Glass Bonding Adhesive

The marriage of transparency and strength is a coveted feat in modern design and manufacturing. Recently, glass bonding adhesives have surfaced as a revolutionary solution, fundamentally transforming the process of joining glass components. Whether in architecture, automotive, electronics, or art, glass bonding adhesive offers a versatile and reliable way to create seamless connections, realizing intricate designs and structures that push the boundaries of creativity. This comprehensive exploration delves into glass bonding adhesive, unveiling its mechanisms, applications, benefits, and indelible impact on diverse industries that value aesthetics and durability.
Unveiling Glass Bonding Adhesive
Introducing the groundbreaking innovation in adhesive technology: the Unveiling Glass Bonding Adhesive. This cutting-edge adhesive solution represents a new era in glass bonding, offering unparalleled strength, versatility, and reliability. This adhesive, designed to revolutionize the automotive and construction industries, is set to redefine the joining of glass components. Here’s a closer look at what sets the Unveiling Glass Bonding Adhesive apart:
- Unmatched Strength:The adhesive’s advanced formulation ensures a strong bond between glass surfaces, providing structural integrity and durability that surpasses traditional bonding methods. This strength opens new design possibilities, enabling the creation of sleeker and more lightweight glass-intensive structures.
- Versatility Redefined:From intricate glass artworks to complex architectural facades, the Unveiling Glass Bonding Adhesive adapts seamlessly to various applications. Its adaptability across different glass types, including tempered, laminated, and even specialty glasses, makes it a game-changer for diverse projects.
- Enhanced Aesthetics:Traditional bonding methods often introduce visible elements that comprise the aesthetic appeal of glass structures. This transparent adhesive eliminates unsightly seams, bolts, or brackets, enabling it to join glass components while preserving their pristine appearance seamlessly. The result is a visually stunning finish that emphasizes the elegance of the glass.
- Streamlined Application:The adhesive’s user-friendly application process minimizes the complexities associated with traditional glass bonding techniques. With reduced curing times and simplified procedures, manufacturers and artisans can optimize their production processes and achieve higher output levels without compromising quality.
- Exceptional Weather Resistance:Glass structures often face the harsh challenges of weather and temperature fluctuations. The Unveiling Glass Bonding Adhesive boasts outstanding resistance to environmental stressors, ensuring that bonded glass components remain steadfast even in the most demanding conditions.
- Safety First:Unlike some solvent-based adhesives that can release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), this adhesive prioritizes safety. Its low VOC emissions and non-toxic properties make it a reliable choice for projects requiring structural integrity and environmental consciousness.
Challenges in Bonding Glass
Bonding glass is a complex and crucial process in various industries to create solid and durable assemblies, from automotive to electronics. However, this seemingly straightforward task poses several challenges that engineers and manufacturers must address to ensure the integrity of the final product. Understanding these challenges is essential for achieving reliable glass bonding.
Surface Contamination
One of the primary hurdles in bonding glass is the presence of surface contaminants. Glass surfaces often accumulate oils, dust, and other impurities during manufacturing and handling. These contaminants can hinder the adhesive’s ability to bond effectively. To address this challenge:
- Cleaning:Thoroughly clean the glass surfaces using specialized solvents or cleaning agents to remove contaminants.
- Surface Activation:Employ surface treatments like plasma cleaning or UV/ozone exposure to activate the glass’s surface, making it more receptive to adhesives.
Glass Composition and Variability
The glass comes in various compositions and thicknesses, and these differences can affect bonding processes. The challenges related to glass composition include the following:
- Thermal Expansion:Different glass types have varying coefficients of thermal expansion, which can lead to stress during temperature fluctuations.
- Brittleness:Some types of glass are more brittle than others, making them prone to cracking during bonding.
- Chemical Compatibility:Ensure the chosen adhesive compatible with the specific glass composition to prevent degradation over time.
Adhesive Selection
Selecting a suitable adhesive is critical for successful glass bonding. Factors to consider include:
- Adhesion Strength:Ensure the adhesive provides sufficient bonding strength for the intended application.
- Curing Time:The curing time can vary depending on the adhesive type, impacting production efficiency.
- Thermal Properties:Consider the adhesive’s resistance to extreme temperatures, especially in applications like automotive glazing.
Handling and Alignment
Properly aligning glass components during bonding is crucial for achieving a strong and aesthetically pleasing bond. Challenges in this area include:
- Glass Weight and Fragility:Large or heavy glass pieces may require specialized equipment for precise alignment without breakage.
- Tolerance Control:Maintaining tight tolerances in alignment ensures a uniform bond line.
Quality Control
Ensuring the quality and reliability of bonded glass assemblies is a continuous challenge. Employ techniques such as:
- Non-Destructive Testing:Use ultrasonic testing or optical inspection to detect defects without damaging the glass.
- Performance Testing:Conduct rigorous tests to verify the strength and durability of the bonded glass under real-world conditions.
Mechanisms of Glass Adhesion
Understanding the mechanisms behind glass adhesion is crucial for engineers and manufacturers seeking to create reliable and durable bonded structures. Glass adhesion relies on a combination of physical and chemical processes, each contributing to the overall strength and stability of the bond. Let’s delve into the key mechanisms of glass adhesion.
Chemical Bonding
- Covalent Bonds: Some adhesives form covalent bonds with the glass surface by sharing electrons—this type of bonding results in extreme adhesion.
- Chemisorption: Chemical adhesion occurs when adhesive molecules chemically react with the glass surface to form a solid and permanent bond.
Physical Bonding
- Van der Waals Forces: Weaker than chemical bonds, Van der Waals forces involve temporary attractions between molecules. While individually weak, the cumulative effect can be significant.
- Capillary Action: Liquid adhesives can infiltrate microscopic surface imperfections and irregularities, creating a mechanical bond through capillary action.
- Mechanical Interlocking: Some adhesives have physical structures or contours that interlock with the rough surface of the glass, enhancing adhesion.
Electrostatic Forces
- Electrostatic Attraction: In some cases, static electricity can facilitate adhesion by attracting opposite charges between the glass and the adhesive. This phenomenon is particularly relevant for certain types of silicone adhesives.
Wetting and Surface Energy
- Contact Angle: The contact angle between a droplet of adhesive and the glass surface influences the wetting ability of the bond. A lower contact angle indicates better wetting and adhesion.
- Surface Energy Matching: Adhesives with surface energy similar to glass tend to adhere more effectively due to favorable interactions.
Hydrogen Bonding
- Hydrogen Bonds: Some adhesives can form hydrogen bonds with functional groups on the glass surface, enhancing adhesion. It is a common occurrence with adhesive varieties such as epoxies and polyurethanes.
Surface Preparation
- Cleaning: Properly cleaning and preparing the glass surface is essential to maximize adhesion by removing contaminants and creating a receptive surface for bonding.
- Surface Activation: Techniques like plasma treatment or UV/ozone exposure can modify the glass surface, increasing its adhesion potential by introducing new functional groups.
Surface Preparation for Glass Bonding
Surface preparation is a critical step in achieving successful glass bonding. Properly preparing the glass surface ensures the removal of contaminants and optimization of the cover for adhesion, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable bonds. Let’s explore the key aspects of surface preparation for glass bonding.
Cleaning and Contaminant Removal
- Contaminant Types: Glass surfaces can accumulate various contaminants, including oils, dust, fingerprints, and residues from previous manufacturing processes. Thoroughly remove these contaminants, as they can hinder adhesion.
- Cleaning Methods: Employ specialized cleaning agents or solvents to remove contaminants effectively. You can also use ultrasonic cleaning and precision wiping techniques for thorough cleaning.
Abrasion and Roughening
- Mechanical Abrasion: Abrading the glass surface, often with fine abrasive materials or sandblasting, creates a rougher texture that enhances adhesion by providing more surface area for the adhesive to grip.
- Etching: Chemical etching using acids or alkaline solutions can modify the glass surface by creating microstructures that improve adhesion.
Surface Activation
- Plasma Treatment: Plasma cleaning or plasma activation exposes the glass surface to ionized gas, modifying its chemical properties and increasing surface energy, which promotes better adhesion.
- UV/Ozone Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light combined with ozone can activate the glass surface, introducing functional groups that enhance adhesion capabilities.
Surface Priming
- Primer Application: Sometimes, a primer on the glass surface can improve adhesion. Formulators specifically design primers to enhance the compatibility between the glass and adhesive.
- Primer Selection: The choice of primer depends on the adhesive system and the type of bonded glass. It’s essential to select a primer that is compatible with both.
Surface Drying and Contamination Prevention
- Drying: After cleaning and surface modification, it’s crucial to ensure the glass surface is completely dry to prevent moisture-related issues, which can compromise adhesion.
- Contamination Prevention: Implement procedures to safeguard the prepared surface from contamination before the adhesive is applied. Contaminants introduced after surface preparation can compromise the bond.
Quality Control and Inspection
- Adhesion Test: Conduct adhesion tests to ensure the effectiveness of surface preparation. These tests can include peel tests, shear tests, or other relevant methods to measure bond strength.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the glass surfaces you’ve prepared for any defects, residue, or contamination that might have been missed during the initial preparation.
Types of Glass Bonding Adhesives
Glass bonding adhesives are essential in various industries, creating durable, secure, and aesthetically pleasing glass assemblies. We specially formulate these adhesives to adhere to the unique properties of glass surfaces. Several types of glass bonding adhesives are available, each with distinct characteristics and applications:
1.Silicone Adhesives:Silicone-based adhesives offer excellent flexibility and resistance to temperature extremes, making them popular for structural and weatherproof bonding in construction and automotive applications. They also adhere well to glass due to their compatibility with its smooth surface.
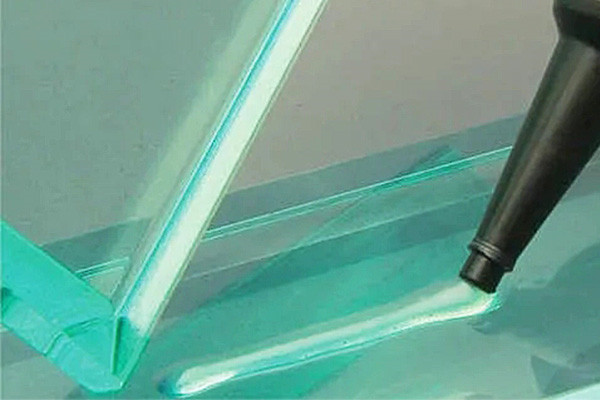

2.Epoxy Adhesives:Epoxy resins are renowned for their exceptional bonding strength and chemical resistance. People commonly use them in electronics, optics, and the automotive industry for applications that require a robust and durable bond. Epoxy adhesives often require precise mixing and curing.
3.UV-Curable Adhesives:UV-curable adhesives, as the name suggests, cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. They are suitable for applications requiring rapid bonding and curing, such as electronics and medical devices. UV adhesives offer good transparency, making them ideal for bonding glass in optical systems.
4.Cyanoacrylate Adhesives:Cyanoacrylates, also known as super glues, are known for their fast curing time and strong bond. You commonly use them to bond glass in small-scale applications like hobby projects and minor repairs. However, they may not be as durable as other adhesive types in demanding environments.
5.Polyurethane Adhesives:Users prize polyurethane adhesives for their flexibility and resistance to moisture and chemicals. They are suitable for bonding glass in automotive and construction applications where environmental factors play a significant role.
6.Hybrid Adhesives:Hybrid adhesives combine the best attributes of different adhesive types, offering a balance of strength, flexibility, and durability. They are versatile and used in various applications, including structural bonding in glass facades and automotive assemblies.
7.Acrylic Adhesives:Acrylic adhesives offer good bonding strength, UV resistance, and clarity. People commonly use them for bonding glass components in the signage, display, and automotive industries.
8.Methyl Methacrylate (MMA) Adhesives:MMA adhesives are known for their excellent adhesion to various substrates, including glass. Commonly used in automotive assembly, they bond glass panels and structural components.
Structural Glass Adhesives
Structural glass adhesives represent a specialized class for bonding glass elements in architectural and structural applications. These adhesives are pivotal in modern construction, allowing architects to create awe-inspiring glass structures, seamlessly blending aesthetics with functionality. Key characteristics and applications of structural glass adhesives include:
- High Bond Strength:Engineers design structural glass adhesives to provide exceptional bond strength, ensuring the integrity and stability of glass assemblies. This strength is vital in applications such as glass curtain walls, glass canopies, and glass bridges, where safety and load-bearing capacity are paramount.
- Transparency and Aesthetics:These adhesives offer optical clarity and minimal visible lines, enhancing the visual appeal of glass structures. This transparency allows natural light to penetrate interiors, promoting energy efficiency and creating stunning architectural designs.
- Weather Resistance:Manufacturers formulate structural glass adhesives to withstand environmental challenges, including UV exposure, temperature variations, and moisture. They maintain their bond strength and aesthetic properties even in harsh outdoor conditions.
- Flexibility:Many structural glass adhesives exhibit a degree of flexibility, which helps absorb structural movements and vibrations, preventing glass breakage. This flexibility is particularly crucial in earthquake-prone regions.
- Ease of Application:These adhesives are often available in user-friendly formats, such as cartridges or two-component systems. Simplifying installation in this way reduces labor costs and construction time.
- Customization:Manufacturers can tailor structural glass adhesives to meet specific project requirements, including curing time, viscosity, and adhesion to different glass and substrates. This versatility ensures that they can accommodate a wide range of architectural designs.
- Certifications and Standards:Many structural glass adhesives comply with industry standards and certifications to guarantee safety and quality, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of construction regulations.
- Sound Insulation:Some structural glass adhesives possess sound-dampening properties, which can be advantageous in urban environments, providing noise reduction in addition to their structural benefits.
UV-Curable Adhesives for Glass
UV-curable adhesives represent a specialized class of adhesives that have gained significant traction in the glass industry due to their rapid curing, high bond strength, and versatility. These adhesives offer unique advantages when bonding glass surfaces, making them invaluable in various applications across different industries.
Key Characteristics and Advantages:
- Ultra-Fast Curing:UV-curable adhesives cure almost instantly when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This rapid curing significantly reduces assembly time, making them ideal for high-volume production processes.
- High Bond Strength:UV-curable adhesives provide robust adhesion to glass substrates. The bonds they create are strong, durable, and resistant to environmental factors, ensuring long-lasting performance.
- Excellent Clarity:These adhesives offer exceptional optical clarity, making them ideal for applications where maintaining transparency is crucial. This clarity is vital in architectural designs’ optical devices, displays, and glass-to-glass bonding.
- Minimal Heat Generation:UV-curing is a cold curing process that generates minimal heat during curing. This feature is essential when bonding delicate or heat-sensitive glass components, preventing thermal stress and damage.
- Low Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):UV-curable adhesives typically have low VOC emissions, contributing to a more environmentally friendly bonding process.
- Versatility:UV adhesives can bond different types of glass, including clear, frosted, and coated glass. They are also compatible with various substrates, such as metals, plastics, and ceramics, expanding their applications.
Applications:
- Electronics:Electronics manufacturers widely use UV-curable adhesives to bond glass components in displays, touch screens, and optical sensors. Their quick curing time and optical clarity are essential in these applications.
- Optics:Optical devices like lenses, prisms, and filters often rely on UV adhesives for precise and transparent bonding, ensuring minimal distortion and light loss.
- Medical Devices:In medical applications, UV-curable adhesives play a crucial role in bonding glass components in diagnostic equipment, lab-on-a-chip devices, and medical sensors, where a combination of optical clarity and fast curing is critical.
- Architectural Glass:Architects utilize these adhesives for glass-to-glass bonding in architectural designs, including glass facades, canopies, and balustrades. Their clarity and durability enhance the aesthetics and structural integrity of such projects.
- Automotive:UV adhesives are employed in the automotive industry for bonding glass panels, such as windshields and sunroofs, ensuring high-strength, weather-resistant bonds.
Silicone Adhesives and Glass Joining
Silicone adhesives have become a cornerstone in Glass joining, serving as a versatile and reliable solution for bonding glass components across diverse industries. With their unique properties, silicone adhesives have transformed how Glass is integrated into various applications, offering numerous advantages.
Exceptional Flexibility and Elasticity
One of the standout qualities of silicone adhesives is their remarkable flexibility and elasticity. Glass is notorious for its brittleness, prone to cracking or shattering when subjected to stress or temperature fluctuations. With their high flexibility, silicone adhesives serve as a cushion, absorbing mechanical stresses and accommodating thermal expansion differences between glass components. This elasticity ensures that pressure is evenly distributed, minimizing the risk of glass breakage and ensuring a robust and enduring bond.
Strong Adhesion to Glass Surfaces
Silicone adhesives boast exceptional adhesion to glass surfaces. This property is pivotal for creating a lasting and resilient bond with Glass, essential for maintaining structural integrity. Whether used in architectural glass facades or the construction of aquariums, this adhesion capability ensures that glass components can withstand external forces and environmental conditions.
Resilience Against Moisture and UV Radiation
In many glass applications, exposure to moisture and UV radiation is inevitable. Silicone adhesives excel in these conditions, offering robust protection against water infiltration and degradation caused by sunlight. This resistance is a critical factor in applications such as outdoor glass paneling on buildings or the encapsulation of solar panels.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Beyond their adhesive qualities, silicone adhesives provide excellent electrical insulation properties. The exceptional qualities of these adhesives make them indispensable for sealing and joining glass components in electronic devices and instruments, preventing moisture and contaminants from compromising the integrity and longevity of sensitive electronics.
Automotive Applications
Silicone adhesives are vital in bonding glass windows and windshields in the automotive industry. Their ability to maintain a secure bond under extreme temperature variations and vibrations is crucial for passenger safety and the vehicle’s structural integrity.
Acrylic Adhesives for Transparent Bonds
Acrylic adhesives have become a go-to solution for creating transparent bonds across various applications. Their unique properties make them ideal for achieving clarity and strength in multiple industries.
Unparalleled Transparency
One of the most significant advantages of acrylic adhesives is their ability to create transparent bonds. Maintaining optical clarity is essential when bonding fine materials, such as glass or plastics. Unlike other glues that may leave a visible residue or haze, acrylic adhesives remain virtually invisible once cured. This transparency is crucial in industries like electronics, where displays and touchscreens demand a seamless and transparent appearance.
Exceptional Bond Strength
Acrylic adhesives offer a remarkable combination of strength and durability. They form robust bonds that withstand substantial mechanical stress, making them suitable for demanding applications. Whether used in aerospace for structural bonding or automotive manufacturing for bonding clear lenses, acrylic adhesives deliver the necessary strength to ensure long-lasting performance.
Versatile Adhesion
Acrylic adhesives exhibit excellent adhesion to various materials, including plastics, metals, glass, and even dissimilar substrates. This versatility is advantageous in industries where bonding different materials is commonplace, as it eliminates the need for multiple adhesive types and simplifies the bonding process.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Another noteworthy feature of acrylic adhesives is their resistance to environmental factors. They are highly resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. This resistance ensures the longevity and stability of transparent bonds, making them suitable for outdoor applications like sign manufacturing or architectural glazing.
Rapid Curing and Bonding
Acrylic adhesives are known for their quick curing times. They typically cure within minutes to hours, depending on the specific formulation. This rapid bonding capability is advantageous in manufacturing settings where efficiency and productivity are paramount.
Applications in Various Industries
Acrylic adhesives find extensive use in a range of industries. In the medical field, they bond transparent components in medical devices, ensuring the optical clarity necessary for accurate readings and diagnostics. The construction industry attaches fine building materials, like windows and skylights, to structures. Furthermore, acrylic adhesives have made their mark in the arts and crafts sector, enabling hobbyists and artists to create transparent bonds in various creative projects.
Architectural Glass Bonding
Architectural glass bonding has revolutionized how modern buildings incorporate glass, representing a cutting-edge construction technique. It involves the fusion of glass panels using specialized adhesives for bonding systems, resulting in stunning architectural designs that seamlessly blend transparency, strength, and aesthetics. This innovative approach has become increasingly popular in contemporary architecture for several reasons.
One of the most significant advantages of architectural glass bonding is its ability to create a sense of openness and lightness within a structure. By eliminating the need for traditional framing systems, such as metal or wood, architects can design spaces with uninterrupted expanses of glass. This design approach maximizes natural light penetration and provides breathtaking views of the surrounding environment, effectively blurring the lines between indoor and outdoor spaces.
Additionally, architectural glass bonding enhances structural integrity. The adhesive used in this process is robust and durable, capable of withstanding extreme environmental conditions, including wind, seismic activity, and temperature fluctuations. These qualities make it a viable choice for skyscrapers, bridges, and other large-scale architectural projects where safety and longevity are paramount.
Furthermore, glass bonding offers an array of design possibilities. Architects and designers can explore curved, faceted, or irregular shapes that were once challenging to achieve with conventional glass installation methods. The absence of visible joints and the ability to create fluid, continuous surfaces result in truly unique and iconic structures pushing architectural imagination’s boundaries.
In terms of sustainability, architectural glass bonding can contribute to energy efficiency. High-performance coatings and laminates can be integrated into the glass panels, reducing heat gain and loss, thereby improving a building’s thermal performance. These features enhance occupant comfort and lower energy consumption, aligning with the growing trend of environmentally responsible construction practices.
Automotive Glass Applications
Automotive glass plays a critical role in vehicle safety, aesthetics, and functionality. Glass bonding adhesives are indispensable in ensuring that automotive glass remains secure, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. This overview delves into the significance of glass bonding adhesives in various automotive glass applications.
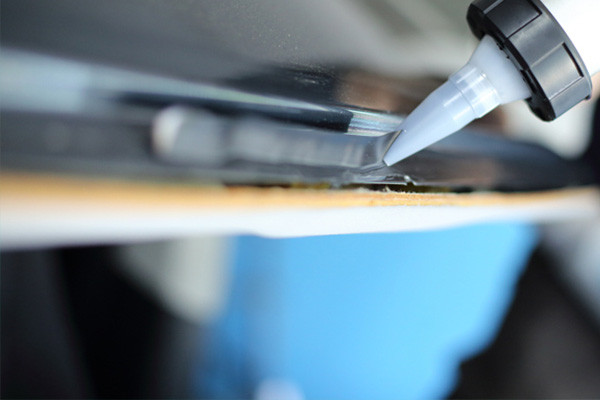

Windshield Installation
- Safety:Glass bonding adhesives are essential for securely attaching windshields to the vehicle frame, ensuring the car’s structural integrity during accidents.
- Vibration Damping:They absorb vibrations, reducing noise and enhancing the comfort of the vehicle occupants.
- Waterproofing:These adhesives create a watertight seal, preventing water leakage and safeguarding the interior.
Side and Rear Windows
- Strength:Glass bonding adhesives increase the strength of side and rear windows, preventing shattering during accidents.
- Aesthetics:They enable seamless, flush installations, enhancing the vehicle’s visual appeal.
- Noise Reduction:These adhesives reduce road noise, enhancing passenger comfort.
Sunroof Installation
- Leak Prevention:Glass bonding adhesives create a watertight seal around sunroofs, preventing leaks during rain.
- Durability:They ensure the sunroof remains securely in place, even during high-speed driving.
Glass Roof Systems
- Structural Integrity:Glass roof systems often rely on bonding adhesives for structural support, ensuring safety and stability.
- Panoramic Views:These adhesives enable larger, unobstructed glass surfaces for panoramic views.
Headlight and Taillight Bonding
- Protection:Adhesives bond protective glass covers to headlights and taillights, thus protecting bulbs from environmental factors.
- Optical Clarity:They ensure optical clarity for proper lighting.
Interior Glass Components
- Enhanced Aesthetics:Glass bonding adhesives attach decorative elements to the vehicle’s interior, such as center console panels.
- Customization:They allow for customization options, including colored and textured glass.
ADAS Integration
- Camera and Sensor Mounting:Bonding adhesives secure cameras and sensors to the windshield, facilitating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Accuracy:A robust adhesive connection ensures precise positioning for accurate ADAS functionality.
Electric Vehicle Applications
- Battery Enclosures:In electric vehicles, glass bonding adhesives are used in battery enclosures, ensuring safety and insulation.
- Aerodynamics:Bonding adhesives help maintain aerodynamic efficiency in EVs by securing the glass components.
Benefits of Glass Bonding Adhesives
- Safety:They enhance vehicle safety by providing solid and reliable bonds that prevent the glass from detaching during accidents.
- Aesthetics:These adhesives enable seamless, aesthetically pleasing glass installations.
- Comfort:They reduce noise and vibrations, enhancing the ease of vehicle occupants.
- Durability:Glass bonding adhesives contribute to the long-term durability of automotive glass components.
- Waterproofing:Preventing leaks and water ingress protects the vehicle’s interior and electronic components.
Electronics Display Bonding
Electronics display bonding is a critical process in modern electronic device manufacturing. It securely attaches various components like displays, touch sensors, and protective layers. This process ensures device durability, performance, and user experience.
The Essence of Electronics Display Bonding
Electronics display bonding creates a unified unit from disparate components. This process involves:
Substrate Preparation
The base layer, often glass or plastic, is meticulously cleaned and prepared for subsequent layers’ attachment.
Adhesive Application
Manufacturers apply specialized adhesives to the substrate as bonds and optical enhancers.
Component Placement
Display panels, touch sensors, and protective layers are carefully positioned on the adhesive-coated substrate, requiring precision alignment.Curing and Bonding
Heat or UV light cures the adhesive, establishing a robust and resilient bond.
Quality Control
Strict quality checks detect defects like air bubbles or misalignments, ensuring a top-tier product.
Advantages of Electronics Display Bonding
This process offers several key benefits:
Enhanced Durability
Bonded displays better withstand shocks, impacts, and vibrations, extending device lifespans.
Superior Clarity
Specialized adhesives maintain excellent visual quality with minimal distortion.
Reduced Thickness
Eliminating mechanical fasteners allows for thinner, sleeker devices.
Improved Touch Sensitivity
Direct bonding enhances touch sensitivity and accuracy, elevating the user experience.
Water and Dust Resistance
Proper bonding enhances resistance to environmental factors, making devices more robust.
Challenges in Electronics Display Bonding
However, it comes with its own set of challenges:
Precision and Alignment
Achieving precise alignment during bonding to prevent display defects and touch sensitivity issues.
Material Compatibility
Selecting compatible adhesives and materials can be complex due to varying coefficients of thermal expansion.
Cost Considerations
High-quality adhesives and precise manufacturing can raise production costs, impacting device pricing.
Art and Design Installations
Glass bonding adhesive is pivotal in art and design installations, providing a versatile and innovative way to create stunning structures and artworks. This specialized adhesive allows artists and designers to fuse glass elements seamlessly, opening up possibilities for functional and aesthetic projects.
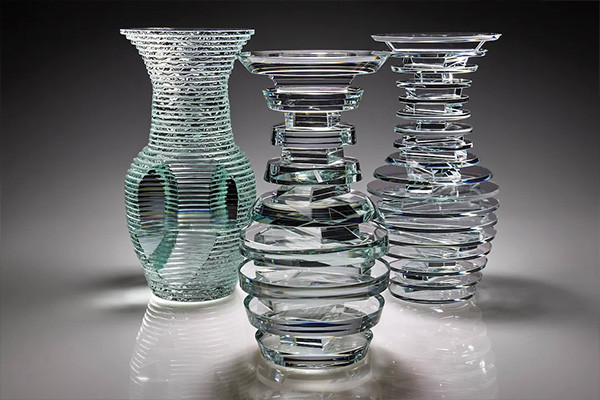

The Versatility of Glass Bonding Adhesive
Glass bonding adhesive is a highly versatile material used across various art and design disciplines. In architectural installations, it enables the creation of intricate glass facades, staircases, and bridges that appear to defy gravity. In contemporary art, artists use it to craft delicate and intricate sculptures that capture the interplay of light and transparency. The versatility of glass bonding adhesive allows for the realization of large-scale architectural wonders and complicated artistic masterpieces.
Strength and Durability
One of the critical advantages of glass bonding adhesive is its exceptional strength and durability. This adhesive can withstand extreme temperatures and environmental conditions, ideal for outdoor installations and public art. Its ability to securely bond glass ensures structures remain structurally sound and visually stunning for years.
Transparency and Aesthetics
Glass bonding adhesive maintains the inherent beauty of glass by providing a clear and almost invisible bond. This transparency enhances the aesthetics of glass installations, allowing light to pass through seamlessly and creating mesmerizing visual effects. Artists and designers can exploit this quality to play with light and shadow, creating captivating and dynamic art pieces.
Challenges and Precision
Working with glass bonding adhesive also presents challenges. Achieving the precise alignment of glass components demands meticulous attention to detail and a skilled hand. Even the slightest deviation can affect the overall quality of the installation. Moreover, artists and designers must consider the bonded glass elements’ weight and balance to ensure their creations’ structural integrity.
Innovation and Future Trends
As technology advances, so does the potential of glass bonding adhesive in art and design installations. Innovations in adhesive formulas may lead to stronger bonds and greater design flexibility. Additionally, integrating smart glass and interactive elements into adhesive-bonded structures represents an exciting avenue for future creativity.
Glass-to-Metal Bonding
Glass-to-metal bonding is a specialized process that involves joining glass and metal components to create durable and reliable connections. This technique finds applications in various industries, from electronics to aerospace, and is crucial in developing cutting-edge technologies.
The Science Behind Glass-to-Metal Bonding
At its core, glass-to-metal bonding relies on the differential coefficients of thermal expansion between glass and metal. This characteristic means that these materials expand and contract at different rates when heated and cooled. Precise control over temperature and pressure is necessary to achieve a successful bond. A carefully designed glass frit (a powdered glass mixture) is an intermediary material between the metal and glass surfaces. The frit flows when heated to its softening point, creating a mechanical and chemical bond with both materials as it cools and solidifies.
Applications in Electronics and Microelectronics
Glass-to-metal bonding is indispensable in the electronics industry, creating airtight seals for sensitive electronic components. These seals protect internal electronics from environmental factors such as moisture, gases, and contaminants, ensuring the longevity and reliability of devices like transistors, sensors, and connectors. Furthermore, glass-to-metal seals enable electrical feed-throughs, allowing signals and power to pass between electronic devices’ internal and external components.
Aerospace and High-Performance Engineering
In aerospace and high-performance engineering, glass-to-metal bonding is instrumental in developing sensors, instruments, and communication devices. The hermetic and highly reliable seals created by this process are essential for ensuring the functionality of critical components in extreme conditions, including extreme temperatures, high pressures, and radiation exposure. Whether in space exploration, aviation, or military applications, glass-to-metal bonding helps guarantee the safety and success of missions.
Medical and Scientific Instruments
Glass-to-metal bonding also finds its way into medical and scientific instruments, where precision and reliability are paramount. For instance, analytical devices, laboratory equipment, and medical implants like pacemakers utilize glass-to-metal seals. These seals provide a sterile and stable environment for sensitive components, ensuring the accuracy and safety of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
High-Temperature Glass Bonding
High-temperature glass bonding is a specialized process that involves joining glass components at elevated temperatures, resulting in strong and durable bonds capable of withstanding extreme heat and environmental conditions. This technique finds applications in various industries, from manufacturing to aerospace, where maintaining structural integrity and functionality under high temperatures is crucial.
Benefits and Challenges of High-Temperature Glass Bonding
High-temperature glass bonding offers a range of benefits, including:
- Exceptional Durability: Bonds formed through high-temperature processes are remarkably strong and resistant to thermal expansion, making them suitable for environments with rapid temperature fluctuations.
- Hermetic Seals:The bonds achieved are often airtight and impervious to gases and liquids, making them ideal for applications requiring sealed enclosures.
- Consistent Performance:High-temperature bonding creates bonds with uniform properties, ensuring consistent performance across various conditions.
However, this process comes with its challenges:
- Precise Control:Achieving the correct temperature and pressure conditions requires careful control to avoid overheating or thermal stress on the glass components.
- Material Compatibility:Compatibility between glass types and bonding materials is essential for successful high-temperature bonding.
Applications in Aerospace and Manufacturing
High-temperature glass bonding finds extensive use in aerospace and manufacturing industries due to its unique properties:
- Aerospace:Components of spacecraft, satellites, and aerospace instruments require reliable bonds that can endure the extreme conditions of space travel, including intense heat during reentry.
- Manufacturing:High-temperature bonding produces glass-to-metal seals in sensors, semiconductors, and vacuum tubes. It ensures stable performance even in demanding industrial processes.
Advanced Materials and Techniques
In recent years, advancements in materials and techniques have expanded the possibilities of high-temperature glass bonding:
- New Bonding Materials:Researchers have developed innovative adhesive materials and glass frit compositions to enhance bond strength and temperature resistance.
- Laser-Assisted Bonding:Increasingly, laser technology facilitates high-temperature bonding by providing controlled and localized heating, thus minimizing thermal stress.
Future Prospects
As industries continue to demand materials capable of withstanding higher temperatures, high-temperature glass bonding will play a vital role in enabling innovation and progress:
- Energy Sector:High-temperature bonding can contribute to developing efficient energy systems, such as solar concentrators and thermal storage devices.
- Emerging Technologies:Fields like advanced electronics and high-performance optics will benefit from the heat-resistant properties of high-temperature bonds.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing and quality assurance are integral aspects of the glass bonding adhesive industry, ensuring that adhesive products meet stringent performance, safety, and reliability standards. These processes encompass a range of tests and inspections to verify the adhesive’s properties and adherence to industry-specific requirements.
Key Testing Methods
Adhesion Strength Testing: This crucial test evaluates the adhesive’s ability to bond glass to various substrates and assesses the strength of the bond. Common methods include:
- Shear Strength Test: Measures the adhesive’s resistance to a force applied parallel to the adhesive-substrate interface.
- Tensile Strength Test:Evaluates the adhesive’s resistance to a force applied perpendicular to the bond line.
Thermal Resistance Testing: Given the frequent exposure of glass bonding adhesive to temperature fluctuations, thermal resistance testing is vital. Key aspects include:
- Thermal Cycling Tests: To assess their ability to withstand thermal stress, subject adhesive bonds to repeated temperature changes.
- Heat Aging Tests:Determine the adhesive’s performance and stability when exposed to high temperatures for an extended period.
Chemical Resistance Testing: Assess the adhesive’s resistance to various chemicals and solvents, especially important in applications where chemical exposure is likely.
Environmental Aging Tests: Evaluate how the adhesive withstands environmental factors such as UV radiation, humidity, and salt spray, which can affect long-term performance.
Quality Assurance Protocols
- ISO Certification:Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards, ensuring consistent quality and environmentally responsible practices.
- Material Traceability:Comprehensive documentation tracks the adhesive materials used in each batch, allowing for traceability in case of issues or recalls.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC):Employed during manufacturing, SPC monitors and controls critical process parameters to maintain consistent product quality.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- Ultrasonic Testing:This NDT technique uses sound waves to detect flaws within the adhesive bond, offering insights into the integrity of the adhesive.
- Thermography:By analyzing the heat patterns generated during adhesive curing, thermography can identify potential bonding issues.
Performance Standards and Certifications
- ASTM Standards:The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) sets industry standards for testing methods and specifications, ensuring uniformity in quality assessment.
- UL Certification:Products that adhere to Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standards undergo rigorous testing for safety and performance.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Optical clarity and transparency are essential characteristics of glass bonding adhesive. They enable the creation of visually stunning structures and artworks while maintaining the integrity of the glass components. The use of transparent adhesives in glass bonding has broad applications across various industries, emphasizing aesthetics, functionality, and safety.
Achieving Crystal-Clear Bonds
- Transparent Adhesive Formulation:Manufacturers formulate glass bonding adhesives to ensure minimal interference with light transmission. This transparency relies on the careful selection of materials and precise manufacturing processes.
- Invisible Bonds:High-quality glass bonding adhesive creates virtually invisible bonds when correctly applied. This feature is precious in artistic and architectural applications where aesthetics are paramount.
Applications in Architectural Design
- Facade Systems:Transparent adhesive plays a pivotal role in modern architecture, where the creation of all-glass facades is a defining trend. These adhesives enable architects to design buildings with sleek, uninterrupted glass surfaces.
- Structural Glazing:Structural Glazing involves using transparent adhesives to bond glass panels to a building’s structural framework, thus enhancing the building’s appearance and energy efficiency.
Artistic Expression
- Contemporary Art Installations:Artists use transparent adhesives to create sculptures and installations that manipulate light and transparency, producing captivating visual effects.
- Stained Glass Restoration:In restoring stained glass windows and artworks, the transparent adhesive is indispensable for seamlessly repairing damaged glass pieces while preserving the original aesthetics.
High Performance and Durability
- Resistance to Environmental Factors:Engineers design transparent adhesives to withstand environmental factors, including UV radiation, humidity, and temperature fluctuations, to ensure long-term durability and preserve optical clarity.
- Hermetic Sealing:In applications requiring airtight seals, such as scientific instruments or electronic enclosures, transparent adhesives maintain optical clarity while providing a reliable tight barrier.
Innovations and Future Trends
- Smart Glass Integration:Integrating intelligent glass technologies with transparent adhesives, such as electrochromic or photochromic glass, opens possibilities for adaptive and interactive architectural and artistic installations.
- Improved Formulation: Ongoing research and development efforts focus on enhancing the optical properties of glass bonding adhesive, aiming for even higher clarity levels, reduced yellowing over time, and improved resistance to environmental factors.
Dispensing Techniques for Precision
Precision glass bonding adhesive plays a critical role in various industries, enabling the creation of intricate glass structures and devices. Whether in electronics, optics, or medical devices, the quality and accuracy of glass bonding are paramount. To achieve precision in glass bonding, mastering dispensing techniques that ensure the adhesive bonds’ uniformity, strength, and durability is crucial. This article delves into the essential dispensing techniques for precision glass bonding adhesive, highlighting the key factors contributing to successful bonding outcomes.
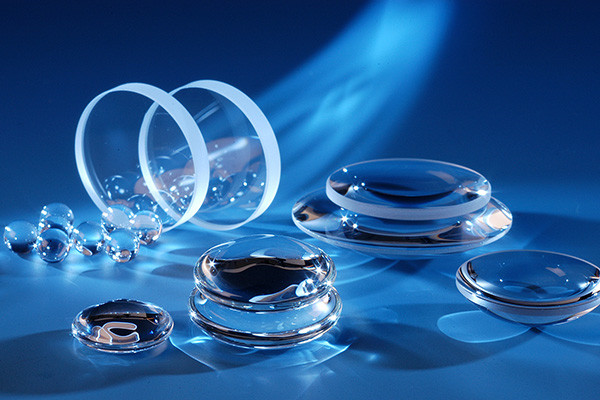

Selecting the Right Adhesive
Choosing the appropriate adhesive is the first and foremost consideration in achieving precision glass bonding. One should carefully evaluate substrate compatibility, thermal resistance, and curing time. For precision applications, opt for adhesives specifically designed for glass bonding, as they offer superior adhesion and long-term stability.
Dispensing Equipment and Techniques
Investing in high-quality dispensing equipment is crucial for precise adhesive application. Equipment like precision dispensers, syringe barrels, and dispense tips allow for accurate control over adhesive volume and placement. The choice between manual and automated dispensing depends on the project’s scale and requirements. Computerized systems often provide more consistent results, especially when dealing with intricate designs and large quantities.
Surface Preparation and Cleaning
Achieving a solid bond begins with proper surface preparation. Meticulously cleaning glass surfaces and, in some cases, treating them is necessary to enhance adhesion. Techniques such as plasma cleaning or UV ozone treatment can remove contaminants and activate the glass surface for improved bonding.
Optimizing Dispensing Parameters
The success of precision glass bonding hinges on controlling dispensing parameters such as flow rate, dispensing pressure, and nozzle size. Fine-tuning these parameters ensures that the adhesive is applied evenly and consistently. Controlling environmental factors like temperature and humidity can also influence adhesive curing and bonding strength.
Quality Control and Inspection
Integrate quality control and inspection processes into the bonding workflow to ensure precision. Regularly checking bond strength, alignment, and visual defects can help catch issues early on, preventing costly rework or product failure downstream.
Future Innovations in Glass Bonding
Glass bonding has come a long way in enabling cutting-edge technology and design across various industries. However, innovation in this field continues to evolve as new materials, techniques, and applications emerge. This paragraph explores the exciting future innovations in glass bonding, shedding light on how they promise to revolutionize industries ranging from electronics to architecture.
Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology
Future innovations in glass bonding are likely closely tied to developing advanced materials and nanotechnology. Researchers are working on creating adhesives with enhanced properties, such as higher heat resistance, greater transparency, and increased strength. Nanomaterials, like carbon nanotubes and graphene, may be incorporated into adhesives to improve their performance, making glass bonds even more resilient and versatile.
Enhanced Precision with Robotics
Robotic technology will play a significant role in the future of glass bonding. Automated mechanical systems equipped with precision dispensers and vision systems can achieve unparalleled accuracy in adhesive application. This technology speeds up production processes and ensures consistent, high-quality bonding in complex designs, from electronics to medical devices.
Green and Sustainable Solutions
As sustainability becomes a paramount concern, future innovations in glass bonding will include eco-friendly adhesive alternatives. Researchers are developing bio-based adhesives derived from renewable resources and recyclable bonding materials to reduce the environmental impact of glass bonding processes. These innovations align with the global push for greener manufacturing practices.
Integration with IoT and Smart Glass
Innovations in glass bonding are converging with the Internet of Things (IoT) and innovative glass technologies. Bonding techniques that seamlessly integrate sensors, displays, and connectivity features into glass structures are poised to reshape industries like automotive, architecture, and consumer electronics. Smart glass with dynamically adjustable transparency and augmented reality capabilities exemplify what’s on the horizon.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing and additive manufacturing are poised to transform glass bonding. This technology allows for fabricating intricate, customizable glass structures layer by layer. Advances in 3D printing methods for glass bonding will enable the creation of complex shapes and structures that were previously challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Sustainability in Glass Adhesive Applications
Sustainability is a pressing concern across industries, and glass adhesive applications are no exception. As the demand for environmentally responsible practices grows, there is a compelling need to adopt sustainable approaches in glass bonding. This paragraph explores the critical aspects and innovative strategies driving sustainability in glass adhesive applications, focusing on materials, manufacturing processes, and the broader environmental impact.
Eco-friendly Adhesive Formulations
Bio-based Adhesives: Developing adhesives derived from renewable resources like soy, starch, or lignin reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers the carbon footprint of glass bonding.
Water-based Adhesives: Water-based adhesives emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants and offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based counterparts.
Recyclable Adhesives: Adhesives designed for easy separation or recycling of bonded glass components contribute to a circular economy by reducing waste.
Reducing Energy Consumption
- Low-Temperature Curing:Adhesives that cure at lower temperatures minimize energy consumption during bonding and prevent damage to heat-sensitive materials.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment:Employing energy-efficient dispensing and curing equipment reduces electricity usage in glass bonding operations.
- Solar-powered Facilities:Integrating solar energy systems into manufacturing facilities can make glass bonding processes more sustainable by reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
- Material Efficiency:Precision dispensing techniques and robotic automation minimize adhesive wastage, ensuring that only the necessary amount of adhesive is applied.
- Recycling Programs:Implementing recycling programs for glass substrates and adhesive containers reduces the overall environmental impact of glass bonding operations.
- Lifecycle Assessments and Environmental Standards
- Environmental Impact Assessments:Conducting thorough lifecycle assessments helps identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about materials and processes.
- Compliance with Eco-labels:Adhering to recognized environmental certifications, such as LEED or ISO 14001, demonstrates a commitment to sustainability in glass adhesive applications.
Collaborative Industry Initiatives
- Knowledge Sharing:Industry collaborations and forums enable sharing of best practices and developing sustainability benchmarks for glass bonding.
- Research and Development:Joint research efforts facilitate the discovery of innovative, sustainable adhesive materials and processes.
Glass bonding adhesive has opened new vistas in design and engineering, enabling the creation of transparent structures that seamlessly merge strength and aesthetics. Its role in bridging the gap between traditional bonding methods and modern architectural and industrial demands cannot be overstated. As industries seek innovative ways to enhance visual appeal and structural integrity, glass bonding adhesive remains vital. With advancements in adhesive technology and a growing focus on sustainability, the potential for glass bonding adhesive to shape the future of architecture, design, and manufacturing is boundless.