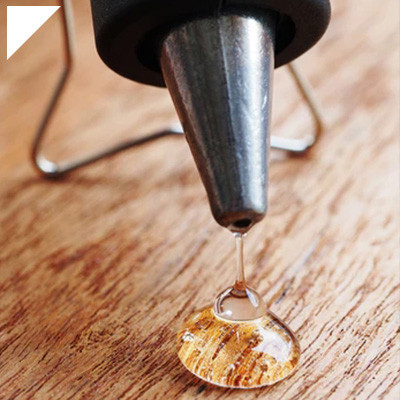
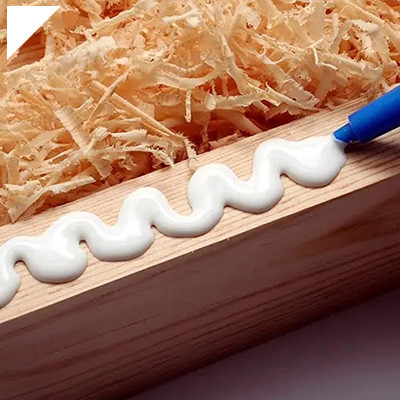
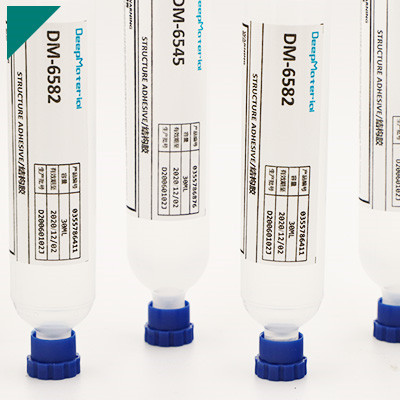
Magnet Bonding Adhesive
In the fascinating realm of material science and engineering, magnet bonding adhesives have emerged as a remarkable solution, enabling the secure attachment of magnets to various surfaces. This innovative approach goes beyond traditional methods, offering a reliable way to harness the power of magnetism while ensuring strong and durable adhesion. Whether in manufacturing, electronics, automotive, or even creative projects, magnet bonding adhesives provide a unique way to create versatile connections that combine the strength of magnets with the versatility of adhesives. This comprehensive exploration delves into the world of magnet bonding adhesives, uncovering their mechanisms, applications, benefits, and their pivotal role in uniting two powerful forces.
Introducing Magnet Bonding Adhesives
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial assembly and engineering, the introduction of Magnet Bonding Adhesives marks a groundbreaking leap forward. These innovative adhesives are poised to revolutionize how we construct, repair, and innovate across many industries, from electronics and automotive to aerospace and healthcare. At the heart of this transformation lies the seamless fusion of adhesive technology with the remarkable properties of magnets.
Engineers design Magnet Bonding Adhesives to offer robust and reliable magnetic bonding solutions beyond traditional mechanical fastening methods. Their unique composition, often featuring advanced polymer matrices infused with magnetic particles, creates an adhesive with extraordinary bonding strength, flexibility, and versatility. This breakthrough adhesive technology not only streamlines the assembly process but also opens up new design possibilities, as it allows for the attachment of magnetic components to a wide range of surfaces, even non-magnetic ones.
Magnet Bonding Adhesives’ standout features are their ability to maintain structural integrity under various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and vibration. This resilience makes them ideal for applications in automotive manufacturing, where they can securely affix sensors and actuators within engine bays, or in renewable energy systems, where they can facilitate the assembly of wind turbine components. Furthermore, their non-invasive nature proves invaluable in the medical field, where they enable the creation of magnetic attachments for prosthetic limbs, ensuring both comfort and ease of use for patients.
The versatility of Magnet Bonding Adhesives extends beyond industrial settings. They have found applications in consumer electronics, where they contribute to sleeker and more compact device designs, and in the construction industry, where they simplify the installation of magnetic fixtures in buildings. Additionally, they have environmental benefits by reducing the need for traditional fastening methods that require drilling and waste-intensive practices.
Challenges in Magnet Attachment
Various industries, from manufacturing to electronics, widely use magnet attachment. However, engineers and designers must navigate their fair share of challenges to ensure effective and reliable magnet attachment. Below are some key challenges associated with magnet attachment:
Alignment and Polarity
- Ensuring proper alignment of magnets with their intended counterparts is crucial for their functionality.
- Managing the polarity of magnets is essential to prevent repulsion and ensure attraction where needed.
Temperature Sensitivity
- Magnets can lose their magnetic strength at elevated temperatures, making selecting attractions with appropriate temperature tolerances vital.
- In applications like aerospace, it’s essential to consider how extreme cold can affect magnet performance.
Surface Preparation
- Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving strong adhesion. Surfaces need to be clean, smooth, and free from contaminants.
- Surface treatments, such as sandblasting or chemical etching, might be necessary to enhance adhesion.
Magnet Bonding Adhesives
Engineers often turn to specialized magnet bonding adhesives to address the challenges in magnet attachment. Formulators create these adhesives to establish robust and durable bonds between magnets and various substrates. Here are some key considerations and benefits associated with magnet bonding adhesives:
Adhesive Selection
Choosing a suitable adhesive is crucial. Epoxies and cyanoacrylates are common choices because they offer high bond strength and resistance to temperature fluctuations.
The flexibility and viscosity of the adhesive should match the application requirements.
Surface Compatibility
Designers create magnet bonding adhesives to adhere to various surfaces, including metals, ceramics, and plastics, ensuring compatibility with multiple magnet materials.
Thermal Stability
High-quality bonding adhesives offer excellent thermal stability, maintaining their bond strength over a wide temperature range.
Chemical Resistance
Some applications may expose magnets to chemicals or solvents. Magnet bonding adhesives can be selected or formulated to resist such corrosive agents.
Mechanical Strength
Engineers design magnet bonding adhesives to provide mechanical solid bonds, ensuring magnets stay securely attached even in demanding environments.
Ease of Application
Many magnet bonding adhesives are available in easy-to-use forms, such as two-part epoxy systems or pre-mixed formulations, simplifying the attachment process.
Mechanisms of Magnetic and Adhesive Bonding
Magnetic and adhesive bonding mechanisms play crucial roles in various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to consumer electronics and automotive engineering. These mechanisms enable the creation of solid and reliable connections between materials and components, facilitating the development of innovative products. This comprehensive exploration delves into the fundamental principles behind these two bonding mechanisms, shedding light on how they work and their diverse applications.
Magnetic Bonding Mechanism
Magnetic Forces at Play
Magnetic bonding relies on the fundamental principles of attraction between magnetic materials. Ferrous materials like iron and steel are particularly receptive to magnetic forces. When a magnetic field is applied, these materials align their magnetic domains in the direction of the area, generating an attractive energy that holds them together. This mechanism finds application in various parts, including manufacturing magnetic clasps in jewelry, closures in bags, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in healthcare.
Permanent vs. Temporary Magnets
Understanding the nature of magnets is essential. Permanent magnets, like those found in refrigerator doors, maintain their magnetic properties without an external field. In contrast, temporary attractions, like electromagnets, require a current to induce a magnetic field. This distinction impacts the versatility of magnetic bonding across industries.
Adhesive Bonding Mechanism
Chemical Bonds in Adhesion
Adhesive bonding relies on chemical bonds formed between sticky substances and the surfaces they join. This mechanism encompasses various adhesives, including epoxies, glues, and sealants, which create cohesive forces at the molecular level—chemical reactions between adhesive molecules and the substrate result in strong bonds. Automotive manufacturing employs adhesive bonding extensively for assembling car components due to its lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties.
Surface Preparation and Bond Strength
Achieving optimal adhesive bonding necessitates meticulous surface preparation. Contaminants, such as oils and dust, can weaken bonds. Surface treatments like sanding, cleaning, and priming enhance adhesion by promoting intimate contact between the adhesive and substrate. The type of adhesive, curing conditions, and the materials being bonded influence adhesive bonding strength.
Types of Magnet Bonding Adhesive Formulations
Magnet bonding adhesive formulations are critical in various industries, from electronics to automotive and renewable energy. These formulations ensure that magnets are securely attached to different substrates, providing stability and longevity to the final product. There are several types of magnet bonding adhesive formulations, each designed to meet specific requirements:
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (CA):
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as superglues, are famous for magnet bonding due to their fast curing and strong bond. They suit small, lightweight magnets and work well on various surfaces, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
Epoxy Resin Adhesives:
Epoxy resin adhesives are versatile and offer excellent strength and durability. They come in different formulations, including standard and flexible options, making them suitable for a wide range of magnet applications. Epoxies also provide good thermal and chemical resistance.
Acrylic Adhesives:
Acrylic adhesives are known for their high peel and shear strength, making them ideal for applications where magnets must withstand stress and vibration. They offer good resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation and moisture.
Polyurethane Adhesives:
Polyurethane adhesives are flexible and provide excellent shock and impact resistance. People commonly use them in automotive and construction applications where magnets may experience mechanical stress.
Silicone Adhesives:
Silicone adhesives are highly flexible and maintain their bond even at extreme temperatures. People often use them when magnets must withstand high and low-temperature variations.
Magnetic Adhesives:
Manufacturers specially design some formulations as magnetic adhesives, incorporating magnetic particles to enhance the overall magnetic strength of the assembly. Manufacturers use these adhesives when they require both bonding and magnetic properties.
Anaerobic Adhesives:
Anaerobic adhesives cure without oxygen and suit magnet bonding in threaded assemblies or when securing magnets in metal housings is necessary. They provide excellent resistance to vibration and environmental factors.
Choosing the right magnet bonding adhesive formulation depends on the magnets, substrate material, operating conditions, and desired bond strength. It’s essential to consider these factors carefully to ensure the adhesive meets the application’s specific requirements, ensuring the bonded magnets’ longevity and performance.
Permanent Magnet Bonding Solutions
In modern technology and engineering, the need for reliable and robust bonding solutions for permanent magnets has never been greater. Permanent magnets are pivotal in various applications, from electric motors and generators to medical devices and consumer electronics. Ensuring these magnets remain securely bonded is crucial for the efficiency and longevity of these systems. Magnet bonding adhesives offer innovative and efficient solutions for permanent magnet assembly and bonding, addressing this need.
The Importance of Magnet Bonding
Permanent magnets are used extensively in numerous industries because they generate a consistent magnetic field without needing an external power source. However, keeping them in place within a system or assembly is a challenging task. Magnet bonding adhesives prove indispensable in various ways, offering several key benefits:
- Secure Bonding:Magnet bonding adhesives provide a strong and durable bond, preventing magnets from shifting or dislodging during operation.
- Temperature Stability:Many applications expose materials to extreme temperatures, and designers create these adhesives to maintain their integrity and bonding strength in such conditions.
- Vibration and Shock Resistance:In applications where vibration and shock are prevalent, such as automotive and aerospace, these adhesives ensure magnets remain firmly affixed.
- Corrosion Protection:Magnet bonding adhesives can act as a barrier against moisture and corrosion, safeguarding the magnets’ long-term performance.
- Design Flexibility:Designers can apply these adhesives to various magnet shapes and sizes, allowing for versatile design options.
- Reduced Weight:Unlike traditional mechanical fastening methods, bonding with adhesives can reduce weight and enhance the efficiency of the assembly.
Choosing the Right Magnet Bonding Adhesive
Selecting the appropriate adhesive is paramount to the success of any magnet bonding application. Designers or engineers must consider several factors:
- Magnet Type:Different magnets (e.g., neodymium, ferrite, samarium-cobalt) may require specific adhesives tailored to their properties.
- Application Environment:Understanding the temperature, moisture, and vibration conditions the assembly will endure is essential.
- Bond Strength:Assess the required bonding strength based on the application’s demands.
- Adhesive Curing Time:Consider the time available for adhesive curing and whether rapid curing options are needed.
- Compatibility:Ensure you choose an adhesive compatible with the magnets and the substrates to which you will bond them.
Flexible and Rigid Magnet Bonding
Regarding magnet bonding, two distinct categories emerge flexible and rigid bonding solutions. These adhesives cater to different applications and challenges, providing versatile options for securing magnets in various contexts.
Flexible Magnet Bonding
Overview: Designers create flexible magnet bonding adhesives to accommodate applications requiring movement, flexibility, or adaptability. These adhesives offer unique advantages, especially in environments subject to vibrations or dynamic stresses.

Applications:
- Flexible magnet bonding adhesives find their niche in industries like automotive, where they are used to secure magnets in anti-lock braking systems, airbag sensors, and electric power steering motors.
- In the medical field, they are utilized in portable medical devices and wearable sensors, ensuring magnets remain securely bonded despite patient movement.
Benefits:
- Shock Absorption: These adhesives can absorb shocks and vibrations, preventing damage to the magnets or the surrounding components.
- Flexibility:They allow slight movements or deformations without compromising the bond, making them ideal for applications with variable stress loads.
- Damping: Flexible adhesives can dampen vibrations, reducing noise and improving system performance.
Rigid Magnet Bonding
Overview: Designers tailor rigid magnet bonding adhesives for applications with paramount stability, precision, and minimal movement. They provide a high-strength, immovable bond between magnets and substrates.
Applications:
- Rigid magnet bonding adhesives are commonly used in the aerospace industry to secure magnets in avionic equipment, where minimal movement is crucial for accuracy.
- They are also prevalent in the electronics industry, where rigid bonding is required to ensure consistent magnet positioning in devices like loudspeakers.
Benefits:
- Stability: These adhesives create a rigid and stable bond, preventing undesired magnet movement.
- Precision:They are ideal for applications demanding precise alignment, as they maintain magnet positions with minimal deviation.
- High Bond Strength:Rigid adhesives offer exceptional bond strength, ensuring magnets stay in place under extreme conditions.
Choosing the Right Bonding Solution
Selecting between flexible and rigid magnet bonding adhesives hinges on the specific needs of the application:
- Dynamic Environments:Opt for flexible adhesives when the application involves vibrations or movement.
- Precision and Stability: Rigid adhesives are the go-to choice for applications where minimal deviation and high stability are crucial.
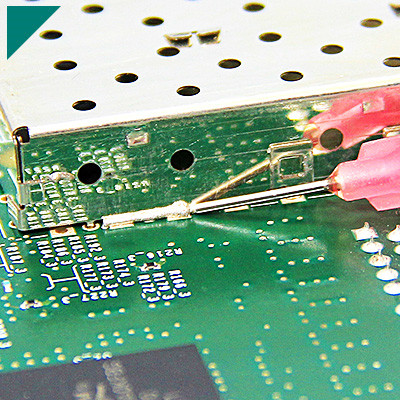
Magnetic Attachment in Electronics
Magnetic attachment plays a pivotal role in modern electronics, enabling the secure and efficient integration of components within devices ranging from smartphones and tablets to high-performance laptops and industrial machinery. Using magnet bonding adhesives in the electronics industry has become a standard practice because they provide reliable attachment solutions while offering several advantages over traditional fastening methods.
Applications in Electronics
- Smartphones and Tablets:Consumer electronics use magnets for various purposes, including mounting phone covers, attaching detachable accessories, and aiding in wireless charging. Magnet bonding adhesives ensure these magnets remain firmly affixed to the device’s housing.
- Laptops and Detachable Keyboards:In notebooks and 2-in-1 devices, magnetic bonding secures components like detachable keyboards, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly while maintaining stability.
- Industrial Electronics:In industrial settings, professionals use magnetic attachments for control panels, mounting sensors, and securing components within rugged machinery. Bonding adhesives are crucial in ensuring these magnets withstand harsh operating conditions.
Advantages of Magnet Bonding Adhesives in Electronics
- Precision and Alignment:These adhesives enable precise alignment of magnets and components during assembly, ensuring the desired functionality and aesthetics.
- Reduced Weight and Size:Compared to mechanical fastening methods, magnet bonding adhesives contribute to lighter and more compact electronic devices, a crucial consideration for portable gadgets.
- Quick Assembly:Magnetic bonding speeds up manufacturing by simplifying assembly and reducing the need for complex mounting hardware.
- Durability:Formulators create adhesives to withstand temperature fluctuations, humidity, and environmental stressors, ensuring long-term performance and reliability in electronic devices.
- Reduced Vibration and Noise:In applications such as hard disk drives, magnets are secured using these adhesives, reducing vibration and noise, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
Challenges and Considerations
- Temperature Sensitivity:It’s essential to select adhesives with appropriate temperature resistance, especially in electronics prone to heating during operation.
- Compatibility:To prevent demagnetization, ensure compatibility between the adhesive and the magnet material.
- Assembly Process:Adhesive curing times and manufacturing processes must be optimized to maintain efficiency while meeting quality standards.
Automotive Applications of Magnet Bonding
Magnet bonding adhesives are increasingly prevalent in the automotive industry, transforming how manufacturers incorporate magnets into various components and systems. These innovative adhesives offer numerous advantages, from improved efficiency to enhanced safety and durability.
Applications in the Automotive Sector
- Electric Powertrains:In electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid cars, magnet bonding adhesives secure potent magnets in electric motors, ensuring efficient energy conversion and quiet operation. These adhesives are indispensable in achieving high torque and power output.
- Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS): ABS relies on magnetic sensors to monitor wheel speed and prevent skidding during braking. Magnet bonding adhesives hold these sensors in place, ensuring their precise alignment and reliable performance.
- Sensors and Actuators:Various sensors and actuators in modern vehicles employ magnets for airbag deployment, cruise control, and parking assistance. Magnet bonding adhesives guarantee the attractions remain securely affixed.
Benefits of Magnet Bonding Adhesives in Automotive Applications
- Vibration Dampening:Vibration from road conditions and engine operation are common in vehicles. Magnet bonding adhesives absorb these vibrations, ensuring that magnets stay positioned and sensors provide accurate readings.
- Reduced Weight:Compared to traditional mechanical fasteners, adhesives reduce weight, improving fuel efficiency in conventional vehicles and extending battery range in EVs.
- Temperature Stability:Adhesives formulated for automotive use can withstand extreme temperature variations, ensuring magnet integrity in hot and cold climates.
- Cost Efficiency:By simplifying assembly processes and reducing the need for additional hardware, magnet bonding adhesives lower manufacturing costs.
- Corrosion Resistance:Adhesives provide a protective barrier, safeguarding magnets from moisture and corrosion in various automotive environments.
Considerations in Automotive Magnet Bonding
- Adhesive Selection:People must choose the suitable adhesive for the intended purpose from different bonds designed for specific applications and temperature ranges, which is critical.
- Assembly Line Integration:Implementing adhesives into the automotive production process may require adjustments to ensure efficient curing and bonding.
- Durability Testing:Rigorous testing is essential to ensure that magnet bonding adhesives meet the automotive industry’s stringent safety and reliability standards.
Creative and Decorative Uses
In addition to their industrial applications, magnet bonding adhesives offer exciting opportunities for creative and decorative projects, adding a touch of innovation and functionality to various endeavors.
Artistic Expression
- Interactive Art:Artists can use magnet bonding adhesives to create interactive art installations where they can rearrange magnetic elements, fostering engagement and creativity.
- Mixed Media Collages:These adhesives allow artists to attach three-dimensional objects to their mixed media artwork, adding depth and texture to their compositions.
Home Decor and Organization
- Magnetic Wall Decor:Homeowners can easily display artwork or photos on decorative wall panels using these adhesives, adding a dynamic element to their interior design.
- Magnetic Bulletin Boards:Crafting custom magnetic bulletin boards for schedules, notes, and reminders becomes simple, merging practicality with aesthetics.
Practical and Playful Applications
- Magnetic Furniture and Fixtures:Designers can incorporate magnets into furniture and fixtures, such as floating shelves or detachable hooks, using bonding adhesives to ensure stability and sleek aesthetics.
- Educational Toys:DIY educational toys and games become more engaging with magnet bonding adhesives, offering children a hands-on approach to learning about science and physics.
Benefits of Magnet Bonding Adhesives in Creative Projects
- Ease of Use:These adhesives simplify magnet attachment, making creative endeavors accessible to individuals of all skill levels.
- Removability:While ensuring secure bonding, these adhesives also allow for easy removal and repositioning of magnets, facilitating flexibility in creative projects.
- Durability:The strong bond ensures that decorative elements and magnets remain in place over time, maintaining the project’s integrity.
- Customization:By selecting suitable adhesives for material compatibility and desired strength, artists and designers can tailor their projects to their specifications.
Considerations in Creative Magnet Bonding
- Adhesive Selection:Choosing the appropriate adhesive for material compatibility and desired strength is crucial for project success.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and roughening, is essential to achieving a robust bond between the adhesive and the substrate.
- Safety Precautions:Adhering to safety guidelines, such as proper ventilation and protective equipment, is essential when working with adhesives.
Magnetic Signage and Displays
Magnetic signage and displays play a pivotal role in visual communication and marketing. Magnet bonding adhesives have emerged as a game-changing technology in this field, revolutionizing the creation, mounting, and presentation of signs and displays. These adhesives offer a range of benefits that enhance the flexibility, durability, and aesthetics of magnetic signage and displays.
Advantages of Magnet Bonding Adhesives in Signage and Displays
- Versatility:Magnet bonding adhesives cater to a wide array of applications in this sector, from temporary promotional displays to permanent storefront signage.
- Reusability:These adhesives bond magnets in a way that allows for easy removal and repositioning, making them an ideal choice for frequently changing displays or events.
- Damage-Free Mounting:Unlike traditional mounting methods that may damage surfaces, adhesives provide a non-invasive way to secure signs and displays.
- Customization:These adhesives offer a high degree of customization, allowing businesses to create magnetic signage that suits their branding and messaging.
- Enhanced Aesthetics:Magnet bonding adhesives ensure a flush, seamless appearance with no visible screws or brackets, preserving signage and displays’ clean and professional look.
Applications in Magnetic Signage and Displays
- Retail Signage:Stores frequently use magnetic signage for seasonal promotions, sales, and product displays. Magnet bonding adhesives enable quick and damage-free mounting.
- Trade Shows and Events:Businesses rely on magnetic displays for easy setup and teardown at trade shows and events. Magnet bonding adhesives simplify the installation process.
- Vehicle Graphics:In vehicle advertising, magnet bonding adhesives secure promotional graphics without damaging the vehicle’s surface, offering versatility and removability.
Considerations and Best Practices
- Surface Compatibility:Ensure the adhesive is compatible with the mounting surface and the magnetic material to avoid bonding issues or surface damage.
- Weight and Size:Match the adhesive’s strength to the size and weight of the signage or display for secure attachment.
- Environmental Conditions:Consider the exposure to weather and other environmental factors when selecting adhesives to ensure durability.
Medical Devices and Magnetic Attachment
The intersection of medical devices and magnet bonding adhesives has opened up innovative possibilities in healthcare. These adhesives have become indispensable in creating secure and reliable magnetic attachments in various medical applications, where precision, durability, and safety are paramount.
Applications in Medical Devices
- Diagnostic Equipment:Magnetic bonding adhesives are extensively used in medical imaging devices like MRI machines, securing critical components such as gradient coils and ensuring precise and stable imaging.
- Prosthetics and Orthopedics:In prosthetic limbs and orthopedic devices, magnet bonding adhesives enable the attachment of removable components, offering patients greater comfort and mobility.
- Dental Appliances:Magnetic attachments in dental prosthetics, such as dentures or braces, enhance ease of use and patient comfort while ensuring secure retention.
Advantages of Magnet Bonding Adhesives in Medical Devices
- Biocompatibility:Adhesives designed for medical applications are biocompatible, ensuring they do not cause harm when in contact with bodily tissues or fluids.
- Precision and Alignment:These adhesives allow for the precise alignment of magnets and components in medical devices, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Reduced Infection Risk:Magnetic attachments often eliminate the need for screws or fasteners, reducing potential infection risks associated with open wounds.
- Removability and Adjustability:Magnet bonding adhesives allow for easy removal and repositioning of components for devices that require maintenance or adjustment.
Stringent Considerations in Medical Magnet Bonding
- Material Compatibility:Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the specific materials used in medical devices to prevent potential reactions or degradation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhesives used in medical devices must meet strict regulatory standards to ensure patient safety and device efficacy.
- Long-Term Durability:Medical devices often must perform reliably for extended periods, making adhesive selection and application processes critical for long-term performance.
Safety Considerations in Magnetic Bonding
While magnet bonding adhesives offer numerous advantages in various applications, ensuring safety is paramount to their successful and responsible use. These adhesives are potent tools, and users must consider several key safety considerations to prevent accidents, hazards, and potential harm.
Material Safety
- Material Compatibility:It’s crucial to confirm that the adhesive is compatible with the materials it will bond, including both the magnets and the substrate. Incompatibility can lead to weak bonds or material degradation.
- Toxicity and Allergens:Some adhesives may contain harmful chemicals or allergens. Assess the adhesive’s safety data sheet (SDS) to identify potential risks and take necessary precautions.
Health and Safety Measures
- Ventilation:Adequate ventilation is essential when working with adhesives, as many emit fumes that can be harmful if inhaled. Ensure proper ventilation systems are in place.
- Protective Equipment:Depending on the adhesive’s toxicity and potential hazards, individuals may need personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and respiratory protection.
Adhesive Handling
- Storage Conditions:Adhesives often have specific storage requirements regarding temperature, humidity, and exposure to light. Improper storage can affect adhesive performance and safety.
- Spill Handling:Develop protocols for handling adhesive spills, including containment, cleanup, and disposal, to prevent environmental contamination and health risks.
Application Process
- Proper Mixing:If the adhesive involves a multi-component system, such as epoxy, ensure accurate mixing ratios. Improper mixing can lead to compromised bonding strength.
- Curing Time and Conditions:Follow recommended times and conditions for the adhesive to achieve optimal bond strength and prevent potential issues during operation.
Environmental Considerations
- Disposal:Adhesives can be hazardous to the environment if not disposed of properly. Adhere to local regulations and best practices for adhesive disposal.
- Hazardous Waste:Some adhesives may classify as hazardous waste. Correctly identify and handle such waste according to applicable laws.
Training and Education
- Training:Ensure that personnel working with magnet bonding adhesives receive proper training on safe handling, storage, and application procedures.
- Documentation:Maintain records of safety data sheets, training, and safety protocols for reference and compliance.
Surface Preparation for Magnet Adhesion
Surface preparation is critical in ensuring strong and reliable magnet adhesion, whether in industrial applications, creative projects, or medical devices. Properly preparing the surfaces to which magnets and adhesives will bond is essential for optimizing adhesion strength and long-term performance.
Cleaning the Surfaces
Before applying any adhesive, thorough cleaning of both the magnet and the substrate is paramount. Any contaminants, such as dust, grease, or oils, can hinder adhesion and weaken the bond. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Solvent Cleaning:Use appropriate solvents to clean the surfaces depending on the materials involved. Many applications commonly use isopropyl alcohol.
- Abrasion:Light abrasion using sandpaper or a wire brush can be effective for surfaces with stubborn contaminants or rough textures.
Surface Roughening
Roughening the surface can enhance the mechanical adhesion of some adhesives. Using isopropyl alcohol proves especially useful for non-porous materials like plastics or glass. Techniques include:
- Sandblastingcreates a textured surface that adhesives can grip onto more effectively.
- Etching:Chemical etching can roughen surfaces by creating microscopic irregularities.
Priming and Activation
Primers or surface activators may sometimes be necessary to improve adhesion. Designers create these products to promote bonding between the adhesive and the substrate. Consider the following:
- Primer Selection:Choose a primer compatible with the adhesive and the substrate for optimal results.
- Proper Application:Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for applying primers or activators, ensuring uniform coverage.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions during surface preparation and adhesive application can also impact adhesion strength:
- Temperature and Humidity:Adhesive manufacturers often provide guidelines for temperature and humidity ranges suitable for application. Deviating from these ranges can affect the curing process.
- Dust and Contaminants:Ensure the workspace is clean and free from dust or other contaminants that could interfere with the adhesive process.
Quality Control and Testing Standards
Quality control and rigorous testing standards are fundamental in developing and applying magnet bonding adhesives. These measures ensure that the bonds meet specific performance criteria and adhere to safety, reliability, and regulatory requirements, regardless of their intended use in various industries.
Adhesive Testing Standards
Several standardized tests exist to evaluate the performance of magnet bonding adhesives:
- Adhesion Strength:We typically measure adhesive strength by applying force to the bonded magnets until separation occurs. ASTM D1002 is a commonly used standard for testing adhesive lap shear strength.
- Chemical Compatibility:Assessing the adhesive’s chemical resistance is vital, especially in applications where we expect exposure to harsh substances. Various ASTM and ISO standards provide guidelines for such testing.
- Thermal Stability:Adhesives must maintain their integrity under different temperature conditions. Following standards like ASTM E104, thermal cycling tests can determine an adhesive’s resistance to temperature variations.
Quality Control Protocols
Establishing robust quality control protocols is essential for adhesive manufacturers and end-users to ensure consistent performance:
- Material Inspection:Incoming materials, including adhesives and substrates, undergo stringent inspection to confirm compliance with specifications and requirements.
- Batch Consistency:Adhesive manufacturers maintain tight control over production processes to ensure batch-to-batch consistency, reducing variability in performance.
- Adhesive Testing:Routine testing of adhesive properties, such as viscosity, curing time, and chemical composition, helps maintain quality control and identify standard deviations.
Adherence to Regulatory Standards
In several industries, including medical devices, automotive, and aerospace, adhesives must meet specific regulatory standards and certifications to guarantee safety and performance. For example:
- ISO Standards:ISO 10993 is vital for assessing the biocompatibility of adhesives in medical devices, ensuring they are safe for patient use.
- Automotive Standards:Adhesives in automotive applications must meet standards like ISO 16276 for corrosion protection and ASTM D1184 for flexural strength.
- Aerospace Standards:Aerospace adhesives must adhere to rigorous standards like MIL-PRF-23377 for corrosion resistance and ASTM D5572 for bond strength.
End-User Testing and Validation
End-users in various industries often conduct additional testing and validation to ensure that magnet bonding adhesives meet their specific application requirements. These other steps might include:
- Environmental Testing: Subjecting bonded assemblies to environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and vibration to assess adhesive performance under real-world conditions.
- Long-Term Durability: Testing the adhesive’s ability to maintain bond strength over extended periods, simulating the product’s expected lifespan.
Advancements in Magnet Bonding Technology
In recent years, magnet bonding technology has advanced remarkably, revolutionizing how magnets are integrated into various applications. These innovations improve the performance and reliability of magnetic assemblies and expand the range of possible applications. Here are some notable advancements:
Nanomaterial-Enhanced Adhesives
Integrating nanomaterials into adhesive formulations has opened up new bond strength and durability frontiers. Nanoparticles like graphene and carbon nanotubes enhance adhesive properties, making them incredibly strong while remaining thin and lightweight. This innovation has been particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace, where weight reduction is crucial.

Flexible and Stretchable Adhesives
The development of flexible and stretchable adhesives has expanded the application possibilities of magnet bonding. These adhesives can conform to irregular shapes and maintain their bond even under significant deformation or stretching. They are valuable in wearable technology, medical devices, and even creating innovative, flexible displays.
Biocompatible Adhesives for Medical Devices
Advancements in adhesive chemistry have led to biocompatible adhesives specifically designed for medical devices. These adhesives are non-toxic, non-irritating to human tissue, and can withstand sterilization. They are instrumental in applications like securing sensors in wearable health devices and assembling implantable medical devices.
Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Bonding
Incorporating magnetic nanoparticles into adhesive formulations has improved the magnetic strength of bond interfaces. These nanoparticles create more robust, more reliable connections between magnets and substrates. This innovation is especially beneficial in high-stress applications like automotive sensors and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
Self-Healing Adhesives
Self-healing adhesives have emerged as a groundbreaking technology in magnet bonding. These adhesives can autonomously repair minor damage, such as cracks or voids, ensuring the bond remains intact. This innovation is precious in applications where adhesive integrity is critical, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
Compatibility of Magnet Bonding with Different Materials
Ensuring a reliable bond between magnets and diverse materials is paramount in various applications. The compatibility of magnet bonding adhesives with different materials plays a pivotal role in achieving secure and durable attachments.
Metal Substrates
- Ferrous Metals: Bonding magnets to ferrous metals like steel or iron is typically straightforward due to their magnetic properties. Magnetic attraction aids in alignment, and various adhesives work well in these applications.
- Non-Ferrous Metals:Non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and brass lack magnetic properties. The adhesive must offer strong adhesion for a durable bond in these cases. Surface treatments, like abrasion or priming, may enhance adhesion.
Plastics and Composites
Thermoplastics: Bonding magnets to thermoplastics with low surface energy, like PVC or ABS, can be challenging. Adhesives compatible with these materials, such as certain epoxies or cyanoacrylates, might require surface treatment or priming.
- Thermosetting Plastics:Plastics like epoxy or phenolic resins offer better adhesion properties. Adhesive selection should align with the specific thermosetting material used.
- Composites:Composite materials vary widely in composition and surface properties, requiring careful adhesive selection and potential surface preparation for optimal bonding.
Rubber and Elastomers
Adhering magnets to rubber or elastomeric materials necessitates flexible adhesives that maintain adhesion under stress. Rubber-based adhesives, known for flexibility and adequate elastomer adhesion, are commonly used in such applications.
Ceramics and Glass
In high-temperature and technical applications involving ceramics or glass, adhesives designed for high-temperature resistance, such as ceramic-based or glass adhesives, are suitable for bonding magnets to these materials.
Considerations for Compatibility
Selecting the appropriate adhesive for magnet bonding requires considerations like:
- Material Compatibility:Ensuring the adhesive is compatible with both the magnet and substrate materials.
- Surface Preparation: Depending on the substrate, surface preparation like cleaning, roughening, or primers may be necessary to enhance adhesion.
- Adhesive Selection:Different adhesives possess varying properties. Therefore, choose a glue that aligns with the specific application requirements, such as temperature resistance, flexibility, or chemical compatibility.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability and environmental consciousness are increasingly vital in adhesive technology, including magnet bonding adhesives. As industries strive to minimize their ecological footprint, these considerations extend to adhesive selection and usage.
Reducing Chemical Footprint
Choosing low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) and solvent-free adhesives contributes significantly to sustainability efforts. Various industries increasingly favor adhesive formulations that reduce chemical emissions during curing and have a lower environmental impact.
Recyclability and Reusability
The ability to dismantle and recycle magnetic assemblies without significant adhesive residue is a key sustainability factor. Adhesives that allow for the separation of magnets from substrates without causing material degradation contribute to recycling efforts.
Biodegradable Options
In specific applications, biodegradable adhesives provide an eco-friendly alternative. These adhesives break down naturally over time, reducing long-term environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing
Energy-efficient manufacturing processes for adhesives can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Adhesive manufacturers increasingly adopt methods that minimize energy consumption and waste generation during production.
Life Cycle Analysis
Assessing the environmental impact of adhesive use through a comprehensive life cycle analysis (LCA) is becoming standard practice. LCAs consider the entire lifespan of the adhesive, including production, application, and disposal, helping industries make informed choices about adhesive sustainability.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhesive manufacturers adhere to stringent environmental regulations, such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). These regulations limit the use of hazardous substances in adhesives and promote environmentally friendly formulations.
Waste Reduction
Minimizing adhesive waste is crucial. Industries are exploring techniques like precise adhesive dispensing to reduce excess adhesive and minimize disposal requirements.
Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable adhesive packaging materials and practices, such as recyclable containers and reduced packaging waste, contribute to overall sustainability efforts.
Future Prospects of Magnet Bonding Adhesive Development
The future of magnet bonding adhesive development is poised to bring about exciting advancements across various industries, driven by evolving technologies, sustainability initiatives, and expanding application possibilities.
Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology
Integrating advanced materials and nanotechnology is expected to revolutionize magnet bonding adhesives. Nanoparticles with unique properties can enhance adhesives’ strength, durability, and functionality. These innovations will strengthen bonds and open new aerospace, automotive, and electronics possibilities.
Flexible and Stretchable Adhesives
The demand for flexible and stretchable adhesives will continue to grow, driven by wearable technology, robotics, and healthcare applications. Future developments will focus on creating bonds that maintain their integrity while accommodating dynamic movements and deformations.
Sustainability and Biodegradability
The sustainability trend will further influence adhesive development. Biodegradable and eco-friendly adhesives will become more prevalent, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact. Adhesive formulations that minimize waste and emissions will gain prominence.
Smart and Functional Adhesives
Adhesive technologies will evolve to include intelligent and functional properties. Adhesives with sensing capabilities, self-healing properties, or thermal conductivity will enable innovative solutions in various industries, from electronics to construction.
Miniaturization and Microelectronics
Magnet bonding adhesives will play a pivotal role in microelectronics and miniaturized systems as devices continue to shrink in size. Adhesives capable of securely bonding tiny magnets in compact spaces will be in high demand.
Customization and Versatility
Future magnet bonding adhesives will offer greater customization and versatility. Users can access adhesives tailored to specific materials, temperatures, and environmental conditions, ensuring reliable bonds in diverse applications.
Industry-Specific Solutions
Adhesive manufacturers will increasingly provide industry-specific solutions. Aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and renewable energy sectors will benefit from adhesives engineered to meet the unique demands of each field, including extreme temperatures, vibration resistance, and biocompatibility.
Innovative Applications of Magnet Bonding
Magnet bonding adhesives have opened up a world of innovative applications across various industries, pushing the boundaries of what magnets can achieve when securely attached to different materials.
Wearable Technology
In wearable technology, magnet bonding adhesives play a vital role. They enable the creation of compact and durable magnetic closures in smartwatches, fitness trackers, and clothing. These adhesives ensure that wearable devices remain securely fastened while being comfortable and convenient for users.
Microelectronics and Miniaturization
Magnet bonding adhesives are instrumental in microelectronics as devices become smaller and more intricate. They secure tiny magnets in sensors, actuators, and miniature devices, facilitating precise control and sensing capabilities in robotics, medical implants, and microfluidics applications.
Energy Harvesting and Storage
Innovative energy applications employ magnet bonding adhesives. They play a role in assembling magnetic generators for energy harvesting, converting motion into electrical power. Additionally, they play a role in securing magnets within energy storage systems like flywheels and magnetic bearings, improving energy efficiency and sustainability.
Bioengineering and Medical Devices
These adhesives attach magnets to prosthetic limbs, orthopedic implants, and dental appliances in bioengineering and medical devices. These features ensure secure and adjustable connections, enhancing the comfort and mobility of patients.
Magnetic Levitation and Transportation
Innovative transportation systems incorporate magnet bonding adhesives to create magnetic levitation (maglev) vehicles. These adhesives secure magnets in maglev trains, allowing frictionless, high-speed transportation with reduced maintenance requirements.
Art and Interactive Installations
Beyond technical applications, artists and designers embrace magnet bonding adhesives. These adhesives enable interactive art installations where magnetic elements can be rearranged, fostering engagement and creativity. These adhesives allow for the seamless integration of magnets into mixed-media artwork, adding depth and versatility to artistic expressions.
Magnets in Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, including wind turbines and generators, increasingly rely on magnets to generate electricity efficiently. Magnet bonding adhesives play a crucial role in ensuring magnets’ secure and reliable attachment within these systems, contributing to the sustainability and effectiveness of renewable energy technologies.
Permanent Magnet Generators (PMGs)
- Efficient Power Generation:Wind turbines and small-scale hydroelectric systems widely use permanent magnet generators. Bonding adhesives secure the magnets in the generator, allowing for efficient power generation.
- Reduced Maintenance:Securely bonded magnets minimize the risk of detachment, reducing maintenance costs and downtime in renewable energy systems.
Direct-Drive Wind Turbines
- Enhanced Reliability:Direct-drive wind turbines, which eliminate the need for a gearbox, are increasingly popular in the wind energy sector. Magnet bonding adhesives ensure magnets remain securely attached to the generator, enhancing the reliability of these systems.
- Higher Efficiency:The direct-drive design and strong and durable adhesive bonds contribute to higher energy conversion efficiency in wind turbines.
Hybrid Vehicles and Energy Storage
- Electric Vehicle Motors:Magnet bonding adhesives are used in electric vehicle motors, contributing to the efficiency and performance of hybrid and electric vehicles.
- Energy Storage Systems:In renewable energy storage applications, such as flywheels and magnetic bearings, these adhesives secure magnets, improving energy efficiency and storage capacity.
Key Advantages
- Vibration Resistance:Magnet bonding adhesives absorb and distribute vibrations, protecting the integrity of the bond and ensuring magnets remain in place even in high-vibration environments.
- Temperature Resistance:Adhesives designed for renewable energy applications can withstand extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term performance in challenging environmental conditions.
- Customization:You can tailor adhesive formulations to meet the specific requirements of different renewable energy systems, optimizing bond strength and durability.
Magnet bonding adhesives represent a bridge between two worlds: the fascinating realm of magnetism and the precision of adhesion. Their role in creating strong, versatile, secure connections is pivotal in industries requiring magnetism and adhesion. As technology advances and initiatives explore novel ways to harness magnetic properties, magnet bonding adhesives will remain foundational in driving innovation and efficiency. Ongoing research and advancements are poised to shape the future of bonding with these adhesives, contributing to creating products that seamlessly integrate the power of magnets into various applications.