Industrial Adhesive Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Industrial Adhesive Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Industrial adhesives are crucial to numerous industries, offering efficient and durable bonding solutions for various materials, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and more. Unlike traditional mechanical fasteners, adhesives allow for a smoother, aesthetically pleasing finish without compromising strength. This article explores industrial adhesives, their types, applications, and critical considerations for choosing the right adhesive solution.
Understanding Industrial Adhesives
Industrial adhesives are specially formulated to meet the rigorous demands of industrial environments. They provide long-lasting and secure bonding, and their flexibility and compatibility with numerous materials make them essential in industries like automotive, construction, aerospace, electronics, and packaging.
Critical Characteristics of Industrial Adhesives
- Strength and Durability: Industrial adhesives are designed to withstand heavy loads, impacts, and exposure to harsh conditions.
- Flexibility: Some adhesives provide elasticity, allowing bonded materials to handle mechanical stress without breaking.
- Chemical Resistance: Industrial adhesives often resist chemicals, oils, and solvents.
- Temperature Resistance: Many adhesives are built to endure extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, without deteriorating.
- Versatility: These adhesives suit diverse substrates, from metals and plastics to composites and glass.
Industrial adhesives enhance design flexibility, reduce assembly times, and minimize weight in various applications by replacing or supplementing traditional fasteners.
Types of Industrial Adhesives
Several industrial adhesives cater to specific applications, each with unique properties. Understanding the differences between these adhesives helps select the best option for any application.
Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are widely used for their high strength, durability, and excellent chemical resistance. They consist of two components—a resin and a hardener—that form a strong bond suitable for metals, wood, and various plastics when mixed.
Applications:
- Automotive (bonding structural components)
- Electronics (potting and encapsulation)
- Construction (securing structural elements)
Acrylic Adhesives
Acrylic adhesives offer fast curing times, high strength, and environmental resistance. They work well with plastics and metals and are often used in high-performance applications.
Applications:
- Automotive (trim bonding)
- Aerospace (panel bonding)
- Consumer electronics (component assembly)
Polyurethane Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility and resistance to impact and vibration. They also provide excellent bonding strength for materials with different expansion rates, such as glass and metal.
Applications:
- Construction (flooring and insulation panels)
- Marine (bonding hull components)
- Furniture (bonding diverse materials)
Silicone Adhesives
Silicone adhesives offer superior flexibility and resist extreme temperatures and weather conditions. They are also commonly used as sealants.
Applications:
- Electronics (sealing and protecting circuits)
- Automotive (gasket applications)
- Medical devices (biocompatible adhesive applications)
Hot Melt Adhesives
Hot melt adhesives (HMAs) are thermoplastic adhesives applied in a molten state and solidified upon cooling. They are popular due to their fast-setting times and versatility.
Applications:
- Packaging (sealing cartons and cases)
- Textiles (bonding fabric)
- Automotive (interior assemblies)
 Critical Applications of Industrial Adhesives
Critical Applications of Industrial Adhesives
Industrial adhesives are critical across various sectors, ensuring strong, reliable, durable bonds for multiple applications.
Automotive Industry
Adhesives are used in the automotive industry for bonding, sealing, and even damping noise and vibration. Modern vehicles rely on lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, and adhesives enable this shift by bonding dissimilar materials like plastics and metals.
Examples:
- Structural bonding of vehicle frames
- Windshield and glass installation
- Bonding of interior panels and trim
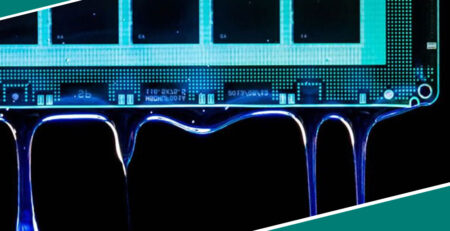
Electronics and Electrical Components
Adhesives are used in the electronics industry to assemble small components, protect sensitive parts, and insulate circuits. They are typically designed to withstand high temperatures, provide electrical insulation, and resist chemicals.
Examples:
- Printed circuit board (PCB) mounting and encapsulation
- Bonding heat sinks to electronic components
- Potting and sealing connectors to prevent moisture
Construction and Infrastructure
Adhesives are commonly used in construction to bond materials like concrete, metal, and glass, allowing for innovative architectural designs and streamlined assembly processes.
Examples:
- Structural glazing and facade bonding
- Flooring installation and tile bonding
- Bonding insulation panels and fireproofing materials
Aerospace Industry
Adhesives in the aerospace industry must meet strict requirements for durability, weight, and reliability under extreme conditions. Lightweight adhesive solutions reduce overall aircraft weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Examples:
- Bonding composite materials in fuselages
- Sealing fuel tanks and protecting against corrosion
- Structural bonding for wing assemblies
Packaging Industry
Adhesives are used in packaging to seal boxes, laminate, and create tamper-evident packaging. Quick-drying and food-safe adhesives are critical in this sector to meet high-speed production requirements and regulatory standards.
Examples:
- Case and carton sealing
- Labeling and branding
- Flexible packaging for consumer goods
Choosing the Right Industrial Adhesive Solution
Selecting a suitable adhesive is critical for ensuring the performance and longevity of the bonded materials. Below are essential factors to consider:
Substrate Compatibility
Not all adhesives are suitable for every substrate. Some adhesives may work well with metals but not with plastics or ceramics. Testing compatibility with different substrates helps determine the best adhesive for specific materials.
Bond Strength and Durability
Different applications require varying levels of bond strength. While some adhesives provide temporary bonding for removable parts, others are designed to create a permanent bond.
Environmental Resistance
To be suitable for outdoor applications or those exposed to harsh conditions, an adhesive must withstand environmental factors like moisture, UV exposure, and temperature changes.
Curing Time
Curing time significantly affects the production process. Quick-drying adhesives are preferred for high-speed manufacturing, while adhesives with longer curing times may be ideal for applications requiring precision and control.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Specific industries, like food, medicine, and electronics, require adhesives that comply with specific safety and regulatory standards. Choosing adhesives that meet these guidelines is essential, especially for food contact applications or medical devices.
Future Trends in Industrial Adhesive Solutions
With technological advancements, the industrial adhesive sector is rapidly evolving. Key trends are shaping the future of adhesive solutions to improve efficiency, sustainability, and functionality.
Eco-friendly and Sustainable Adhesives
There is an increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly adhesives. Bio-based and low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) adhesives are gaining popularity as industries move toward sustainable practices.
Innovative Adhesives with Sensing Capabilities
Innovations in materials science have led to the development of intelligent adhesives that can detect changes in stress, temperature, and other environmental factors. These adhesives are particularly valuable in the aerospace and automotive sectors, where real-time monitoring of bonded joints can improve safety and performance.
Adhesives for Additive Manufacturing
As 3D printing grows, so does the demand for adhesives that bond 3D-printed components. Specialized adhesives are designed for additive manufacturing, enabling greater design flexibility and more complex assemblies.
Improved Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
With electronics’ growing importance, adhesives that can conduct heat or electricity are essential. Thermal conductive adhesives are used for bonding components in electronics that need effective heat dissipation, while electrically conductive adhesives are vital for connecting circuits without soldering.
Faster Curing Adhesives
Adhesives with faster curing times are highly beneficial in industries where rapid production is crucial. UV-curable adhesives, for example, allow for almost instantaneous curing under UV light, streamlining production processes in industries like electronics and medical device manufacturing.
Common Challenges in Using Industrial Adhesives
Despite their advantages, industrial adhesives present specific challenges that must be addressed during the selection and application.
Surface Preparation
Adhesives require proper surface preparation for optimal bonding. Dust, grease, or other contaminants can weaken the bond, leading to potential failure. Preparing the surface by cleaning, roughening, or applying primers can significantly enhance adhesive performance.
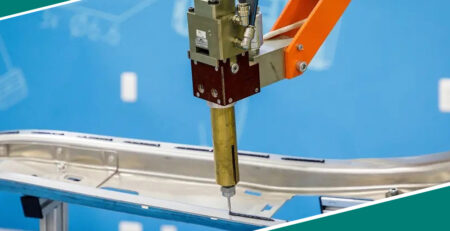
Adhesive Dispensing and Application
Applying the right amount of adhesive is critical for achieving the desired bond strength. Automated adhesive dispensing systems help control application rates and consistency, but manual application can be challenging, particularly for complex shapes or hard-to-reach areas.
Storage and Shelf Life
Adhesives have specific storage requirements and shelf lives that must be adhered to. Storing adhesives in the correct conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.) is essential to prevent degradation and maintain effectiveness.
Health and Safety Considerations
Many adhesives contain chemicals that can be harmful if inhaled or come into contact with skin. When handling industrial adhesives, following safety guidelines, such as using protective equipment and ensuring adequate ventilation, is crucial.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Industrial adhesives are indispensable across industries, providing durable, efficient, and versatile bonding solutions. Adhesives are vital in modern manufacturing and assembly, from automotive and electronics to construction and packaging. Industries can maximize the benefits of these powerful bonding agents by understanding the various types, applications, and considerations for choosing suitable adhesives. As technological advancements push the boundaries, the future of industrial adhesives promises even greater efficiency, sustainability, and functionality, meeting the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
For more about a complete guide to industrial adhesive solutions: a comprehensive guide, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.