength.
- Substrate Materials:Know the materials you are bonding. Different adhesive formulations may be needed for bonding glass-to-glass, glass-to-plastic, or glass-to-ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) coated displays.
- Optical Properties:Consider the visual performance required for your application. Some adhesives may have lower refractive indices, reducing the chance of optical distortion and glare.
- Adhesive Transparency:Choose an adhesive that maintains high transparency to prevent compromising the display’s visual quality.
- Bonding Strength:The adhesive must provide a solid bond to ensure the display and cover glass remain firmly attached even under mechanical stress.
- Thermal Stability:Check the adhesive’s thermal stability and compatibility with the bonded materials, especially if the application involves exposure to high temperatures or thermal cycling.
- UV Resistance:If the application involves outdoor or prolonged exposure to UV light, choose an adhesive that offers UV resistance to prevent degradation over time.
- Curing Method:Understand the curing method required by the adhesive. Some adhesives cure under UV light, while others need heat or chemical curing.
- Application Process:Evaluate the practicality of the adhesive’s application process. Some bonds require specialized equipment, controlled environments, or specific handling procedures.
- Cost Considerations:Balancing performance and cost is essential. High-performance adhesives may be more expensive but worth the investment for critical applications.
- Vendor and Technical Support:Choose a reputable adhesive manufacturer or supplier with technical support, guidance, and expertise to help you choose the suitable adhesive for your specific application.
- Testing and Prototyping:Conduct thorough testing and prototyping before full-scale production. This ensures that the chosen adhesive performs as expected under actual operating conditions.
- Long-Term Reliability:Consider the long-term reliability and durability of the adhesive bond. Factors such as resistance to moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress play a role in the adhesive’s lifespan.
- Regulatory and Environmental Compliance:Ensure the selected adhesive complies with relevant regulations and standards and consider its environmental impact.
- Documentation and Warranty:Check if the adhesive manufacturer provides comprehensive documentation, including application guidelines and warranty information.
Remember that each application is unique and might not be a one-size-fits-all solution. Engaging with adhesive experts and conducting thorough testing will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific requirements and ensures the success of your optical bonding project.
What Are the Challenges Associated with Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Optical bonding adhesive is used to bond various layers of a visual display or touchscreen module, enhancing visual performance and durability. However, there are several challenges associated with this process:
- Bubbles and Imperfections: During the bonding process, air bubbles or other imperfections can get trapped between the layers, leading to optical distortions, reduced visibility, and touch sensitivity issues. Proper vacuum and curing procedures are required to minimize this risk.
- Dust and Contamination: Even a tiny particle of dust or contaminants between the layers can negatively impact optical quality. Special cleanroom conditions and careful handling are necessary to prevent these issues.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: The curing process of optical bonding adhesive often involves specific temperature and humidity conditions. Variations in these parameters can result in inconsistent bonding quality, affecting the overall performance and durability.
- Refraction and Reflection: The refractive index of the adhesive must be carefully matched with the refractive indices of the bonded materials to minimize reflection and refraction. The mismatched index can lead to glare, ghosting, and reduced visibility.
- Adhesive Thickness and Uniformity: Achieving a consistent adhesive layer thickness across the display is challenging. Variations in viscosity can lead to optical distortions and affect touch sensitivity.
- Thermal Expansion: Different materials used in displays and touch screens can have varying coefficients of thermal expansion. This can cause stress and delamination in the adhesive during temperature fluctuations, potentially leading to decreased performance and long-term durability.
- Bonding Process Complexity: Optical bonding is a precise and often labor-intensive process. Skilled personnel and specialized equipment are required to ensure proper alignment, application, and adhesive curing.
- Repair and Replacement: If a bonded module requires repair or replacement of a component, separating the layers can be complicated without damaging the display or the adhesive. This can result in increased repair costs and potential downtime.
- Cost and Scalability: The materials and processes involved in optical bonding can be expensive, making it challenging to implement on a large scale. Cost-effectiveness and scalability are important considerations for manufacturers.
- Compatibility with Display Types: Different displays, such as LCD, OLED, and e-ink, have unique characteristics and requirements. Adhesive selection and bonding parameters must be carefully tailored to match the specific display technology.
- Environmental Considerations: The chemicals used in optical bonding adhesives can have ecological implications. Manufacturers need to consider the environmental impact of these materials and ensure proper disposal and recycling practices.
- Testing and Quality Control: Ensuring consistent optical performance across batches and units requires rigorous testing and quality control measures. This includes checking for uniformity, clarity, touch sensitivity, and other vital parameters.
To produce high-quality optical bonding results, addressing these challenges requires technical expertise, advanced manufacturing processes, and quality assurance protocols.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Impact Outdoor Displays?
Optical bonding adhesive can significantly impact outdoor displays, especially in terms of visibility, durability, and overall performance. Optical bonding is a process where a layer of adhesive is applied between the display panel and the cover glass or touchscreen. This process serves several purposes, and its impact on outdoor displays is as follows:
1.Enhanced Visibility:One of the main benefits of optical bonding is the reduction of reflections and glare on the display surface. The adhesive fills the gap between the display panel and the cover glass, eliminating the air gap that can cause light to scatter and reflect. This results in improved sunlight readability and reduced reflections, making the display more visible in bright outdoor environments.

- Improved Durability:The adhesive used in optical bonding acts as a protective layer between the display and the external environment. It helps to prevent dust, moisture, and other contaminants from entering the gap between the panel and the cover glass. This enhanced protection can extend the display’s lifespan by minimizing the potential for damage caused by these environmental factors.
- Resistance to Vibrations and Impact:Outdoor displays are often subjected to various vibrations and potential impacts, especially in industrial or outdoor settings. Optical bonding can enhance the display’s ability to withstand these vibrations and effects, as the adhesive layer helps to stabilize and reinforce the display assembly.
- Improved Touch Performance:Optical bonding can improve touch accuracy and responsiveness if the outdoor display is a touchscreen. Eliminating the air gap reduces parallax error (the difference between the point of contact and the actual displayed content). It improves the overall touch experience, making it more accurate and user-friendly.
- Reduced Condensation and Fogging:In humid or fluctuating temperatures, condensation can occur within the air gap of non-bonded displays, leading to fogging and reduced visibility. Optical bonding helps mitigate this issue by sealing the gap and preventing moisture from accumulating between the layers.
- Resistance to Extreme Temperatures:Some optical bonding adhesives are designed to withstand various temperatures, including high and low extremes. This makes the display suitable for outdoor installations with significant temperature variations.
- Customization and Aesthetics:Optical bonding can also customize the display’s appearance. The adhesive layer can be tinted or treated to improve contrast and color vibrancy, enhancing the overall visual experience.
It’s important to note that while optical bonding offers several advantages for outdoor displays, there may also be some challenges. The process can add extra cost to the manufacturing process, and improper bonding techniques can lead to issues such as trapped air bubbles or uneven bonding, which can negatively affect display quality.
What Industries Benefit from Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Optical bonding adhesive is a technology used to improve the performance of displays and screens, particularly in outdoor or high-ambient-light environments. It involves bonding a protective layer directly to the display surface, reducing reflections, improving contrast, and enhancing visibility. Several industries can benefit from optical bonding adhesive technology:
- Consumer Electronics:Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other portable devices benefit from improved screen visibility in various lighting conditions. The enhanced display performance provides better user experiences.
- Automotive:In-vehicle displays, such as infotainment systems, navigation screens, and head-up displays, can be difficult to read under direct sunlight. Optical bonding adhesive improves visibility, making these displays safer and more usable for drivers.
- Aviation and Aerospace:Cockpit displays, aircraft cabin entertainment screens and avionic displays can all benefit from optical bonding adhesive. Improved visibility helps pilots and passengers interact with these displays more effectively.
- Marine:Onboard displays, navigation systems, and communication screens on boats and ships can be exposed to bright sunlight and harsh environments. Optical bonding enhances screen performance and durability.
- Medical Devices:Medical equipment with displays, such as ultrasound machines, patient monitors, and surgical navigation systems, can provide better visual information to healthcare professionals using optical bonding adhesive.
- Industrial Equipment:Displays used in industrial settings, such as machinery control panels and outdoor kiosks, benefit from improved visibility and durability by optical bonding adhesive.
- Digital Signage:Outdoor and indoor digital signage displays can attract more attention and deliver more explicit messages with reduced glare and increased contrast.
- Military and Defense:Military applications often require displays that can perform reliably in diverse environments. Optical bonding adhesive can improve the visibility and ruggedness of displays used in tactical situations, military vehicles, and command centers.
- Gaming and Entertainment:Handheld gaming devices, gaming consoles, and VR headsets can provide better visual experiences to users with the help of optical bonding adhesive.
- Retail:Point-of-sale systems, interactive kiosks, and self-service checkout displays in retail environments can benefit from improved screen visibility and durability.
- Outdoor Displays:Public information displays, outdoor advertising boards, and interactive displays in public spaces can provide more precise information and interactivity with reduced glare.
- Telecommunications:Network monitoring screens, equipment displays, and communication devices can be used more effectively with improved screen visibility.
Optical bonding adhesive can be beneficial in any industry where clear and readable displays are essential, especially when exposed to challenging lighting conditions or harsh environments. It’s important to note that the specific benefits and applications may vary depending on the type of optical bonding technology used and the particular requirements of each industry.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Improve Touchscreen Performance?
Optical bonding adhesive is a technology used to improve the performance of touchscreens and other display devices. It involves the application of a transparent adhesive material between the display panel and the outer protective layer (usually glass or plastic). This process offers several benefits that enhance touchscreen performance:
- Reduction of Reflections and Glare: The adhesive layer minimizes the air gap between the display and the cover glass, reducing the number of surfaces light must pass. This reduces the reflection and glare caused by the air gap, resulting in improved visibility and readability in various lighting conditions.
- Increased Contrast and Clarity: By eliminating the air gap between the layers, optical bonding reduces the refraction of light at the interface, which can otherwise scatter light and reduce contrast and clarity. This leads to crisper images and text, enhancing the overall visual experience.
- Enhanced Durability and Impact Resistance: Optical bonding strengthens the display structure by creating a solid and rigid composite. This enhances the durability and impact resistance of the touchscreen, making it more resistant to cracks, scratches, and other forms of damage.
- Improved Touch Sensitivity and Accuracy: Reducing the air gap between layers can enhance touch sensitivity and accuracy. With less space for light to scatter and refract, the touchscreen’s sensors can more accurately detect touch points, resulting in better responsiveness.
- Elimination of Air Pockets and Dust: Traditional displays often have tiny air pockets or particles trapped between layers, distracting and affecting touch performance. Optical bonding eliminates these issues by ensuring a seamless and tight bond between the layers, preventing the entry of dust and the formation of air pockets.
- Water and Moisture Resistance: Optical bonding can improve the display’s water and moisture penetration resistance. This can be particularly beneficial for outdoor applications or devices used in environments where exposure to water is a concern.
- Reduced Parallax Effect: Parallax is the apparent displacement or difference in the position of an object viewed from different angles. Optical bonding can minimize this effect, which can be important for applications where precise alignment and accuracy are crucial, such as interactive displays or drawing tablets.
Optical bonding adhesive helps optimize user interaction and touchscreens by providing a more vibrant, durable, and responsive display experience. It’s precious for applications where image quality, durability, and touch performance are critical, such as industrial equipment, medical devices, digital signage, and consumer electronics.
What is the Role of Refractive Index in Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Refractive index plays a crucial role in optical bonding adhesives, especially in display technologies like touchscreens, LCDs (liquid crystal displays), and other optical devices. Optical bonding is a process where an adhesive material is used to bond optical components like glass or plastic covers to display panels or other visual elements. The primary purpose of optical bonding is to enhance the visual performance and durability of the display assembly. Here’s how the refractive index is relevant in this context:
- Reducing Reflections: When light passes through different mediums with varying refractive indices, a portion of the light gets reflected at the interface due to the difference in the speed of light. This reflection can cause unwanted glare and reduce the display’s contrast and overall image quality. By using an adhesive with a refractive index that closely matches that of the optical components it’s bonding (like the display panel and the cover glass), reflections at the interface can be minimized. This results in improved visibility, better contrast, and reduced glare for the viewer.
- Eliminating Air Gaps: When an adhesive with a refractive index closely matching that of the optical components is used, it reduces the occurrence of air gaps between the components. Air gaps can lead to additional reflections and refractions at the interfaces, degrading the optical quality of the display. An adequately matched refractive index helps minimize these air gaps and maintain consistent light transmission through the assembly.
- Increasing Optical Efficiency: Optical bonding maximizes the light that travels from the display panel to the viewer’s eyes. By minimizing reflections and refractions caused by index mismatches, the optical efficiency of the display is improved, resulting in a brighter and more vibrant image.
- Enhancing Durability: A well-bonded assembly with minimal air gaps is more resilient to environmental factors like moisture and dust ingress. The adhesive’s refractive index can influence the adhesive’s bonding strength and long-term stability, ensuring that the display assembly remains durable and functional over time.
- Touchscreen Performance: Optical bonding can enhance touch accuracy and responsiveness in devices with touchscreens, such as smartphones and tablets. A consistent refractive index throughout the display assembly helps maintain touch-sensing accuracy by reducing interference from reflections and refractions.
How to Ensure Proper Curing of Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Properly curing optical bonding adhesive is crucial for achieving optimal visual performance and the desired mechanical properties. Optical bonding attaches optical components like displays, touch screens, or protective glass to a device’s surface, reducing reflections and improving readability. Here’s how you can ensure the proper curing of optical bonding adhesive:
- Choose the Right Adhesive: Select an adhesive designed for optical bonding applications. These adhesives usually have low refractive indices and are optimized for optical clarity. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for adhesive selection.
- Clean the Surfaces: Before applying the adhesive, make sure that the surfaces to be bonded are thoroughly cleaned. Any dust, oils, or contaminants can affect the bonding quality. Use approved cleaning solutions and techniques to ensure a pristine surface.
- Apply Uniform Thickness: Apply the adhesive evenly and consistently across the bonding area. Too much adhesive can lead to excess stress and non-uniform curing, while too little adhesive may result in poor adhesion or optical performance.
- Minimize Air Bubbles: Air bubbles trapped between the adhesive and the surfaces can lead to uneven optical properties and weaken the bond. Use vacuum equipment or techniques to remove air bubbles during the application process.
- Control Environmental Conditions: Adhesive curing can be affected by temperature, humidity, and exposure to light. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended environmental conditions during the curing process. Usually, controlled environments with controlled temperature and humidity are preferred.
- Use Proper Curing Equipment: Depending on the adhesive used, different curing methods are available. UV curing is a common technique where the adhesive is exposed to ultraviolet light to initiate the curing process. Follow the recommended UV intensity and exposure time provided by the adhesive manufacturer. Some adhesives require thermal curing in an oven or other specialized equipment.
- Monitor Curing Process: Regularly monitor the process to ensure the adhesive is curing uniformly and as intended. This might involve using UV meters to measure UV intensity or thermal sensors for temperature monitoring.
- Post-Cure Inspection: After the curing process is complete, inspect the bonded components for any defects, such as uneven curing, air bubbles, or contamination. Address any issues before moving forward.
- Allow Sufficient Curing Time: Follow the adhesive manufacturer’s recommended curing time. Rushing the curing process can result in incomplete curing and suboptimal bonding properties.
- Test Optical Performance: After curing, test the optical properties of the bonded components to ensure that the desired improvements in optical clarity and reduced reflections have been achieved. Use appropriate testing equipment to measure relevant parameters.
- Adhere to Safety Precautions: There might be safety considerations to consider depending on the adhesive type. Some adhesives emit fumes during curing, so ensure proper ventilation and use protective equipment.
Remember that the specifics of the curing process can vary based on the adhesive you’re using, the equipment available to you, and the application requirements. Always consult the adhesive manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the best results.
What Factors Affect the Durability of Optical Bonding Adhesive?
The durability of optical bonding adhesive, which is used to bond various layers in optical display assemblies, is influenced by several factors. These factors can impact the overall performance and longevity of the connected components. Some key factors affecting the durability of optical bonding adhesive include:
1.Adhesive Selection: The choice of adhesive is crucial. Bonds designed for optical bonding typically have properties that minimize light scattering, maximize light transmission, and exhibit good adhesion to different materials. The adhesive’s chemical composition, curing mechanism, and compatibility with the bonded substrates affect its durability.

2.Substrate Compatibility: The adhesive must be compatible with the bonding materials, including glass, plastics, and other optical elements. Incompatible materials can lead to adhesive degradation or reduced adhesion strength over time.
3.Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential for achieving adhesive solid bonds. Characters must be cleaned thoroughly to remove contaminants, oils, or residues that could interfere with bonding. Surface treatments like plasma cleaning or primers might be necessary to enhance adhesion.
4.Curing Process: Adhesives typically require a curing process to achieve their full strength. The curing conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and curing time, can significantly impact the final bond’s strength and durability. Improper curing can lead to weak sealants that degrade over time.
5.Environmental Conditions: The operating environment of the bonded components plays a crucial role in adhesive durability. Factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity, exposure to UV radiation, and mechanical stress can all impact the adhesive’s integrity. Adhesives formulated to withstand specific environmental conditions should be chosen for optimum durability.
6.Thermal Expansion Coefficients: Different materials expand and contract at different rates when exposed to temperature changes. Mismatched thermal expansion coefficients between bonded materials can cause stress at the adhesive interface, potentially leading to bond failure or reduced durability.
7.Mechanical Stress: Vibrations, shocks, and mechanical loads applied to the bonded components can cause stress concentrations at the adhesive layer. Adhesives with good flexibility and resistance to mechanical stress are more likely to maintain their integrity over time.
8.UV Stability: If the optical assembly is exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet (UV) radiation sources, the UV stability of the adhesive is crucial. UV exposure can cause some adhesives to degrade or discolor, reducing optical performance and bond strength.
9.Chemical Resistance: The adhesive should resist chemicals encountered during the device’s regular operation or maintenance. Chemical exposure can weaken the glue and compromise the bond’s durability.
10.Quality of Application: The application process itself is crucial. Proper adhesive dispensing, uniform layer thickness, and controlled pressure during bonding are all factors that can affect the overall quality and durability of the bond.
11.Aging and Degradation: Over time, even the most durable adhesives can experience aging and degradation due to environmental factors, temperature cycles, and other stressors. Choosing a bond with good long-term stability can help mitigate these effects.
It’s important to carefully select the correct adhesive formulation, consider the specific operating conditions, and follow proper bonding procedures during manufacturing to ensure the highest durability of optical bonding adhesive.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Resist Environmental Stressors?
Optical bonding adhesive is a specialized adhesive used to bond optical components like displays or touchscreens to their protective cover glass or other substrates. This process helps improve the visual performance and durability of the device. Optical bonding adhesive is designed to resist various environmental stressors to ensure the longevity and reliability of the bonded components. Here’s how optical bonding adhesive accomplishes this:
- Physical Protection: Optical bonding adhesive forms a layer between the optical components and the cover glass or substrate. This physical barrier helps protect sensitive optical components from dust, moisture, and other contaminants present in the environment. By sealing off the details, the adhesive minimizes the risk of environmental factors causing damage or degradation.
- Moisture and Dust Resistance: Optical bonding adhesive is formulated to be moisture-resistant and prevent dust particles’ intrusion. It creates an airtight seal that prevents moisture from penetrating the device, which can lead to corrosion, electrical short-circuits, and other forms of damage. Dust resistance helps maintain optical clarity and prevents particles from interfering with the display’s performance.
- Vibration and Shock Absorption: Environmental stressors like vibrations and shocks can impact the structural integrity of devices and their components. Optical bonding adhesive is designed to have sound vibration and shock absorption properties, which helps minimize the impact of these stressors on the bonded parts. This is especially important in applications where the device might experience frequent movement or effects.
- Temperature Variations: Temperature fluctuations can cause materials to expand and contract, potentially leading to delamination or other structural issues. Optical bonding adhesive is engineered to have a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is well-matched to the materials it is bonding. This reduces the likelihood of delamination or detachment due to temperature changes.
- UV and Sunlight Resistance: Some environments expose devices to direct sunlight or UV radiation, which can degrade materials over time. Optical bonding adhesive is often formulated to resist UV degradation, ensuring that it maintains its adhesive properties and optical clarity even when exposed to sunlight for extended periods.
- Chemical Resistance: Certain environments might contain chemicals or solvents that weaken or dissolve adhesives. Optical bonding adhesive is often resistant to various chemicals, protecting the bond and the optical components from damage.
- Optical Performance: Besides its protective qualities, optical bonding adhesive is designed to have minimal impact on visual performance. It aims to eliminate air gaps between components, reducing internal reflections and improving contrast and visibility in high ambient light conditions.
What Future Innovations Can We Expect in Optical Bonding Adhesive Technology?
Remember that developments beyond that date may not be covered in this response. Optical bonding is a technique used to enhance the performance of displays by reducing air gaps between layers, improving readability and durability. Here are some potential directions for innovation:
- Improved Optical Clarity: Researchers might focus on developing adhesives with even higher transparency and lower haze, ensuring minimal distortion of the displayed content. This could involve advancements in material science to create bonds with superior light transmission properties.
- Thinner Bonding Layers: Future innovations could create thinner adhesive layers while maintaining strong bonding properties. Thinner layers reduce weight, increase flexibility, and allow more compact device designs.
- Enhanced Durability and Reliability: Adhesive technology could be improved to withstand a broader range of environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to UV radiation. This would result in functional and visually appealing displays for extended periods.
- Flexible Displays: As flexible and foldable displays become more common, optical bonding adhesives must adapt to these new form factors. Innovations might focus on developing bonds that maintain performance even with repeated bending and flexing.
- Anti-Reflective and Anti-Glare Properties: Adhesives with built-in anti-reflective or anti-glare properties could become more prevalent, enhancing outdoor visibility and reducing reflections in bright environments.
- Faster Curing Times: Shorter curing times for optical bonding adhesives could increase production efficiency, ultimately reducing manufacturing costs and increasing overall throughput.
- Compatibility with New Display Technologies: As new display technologies emerge, such as micro LEDs and OLED, optical bonding adhesives will need to adapt to the unique requirements of these technologies. This might involve considerations like higher thermal resistance and compatibility with organic materials.
- Customization and Application Techniques: Future innovations could involve the development of adhesives that can be tailored to specific devices or display configurations. New application techniques might also be explored to ensure consistent and uniform bonding across different display types.
- Environmental Considerations: With a growing focus on sustainability, future adhesive technologies may emphasize using materials that are more environmentally friendly, biodegradable, or recyclable.
- Advanced Testing and Quality Control Methods: Testing and quality control innovations could lead to more reliable and consistent bonding results, reducing the likelihood of defects and improving overall product quality.
Remember that technological advancement can be rapid, and breakthroughs might have occurred since my last update.
How Does Optical Bonding Adhesive Compare to Other Display Enhancement Techniques?
Optical bonding adhesive is a technique used to enhance displays’ visual quality and durability, particularly in applications where arrays are exposed to challenging environments or need to provide high visibility. This technique involves bonding a protective glass or plastic layer directly onto the display panel using a unique adhesive, eliminating the air gap between the layers. This process has several advantages and disadvantages compared to other display enhancement techniques. Here’s a comparison:
Advantages of Optical Bonding:
- Improved Optical Performance:Optical bonding reduces or eliminates the air gap between the display panel and the protective layer, minimizing reflections and increasing the overall clarity, brightness, and contrast of the display. This leads to better sunlight readability and improved viewing angles.
- Durability and Impact Resistance:The bonded layers create a more rugged display less prone to damage from impacts, vibrations, and moisture. This makes it suitable for outdoor, industrial, and high-impact environments.
- Reduced Internal Reflections:The adhesive in optical bonding can have anti-reflective properties, reducing internal reflections and improving visual experience.
- Dust and Moisture Protection:The bonding process seals the display panel, protecting it from dust, moisture, and other contaminants that can negatively impact display performance.
- Thermal Stability:Optical bonding can enhance the display’s thermal performance by improving heat dissipation, which is beneficial for shows in environments with varying temperatures.
Disadvantages of Optical Bonding:
- Cost:Optical bonding is generally more expensive than other techniques due to the additional manufacturing steps, specialized equipment, and materials.
- Complex Manufacturing Process:Optical bonding requires careful calibration and precise manufacturing processes to avoid defects such as bubbles or inconsistencies in the adhesive layer.
- Thickness and Weight:The bonded layers can add thickness and weight to the display, which may only be suitable for some applications.
- Repair Difficulty:If a display with optical bonding is damaged, repair or replacement can be more complex and costly than non-bonded displays.
Comparison with Other Enhancement Techniques:
- Anti-Glare/Anti-Reflective Coatings:These coatings reduce reflections and improve visibility in bright environments. However, they may provide a different impact protection or durability level than optical bonding.
- Sunlight Readability Enhancements:These techniques involve increasing the display’s brightness to enhance visibility in direct sunlight. While they can improve readability, they may not address other durability or impact-related concerns.
- Waterproof and Dustproof Enclosures:These solutions protect displays by enclosing them in sealed, protective cases. While they offer protection, they can add bulk and reduce overall design aesthetics.
- High Brightness Displays:These displays are designed with exceptionally high brightness levels to enhance outdoor visibility. However, they may not address issues such as reflections or impact resistance.
What Are the Cost Considerations for Implementing Optical Bonding Adhesive?
Implementing optical bonding adhesive involves several cost considerations that can impact a project’s overall budget. Optical bonding is a process in which a transparent adhesive is used to bond a display panel (LCD, OLED, etc.) to a cover glass or touch sensor, reducing reflections and improving the optical performance. Here are some cost considerations to keep in mind:
- Adhesive Material Cost: The cost of the optical bonding adhesive itself is a significant factor. Higher-quality adhesives with better optical properties and durability might come at a higher price. Choosing a bond that meets your project’s requirements while fitting within the budget is essential.
- Volume and Application Method: The adhesive required for your project will impact costs. Larger displays or higher production quantities will require more adhesive material. Additionally, the method of applying the glue, whether it’s manual or automated, can affect labor costs and consistency.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs can include skilled labor for the bonding process and any preparation work, such as cleaning the surfaces and aligning components. More intricate or delicate displays require more time and skill to achieve accurate bonding.
- Equipment and Machinery: Implementing optical bonding might require specialized equipment for applying the adhesive, aligning the components, and curing the adhesive. The cost of acquiring, maintaining, and operating this equipment should be factored into the budget.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential for adequate optical bonding. Cleaning, treating, and ensuring the characters are free from contaminants can incur additional costs in terms of materials and labor.
- Testing and Quality Control: Testing the bonded displays for quality and durability is crucial. This might involve specialized equipment and skilled personnel to ensure the related components meet the required optical and mechanical standards.
- Waste and Yield Loss: There might be adhesive wastage or yield loss due to imperfect bonds during the bonding process. This could impact the overall cost-effectiveness of the process.
- Material Compatibility: Compatibility between the adhesive, display panel, and cover glass is essential for long-term reliability. Opting for materials that work well together might involve higher costs but can prevent issues.
- Project Scale: The scale of your project can influence costs. Larger quantities lead to bulk discounts on adhesive materials or more favorable pricing on equipment.
- Long-Term Considerations: While the upfront costs are significant, it’s also essential to consider the long-term benefits of optical bonding. Improved visual performance, increased durability, and enhanced user experience could outweigh the initial expenses.
- Support and Warranty: Some adhesive suppliers might offer technical support and warranties for their products. This can add value to your project but also affect costs.
When implementing optical bonding adhesive, balancing the upfront costs with the desired optical and mechanical performance is crucial. Consider getting quotes from multiple suppliers, factoring in all the relevant fees, and conducting a cost-benefit analysis to determine your project’s most cost-effective approach.