Industrial Bonding Adhesives: Essential Tools for Modern Manufacturing
Industrial Bonding Adhesives: Essential Tools for Modern Manufacturing
Industrial bonding adhesives are a cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing processes, crucial in creating products and structures across various industries. These adhesives are engineered to provide strong, reliable bonds between materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, wood, and composites. They are indispensable in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, electronics, construction, and packaging. As industries continue to evolve and demand higher performance, industrial bonding adhesives are also advancing, offering new capabilities and solutions for challenging bonding applications.
This article will explore the various types of industrial bonding adhesives, their applications, benefits, and the factors that influence their selection. It will also delve into their role in enhancing productivity, sustainability, and the overall performance of manufactured goods.
Types of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Industrial bonding adhesives come in various formulations, each designed for specific applications and materials. The most common types of adhesives used in industrial settings include:
Epoxy Adhesives
Description: Epoxy adhesives are two-component systems consisting of a resin and a hardener. When mixed, they form a highly durable bond.
Key Features:
- High strength and durability.
- Excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture.
- Ideal for bonding metals, composites, and ceramics.
Common Uses: Aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction.
Polyurethane Adhesives
Description: These adhesives are available in both single-component and two-component formulations. They cure through moisture and are known for their flexibility.
Key Features:
- Flexible and resilient bond.
- Excellent impact and vibration resistance.
- It can bond with various materials, including plastics, metals, and wood.
Common Uses: Automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing.
Acrylic Adhesives
Description: Acrylic adhesives are versatile and often bond plastics and metals.
Key Features:
- Fast curing times.
- High bond strength.
- Resistance to UV radiation and environmental exposure.
Common Uses: Automotive, signage, window glazing, and electrical.
Silicone Adhesives
Description: Silicone adhesives offer exceptional resistance to heat and weathering, making them ideal for harsh environments.
Key Features:
- Extreme temperature resistance.
- Water, UV, and chemical resistance.
- Ideal for flexible bonds.
Common Uses: Automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction.
Hot Melt Adhesives
Description: Hot melt adhesives are thermoplastic polymers that are applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling.
Key Features:
- Fast setting time.
- Bonds a variety of materials.
- Easy to apply using automated equipment.
Common Uses: Packaging, woodworking, and assembly lines.
Contact Adhesives
Description: These adhesives form bonds when two coated surfaces are brought together. They are generally solvent-based.
Key Features:
- Instant bond formation.
- Suitable for large surface areas.
- Highly resistant to heat and water.
Common Uses: Footwear, automotive interiors, and laminating.
Applications of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Industrial bonding adhesives are used in various industries, each requiring specific application properties. The following sections explore some key sectors where these adhesives are essential.
Automotive Industry
Applications:
- Exterior and Interior Components:Adhesives bond exterior panels, trim, and interior parts.
- Windshields and Windows:Advanced adhesives ensure secure attachment of windows and glass elements to the vehicle body.
- Battery Modules:In electric vehicles, adhesives help secure battery packs and prevent vibration-related damage.
Benefits:
- Enhanced strength and safety.
- Reduces the weight of the vehicle by replacing mechanical fasteners like bolts and screws.
- Improved design flexibility for manufacturers.
Aerospace Industry
Applications:
- Composite Materials:Aircraft often use composite materials that require specific adhesives to bond parts without adding excessive weight.
- Structural Bonds: Adhesives ensure the bonding of critical components, providing both strength and lightness.
- Sealing:Adhesives are used for sealing and waterproofing applications in aircraft and spacecraft.
Benefits:
- High temperature and pressure resistance.
- Lightweight yet robust bonds.
- Increased performance and safety in flight operations.
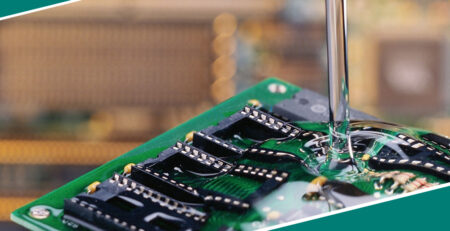
Electronics Manufacturing
Applications:
- Device Assembly:Adhesives secure delicate components such as microchips, screens, and casings.
- Conductive adhesives attach and bond electrical components, ensuring efficient electrical conductivity.
Benefits:
- Ensures precision and reliability in small and intricate parts.
- It offers strong bonds without damaging delicate electronic parts.
- Enhances performance, durability, and product longevity.
Construction and Building Materials
Applications:
- Bonding of Panels and Tiles:Adhesives provide firm, long-lasting bonds in flooring, wall tiles, and other building materials.
- Sealing and Waterproofing:Industrial adhesives also play a critical role in sealing joints and cracks, ensuring building durability.
Benefits:
- Saves Time during construction.
- Provides superior performance compared to traditional mechanical fasteners.
- Reduces material costs and improves the aesthetic appearance.
Packaging Industry
Applications:
- Box Sealing:Hot melt adhesives are commonly used in packaging lines to seal boxes quickly and efficiently.
- Labeling and Assembly:Adhesives are essential for assembling and attaching packaging materials and labels.
Benefits:
- Increased productivity due to fast curing times.
- Offers flexibility in packaging designs.
- Cost-effective and reliable bonding.
Benefits of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
The use of industrial bonding adhesives brings numerous advantages to the manufacturing process, including:
Cost Efficiency
- Adhesives can eliminate the need for expensive mechanical fasteners and welding equipment.
- Reduces labor costs by simplifying assembly processes.
- Minimize material wastage by using adhesives for precise application.
Enhanced Design Flexibility
- Industrial bonding adhesives allow for creating complex designs without the limitations of mechanical fastening systems.
- The ability to bond dissimilar materials expands design possibilities for manufacturers.
Improved Strength and Durability
- Many modern adhesives are formulated to create stronger bonds than traditional methods like welding or riveting, especially for difficult-to-bond materials.
- Industrial adhesives can withstand extreme environmental conditions, ensuring the long-lasting durability of products.
Faster Production Times
- Adhesives cure rapidly and can be applied highly efficiently, reducing manufacturing times.
- Automated systems can apply adhesives controlled, speeding up production rates.
Sustainability
- Many industrial bonding adhesives are now designed with eco-friendly components, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional mechanical fastening.
Some adhesives are free of solvents and harmful chemicals, contributing to a safer work environment.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Selecting the right industrial bonding adhesive depends on various factors. These include:
Material Compatibility
- The adhesive must be compatible with the materials being bonded. For example, epoxy adhesives are often chosen for metals and composites, while polyurethane adhesives work well with wood and plastics.
Environmental Conditions
- Consider the bond’s temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure. Silicone or epoxy adhesives may be more suitable for high-temperature applications.
Curing Time
- The speed at which the adhesive cures can affect production timelines. Fast-curing adhesives are ideal for high-volume applications, while slower-curing ones may be needed for precision work.
Strength Requirements
- Different applications require varying levels of bond strength. Stronger adhesives like epoxies are preferable for critical structural applications, while other types suffice for less demanding jobs.
Cost and Availability
- Cost considerations are essential, particularly in high-volume industries. Choose an adhesive that meets performance requirements without exceeding the budget.

Conclusion
Industrial bonding adhesives have transformed modern manufacturing by providing reliable, strong, and versatile bonding solutions for various materials and applications. These adhesives are indispensable in ensuring product quality, durability, and efficiency, from the automotive and aerospace industries to electronics, construction, and packaging. Manufacturers can enhance production processes, reduce costs, and improve product performance by selecting the right adhesive based on the material, environmental factors, and performance needs. As technology advances, the role of industrial bonding adhesives will continue to expand, meeting the growing demands of industries worldwide.
For more about a complete guide to industrial bonding adhesives: essential tools for modern manufacturing, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.