Glass Adhesive Bonding System: An In-Depth Guide
Glass Adhesive Bonding System: An In-Depth Guide
In the modern world, glass is increasingly utilized in various applications ranging from architecture to electronics and even automotive design. With the rise in demand for glass as a structural and aesthetic material, effective bonding systems have become paramount. Glass adhesive bonding systems offer a reliable and efficient solution for joining glass to itself or other materials. This article will explore the intricacies of glass adhesive bonding systems, their types, applications, advantages, and critical considerations for achieving optimal results.
Understanding Glass Adhesive Bonding Systems
Glass adhesive bonding systems contain specially formulated adhesives to create solid and durable bonds between glass and various substrates. These systems differ significantly from traditional mechanical fastening methods, providing a seamless, aesthetically pleasing finish while distributing stress more evenly across the bonded area. The primary components of glass adhesive bonding systems include the adhesive itself, the bonding surface preparation, and the curing process.
Types of Adhesives Used in Glass Bonding
- Silicone Adhesives: Silicone adhesives are known for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to weathering and UV light. They are instrumental in applications where thermal expansion and contraction are a concern, such as building facades and glazing systems. Silicone adhesives can also accommodate movement without compromising the bond, making them ideal for dynamic environments.
- Epoxy Adhesives: Epoxy adhesives offer high strength and excellent chemical resistance. They are often used in structural applications where a strong bond is essential. Epoxy systems typically consist of a resin and a hardener, which, when mixed, undergo a chemical reaction that leads to curing. Epoxies can bond glass to various materials, including metals and plastics.
- Polyurethane Adhesives: Polyurethane adhesives are versatile and can bond various materials. They exhibit good flexibility and impact resistance, making them suitable for applications in the automotive and construction industries. Polyurethanes also provide excellent moisture resistance, which is advantageous in outdoor applications.
- Acrylic Adhesives: Acrylic adhesives cure quickly and can provide high bond strength. They are often used in applications where speed is essential, such as manufacturing processes. Acrylics are also known for their excellent clarity, which makes them ideal for visible bonding applications.
- UV-Curable Adhesives: These adhesives cure when exposed to ultraviolet light, providing fast processing times and intense bonds. They are commonly used in the electronics industry to bond glass to other materials in devices such as smartphones and tablets.
Surface Preparation for Bonding
Proper surface preparation is critical to achieving adhesive solid bonds. The effectiveness of glass adhesive bonding systems largely depends on the cleanliness and condition of the surfaces to be bonded. Here are some critical steps in the surface preparation process:
- Cleaning: All surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned to remove dust, dirt, oils, and other contaminants. Standard cleaning methods include using isopropyl alcohol or solvents designed for glass cleaning.
- Abrasion: Depending on the adhesive type, surface roughening may enhance adhesion. This can be achieved through sandblasting or abrasive pads to create a rough surface texture.
- Priming: Some adhesives may require a primer to enhance adhesion, particularly when bonding glass to non-glass surfaces. Primers improve the wetting of the adhesive on the surface and enhance bond strength.
- Drying: After cleaning and applying any necessary primer, allowing the surfaces to dry completely before applying the adhesive is crucial.
Curing Process
The curing process varies depending on the type of adhesive used. Temperature, humidity, and the specific requirements of the adhesive formulation can influence curing. To ensure optimal bond strength, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for curing times and conditions.
- Room Temperature Curing: Many adhesives will cure at room temperature, although they may take longer to reach full strength.
- Heat Curing: Some adhesive systems benefit from heat application during the curing process. Heat can accelerate the curing reaction, allowing faster processing times and improved bond characteristics.
- UV Curing: UV-curable adhesives require exposure to UV light to initiate the curing process. This method provides rapid curing times, making it ideal for high-speed manufacturing environments.
Applications of Glass Adhesive Bonding Systems
Glass adhesive bonding systems are utilized in a wide array of applications across various industries:
Construction and Architecture
Glass is frequently used in facades, windows, and curtain walls in construction. Adhesive bonding systems provide the necessary strength to support large glass panels while minimizing the visual impact of mechanical fasteners. Additionally, adhesives allow for greater design flexibility and can create seamless joints that enhance the building’s aesthetics.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, glass adhesive bonding is crucial for attaching windshields, side windows, and rear glass. Adhesives provide structural integrity and support the vehicle’s frame while reducing noise and vibration. Furthermore, adhesive bonding can improve crash performance by allowing glass to absorb energy during impact.
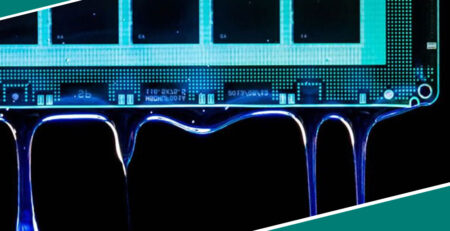
Electronics
In electronics, glass is often bonded to various components such as displays, sensors, and touch panels. UV-curable adhesives are particularly popular due to their rapid curing times and excellent clarity. Solid and precise bonds are essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of electronic devices.
Furniture and Interior Design
Adhesive bonding systems, such as glass tabletops, shelving, and decorative elements, are also used in furniture and interior design applications. Adhesives allow for clean lines and a modern aesthetic while maintaining structural integrity.
Art and Craft
In art, glass adhesive bonding is often employed to create sculptures, stained windows, and mosaics. Artists utilize specialized adhesives to achieve their work’s functional and artistic goals.
Advantages of Glass Adhesive Bonding Systems
- Aesthetic Appeal: Adhesive bonding eliminates the need for visible fasteners, resulting in a cleaner, more modern look.
- Design Flexibility: Adhesives allow for greater design freedom, enabling innovative shapes and configurations that may not be achievable with traditional mechanical fasteners.
- Weight Reduction: Adhesives can contribute to lighter constructions, which is especially beneficial in applications like automotive design, where weight reduction can lead to improved fuel efficiency.
- Stress Distribution: Adhesive bonds distribute stress more evenly across the joint, reducing the likelihood of failure at stress concentration points.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation: Adhesives can help improve thermal and acoustic insulation properties, making them ideal for energy efficiency and noise reduction applications.
Critical Considerations for Glass Adhesive Bonding
Selection of Adhesive
Choosing a suitable adhesive is critical for achieving a successful bond. Factors to consider include the materials being bonded, the environment in which the bond will be used (e.g., exposure to moisture or chemicals), and the required bond strength.
Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions during application and curing. Humidity, temperature, and airflow can affect the curing process and final bond strength. For example, high humidity can interfere with the curing of certain adhesives.
Testing and Quality Control
Implementing rigorous testing and quality control measures is essential to ensure the integrity of adhesive bonds. This may involve conducting peel tests, shear tests, or other relevant assessments to confirm bond strength and durability.
Compliance with Standards
Adhesive bonding systems must comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Familiarity with these requirements is essential, particularly in industries such as automotive and construction, where safety and performance standards are stringent.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Glass adhesive bonding systems have revolutionized how glass is utilized in various industries, providing strong, durable, and aesthetically pleasing bonds. With the right selection of adhesive, proper surface preparation, and adherence to curing guidelines, these systems can deliver exceptional performance in diverse applications. As technology advances, new adhesives and bonding techniques will continue to enhance the versatility and capabilities of glass in modern design and manufacturing. Understanding the intricacies of glass adhesive bonding systems is essential for professionals across multiple sectors, ensuring the longevity and reliability of their applications.
For more about a complete guide to glass adhesive bonding system: an in-depth guide, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.