Industrial Adhesive Solutions for Electronics: Enhancing Reliability and Performance
Industrial Adhesive Solutions for Electronics: Enhancing Reliability and Performance
In today’s fast-evolving electronics landscape, the demand for high-performance, durable, and reliable components is higher than ever. Industrial adhesives have become crucial in meeting these demands, providing essential bonding and sealing solutions that contribute to electronic devices’ overall efficiency and longevity. From smartphones and laptops to automotive electronics and medical devices, these adhesives ensure electronic components function seamlessly under various conditions. This blog post delves into industrial adhesive solutions for electronics, exploring their types, applications, benefits, and considerations.
Types of Industrial Adhesives for Electronics
1. Epoxy Adhesives
Overview: Epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonding capabilities and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. They are commonly used in electronic assemblies where durability and thermal stability are critical.
Applications:
- Bonding components to PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards)
- Encapsulation of electronic parts for protection
- Potting compounds to safeguard against moisture and mechanical stress
Benefits:
- Excellent thermal and chemical resistance
- High shear and tensile strength
- Good electrical insulating properties
2. Silicone Adhesives
Overview: Silicone adhesives are favored for their flexibility, high-temperature resistance, and moisture resistance. They are ideal for applications where expansion and contraction due to temperature changes are a concern.
Applications:
- Sealing electronic enclosures to prevent ingress of dust and moisture
- Bonding components that experience thermal cycling
- Vibration dampening in sensitive electronic equipment
Benefits:
- Wide operating temperature range
- Flexibility and durability in challenging environments
- Superior resistance to UV light and environmental degradation
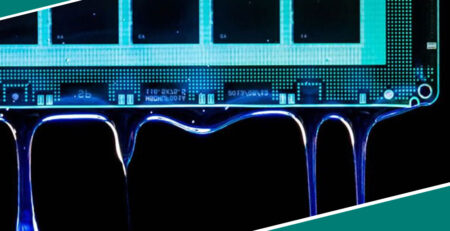
3. Conductive Adhesives
Overview: Conductive adhesives are designed to provide electrical conductivity while adhering to surfaces. They are essential in applications where electrical connections are required between components.
Applications:
- Attaching conductive traces to PCBs
- Creating electrical connections in semiconductor devices
- Bonding components where heat dissipation is required
Benefits:
- Provides electrical connectivity and mechanical bonding
- Reduces the need for soldering, which can be beneficial for heat-sensitive components
- Suitable for high-frequency applications
4. Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs)
Overview: PSAs bond instantly with pressure without requiring heat or solvents. They are used in applications where ease of use and removal are essential.
Applications:
- Mounting electronic displays and touchscreens
- Assembling components in consumer electronics
- Temporary holding and securing during assembly processes
Benefits:
- Easy application and removal
- Can be repositioned during assembly
- No curing time is required
 Benefits of Industrial Adhesives in Electronics
Benefits of Industrial Adhesives in Electronics
Industrial adhesives play a crucial role in the electronics industry, offering a range of advantages that enhance product performance and durability.
Enhanced Structural Integrity
- Bonding Strength:Provides strong adhesion to various substrates, ensuring components stay securely in place.
- Vibration Resistance:Reduces the impact of vibrations and shocks, which can prevent component damage and enhance the longevity of electronic devices.
Improved Thermal Management
- Heat Dissipation:Some adhesives are designed to remove heat from sensitive components, preventing overheating and improving overall system reliability.
- Thermal Stability:Maintaining performance under varying temperature conditions is critical for electronics exposed to fluctuating environments.
Superior Electrical Insulation
- Electrical Isolation:Acts as an insulating barrier to prevent short circuits and protect delicate electronic components.
- Conductive Adhesives:Certain adhesives are formulated to conduct electricity, allowing effective connections between components without traditional soldering.
Design Flexibility and Efficiency
- Lightweight Solutions:Reduces the need for mechanical fasteners, which can contribute to a lighter and more compact design.
- Streamlined Assembly:Facilitates faster and more efficient manufacturing processes by simplifying the assembly and reducing the number of parts.
Durability and Longevity
- Resistance to Environmental Factors:Withstands exposure to moisture, chemicals, and UV light, ensuring electronic devices remain functional and reliable over time.
- Long-Term Performance:Helps maintain device performance and integrity, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
Considerations When Choosing Adhesives
Selecting the suitable industrial adhesive for electronics involves evaluating several vital factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Adhesive Type and Composition
- Epoxy vs. Silicone: Epoxy adhesives offer strong bonding and durability and are suitable for high-stress applications, while silicone adhesives provide flexibility and resistance to temperature extremes.
- Conductive vs. Non-Conductive: Conductive adhesives are essential for creating electrical connections, while non-conductive adhesives are used for insulating and protecting components.
Environmental Resistance
- Temperature Tolerance:Consider the adhesive’s ability to withstand the device’s operating temperatures, including high heat and low cold environments.
- Chemical Exposure:Ensure the adhesive can resist chemicals it may encounter, such as solvents, fuels, or cleaning agents, without degrading or losing its adhesive properties.
Mechanical Properties
- Bond Strength: Evaluate the adhesive’s shear and tensile strength to determine whether it can securely hold components under mechanical stress or vibration.
- Flexibility and Shock Absorption: Determine if the adhesive needs flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction or to absorb shocks to prevent damage to sensitive components.
Application and Curing Process
- Ease of Application: Choose an adhesive that aligns with your manufacturing process, whether a fast-curing option for high-volume production or a more workable adhesive for precision applications.
- Curing Time and Conditions: Consider the time required for the adhesive to fully cure and any specific conditions needed, such as heat or UV light, which may affect production timelines.
Electrical Performance
- Insulation Properties: To prevent electrical failures, assess the dielectric strength and insulation resistance for non-conductive adhesives.
- Conductivity Requirements: Ensure conductive adhesives meet the electrical conductivity levels for effective circuit connections.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): Review safety information to ensure the adhesive complies with regulations and poses minimal health risks during handling and application.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of the adhesive, including its compliance with regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and its recyclability.
Cost and Supply Chain Factors
- Budget Constraints: Balance the cost of the adhesive with its performance benefits, as higher-quality adhesives may come at a premium but offer longer-term advantages.
- Availability: Ensure a reliable supply chain for the adhesive to avoid production delays and maintain consistent quality across batches.
By thoroughly evaluating these considerations, manufacturers can select an adhesive solution that meets their technical requirements and supports efficient production processes and product reliability.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Industrial adhesive solutions are indispensable in the electronics industry, providing essential bonding, sealing, and conductive capabilities that ensure the reliability and performance of electronic devices. By understanding the different types of adhesives available and their specific applications, manufacturers can make informed choices that enhance product durability, functionality, and cost-effectiveness. As technology advances and electronic devices become more complex, the role of industrial adhesives in supporting innovation and maintaining high standards of quality will only become more significant. Investing in the right adhesive solutions is crucial to achieving excellence in electronics manufacturing and assembly.
For more about choosing the best industrial adhesive solutions for electronics: enhancing reliability and performance, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.