Cyanoacrylate Adhesive

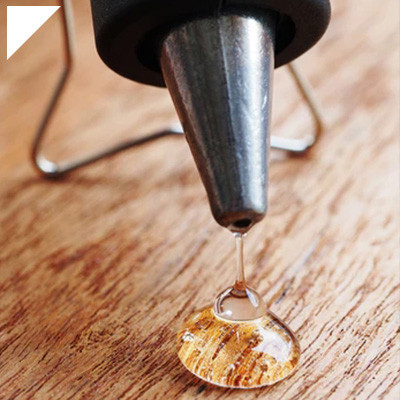
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” is a versatile and widely used adhesive with remarkable bonding properties and practical applications across various industries. The science behind cyanoacrylate adhesive involves its chemical composition, curing process, and bonding mechanisms.
Cyanoacrylate adhesives are a type of fast-curing, one-part adhesive. They typically comprise monomers, small molecules that can polymerize (link together) to form long chains. The primary component of cyanoacrylate adhesive is the monomer, which has the general formula: R-C≡C-O-C(=O)-R’, where R and R’ are alkyl groups.
In adhesive technology, few substances command attention, like cyanoacrylate adhesive. Its unique characteristics distinguish it from its adhesive counterparts, captivating industries and consumers alike.
This adhesive’s exceptional properties have rendered it an invaluable tool in diverse applications, from its rapid bonding process to its compatibility with many materials. Unraveling the molecular intricacies that facilitate its strong bonds, investigating its performance under stress, and understanding its thermal stability are just a few of the compelling aspects that make cyanoacrylate adhesive a subject of fascination.
What Makes Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Special?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, often referred to as “super glue,” is special due to its unique characteristics that set it apart from other types of adhesives. Here are some key features that make cyanoacrylate adhesive special:
- Rapid Bonding:Cyanoacrylate adhesives are known for their incredibly fast bonding capabilities. Depending on the specific formulation and bonded materials, they can form strong bonds in seconds to minutes. This quick setting time makes them ideal for applications where speed and efficiency are crucial.
- Single-Component System:Cyanoacrylate adhesives are typically single-component systems, so they do not require mixing with other substances before use. This simplicity makes them convenient and easy to apply, eliminating the need for complex preparation steps.
- Wide Range of Substrates:Cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond to various substrates, including metals, plastics, rubber, ceramics, glass, and porous materials. This versatility makes them suitable for multiple applications across different industries.
- Excellent Adhesion Strength: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can provide powerful bonds despite their rapid curing time. They can form connections with high tensile, shear, and peel strengths, making them suitable for demanding applications that require secure adhesion.
- No Need for Heat or Pressure: Unlike other adhesives that require heat or pressure to cure effectively, cyanoacrylate adhesives cure at room temperature without needing external factors. This property makes them suitable for bonding delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
- Limited Gap Filling:One of the limitations of cyanoacrylate adhesives is their relatively low gap-filling ability. They work best when applied to surfaces that fit closely together, as the adhesive does not fill significant gaps as effectively as other types of adhesives, such as epoxies.
- Moisture-Curing Variants:Some cyanoacrylate adhesives are formulated to cure in the presence of moisture, which can be advantageous for bonding substrates that might have some level of surface moisture. These moisture-curing variants can help improve bond strength and versatility.
- Transparent and Non-Intrusive Bonds:Cyanoacrylate adhesives dry to form clear and transparent bonds, which can be advantageous when aesthetics are necessary or when the adhesive needs to be inconspicuous.
- Chemical Resistance: Cyanoacrylate adhesives resist various chemicals, including many solvents and oils. This property can be important for applications where the bonded materials will be exposed to multiple environmental conditions.
- Convenient Packaging: Cyanoacrylate adhesives are available in various packaging options, including small tubes, bottles, and even single-use applicators. This wide range of packaging makes them suitable for industrial and consumer applications.
Despite their unique characteristics and advantages, it’s important to note that cyanoacrylate adhesives also have limitations. For example, they may need to perform better in situations involving high temperatures, continuous exposure to moisture, or situations where extreme flexibility is required. It’s always crucial to carefully consider the specific needs of your project and the compatibility of the adhesive with the materials being bonded.
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Form Bonds?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, often known as “super glue” or “instant glue,” forms bonds through polymerization. The primary active ingredient in cyanoacrylate adhesives is a monomer called cyanoacrylate. When the adhesive comes into contact with moisture from the air or the surfaces being bonded, it initiates a rapid polymerization reaction that creates a strong bond.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how cyanoacrylate adhesive forms bonds:
- Monomer Stage:The adhesive comprises cyanoacrylate monomers, small molecules with a reactive double bond between a carbon and a nitrogen atom (C=C). These double bonds are highly reactive and susceptible to opening up to form longer chains.
- Initiation: When the adhesive comes into contact with moisture (water or even the humidity in the air), the moisture acts as a weak base that triggers the breakdown of the cyanoacrylate monomers. The hydroxide ions from the water initiate the process by attacking the carbon-nitrogen double bond in the cyanoacrylate monomer. This breaks the double bond and forms a negatively charged ion (anion) called a carbanion.
- Polymerization: The carbanion reacts with another cyanoacrylate monomer molecule and the negatively charged carbon atom bonds with the adjacent molecule’s positively charged carbon atom. This forms a longer chain, with the new molecule’s carbon-nitrogen double bond now available for further reaction.
- Chain Reaction: This process of breaking the double bond, forming carbanions, and linking them to adjacent molecules repeats rapidly, creating a chain reaction. As more and more cyanoacrylate monomers react, the chain of polymer molecules grows longer and more interconnected.
- Cross-Linking: The polymer chains intertwine and create a strong network, known as a cross-linked polymer. This network of polymer chains forms a solid structure that acts as a bridge between the bonded surfaces.
- Solidification: As the polymerization reaction continues, the adhesive changes from a liquid or semi-liquid state to a solid form. The cross-linked polymer matrix binds tightly to the surfaces it is in contact with, creating a strong adhesive bond.
It’s important to note that the rapidity of the polymerization reaction is a crucial characteristic of cyanoacrylate adhesives. This quick curing process is why they are often called “instant” or “super” glue. Additionally, the bond formed is quite strong and can be used for various materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and more.
However, using cyanoacrylate adhesives in well-ventilated areas is essential, as the fumes generated during curing can irritate the eyes and respiratory system. Also, surfaces should be clean and dry to ensure the best bond formation.
Why Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Bond So Quickly?
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as superglues, bond quickly due to chemical and physical factors. The rapid bonding process can be attributed to the following factors:
- Polymerization Reaction: Cyanoacrylate adhesives undergo anionic polymerization when they come into contact moisture in the air or on bonded surfaces. This reaction involves rapidly forming strong chemical bonds between the adhesive molecules. The polymerization process releases heat as a byproduct, further acceleratiresponseeaction.
- Small Molecule Size: Cyanoacrylate molecules are relatively small and compact. This allows them to penetrate tiny surface imperfections and create a strong bond by effectively surrounding and intertwining with the irregularities on the joined surfaces.
- Lack of Solvent: Unlike many other adhesives that contain solvents or water, cyanoacrylates are solvent-free. This absence of solvents means there is no need for the adhesive to evaporate or dry, which can slow down the bonding process. The immediate contact between the adhesive and the surfaces promotes rapid bonding.
- Hydrophobic Nature: Cyanoacrylate adhesives are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. This hydrophobic nature ensures that the adhesive doesn’t interact significantly with any moisture on the surfaces, allowing the polymerization reaction to occur efficiently.
- Thin Bond Line: The thin layer of adhesive that forms between the bonded surfaces allows for efficient polymerization reaction transmission. The proximity of the adhesive molecules in the thin bond line leads to a faster and more effective bond formation.
- High Bond Strength: The chemical bonds formed during the polymerization process result in a strong adhesive bond. This bond strength contributes to the adhesive’s ability to hold surfaces together quickly.
- Catalytic Effect of Basic Surfaces: Basic surfaces (such as those containing trace amounts of alkaline substances) can act as catalysts for the polymerization reaction of cyanoacrylate adhesives. These surfaces can enhance the speed at which the adhesive cures and bonds the materials.
In summary, the rapid bonding of cyanoacrylate adhesives can be attributed to their anionic polymerization reaction upon contact with moisture, their small molecule size, lack of solvents, hydrophobic nature, thin bond line, high bond strength, and the potential catalytic effects of certain surfaces. These factors collectively contribute to the lightning-fast bonding process for which cyanoacrylate adhesives are known.
What Happens at the Molecular Level During Bonding?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue” or “CA glue,” is a fast-acting and robust adhesive that works on various materials. Its effectiveness across different surfaces is due to its unique chemical properties and bonding mechanism. Cyanoacrylate adhesives polymerize rapidly upon contact with moisture, creating solid and durable bonds. Let’s explore how cyanoacrylate adhesive works on different materials:

- Plastics: Cyanoacrylate adhesives generally work well on many plastics, including acrylic, polycarbonate, ABS, etc. The adhesive forms a bond by chemically reacting with surface moisture, which is commonly present in plastics. However, some plastics may have surface treatments or contaminants that can hinder bonding. Roughening the surface or using a primer specifically designed for plastics can improve adhesion.
- Metals: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond to various metals, such as aluminum, stainless steel, and brass. Similar to plastics, the presence of moisture on metal surfaces facilitates bonding. A primer designed for metals can sometimes enhance adhesion, particularly with smooth or non-porous metals. However, due to their brittle nature, cyanoacrylates may not be suitable for high-stress metal applications.
- Rubber and Elastomers: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond to certain types of rubber and elastomers, such as silicone rubber. However, the bonding success depends on the adhesive’s specific formulation and the rubber type. Some elastomers may not be compatible with cyanoacrylates due to their low surface energy and lack of moisture.
- Wood: Cyanoacrylates can bond well to wood surfaces, creating a solid bond. The porous nature of wood allows for good moisture content, which promotes the curing of the adhesive. It’s essential to ensure the wood surface is clean and free from oils or finishes that could hinder bonding.
- Ceramics and Glass: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can effectively bond ceramics and glass, especially if the surfaces are clean and free from contaminants. The adhesive’s rapid polymerization helps create quick bonds. However, in high-temperature or high-moisture environments, the bond may weaken over time.
- Paper and Cardboard: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond paper and cardboard effectively. However, other types of adhesive may be more commonly used for these materials due to their flexibility and specific requirements.
It’s important to note that while cyanoacrylate adhesives offer strong bonds on many surfaces, their brittleness can be a limitation in some applications where flexibility or impact resistance is required. Additionally, proper surface preparation, such as cleaning, degreasing, and sometimes roughening the surface, can significantly enhance the adhesive’s performance on various materials.
When using cyanoacrylate adhesives, it’s recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for surface preparation, application, and curing to achieve the best results for your specific materials and applications.
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Perform Under Stress?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” is a fast-bonding adhesive that forms strong bonds quickly when exposed to moisture in the air. However, it might stick to only some surfaces due to a combination of factors related to surface chemistry and material properties. Here are some reasons why cyanoacrylate adhesive might not adhere to everything:
- Surface Cleanliness:Cyanoacrylate adhesives bond better to clean and dry surfaces. If a character is dirty, oily, or contaminated with grease, dust, or fingerprints, the adhesive might not be able to establish a proper bond.
- Surface Roughness:Adhesives tend to bond more effectively to surfaces with some roughness. If a character is highly smooth or lacks micro-irregularities, the adhesive might struggle to create a mechanical interlocking and achieve a strong bond.
- Surface Energy:Surface energy refers to the attraction of a surface to other materials. Some materials have high surface energy, making them more receptive to bonding with adhesives. Others have low surface energy, causing adhesives to have difficulty spreading and forming strong bonds.
- Chemical Composition: Different materials have varying chemical compositions, which can affect their interaction with cyanoacrylate adhesive. Some materials have chemical properties that repel or hinder the adhesive’s ability to form strong bonds.
- Moisture Content: Cyanoacrylate adhesives require moisture to polymerize and create a bond. Some materials have very low moisture content, making it difficult for the adhesive to cure correctly and establish a strong bond.
- Temperature: Adhesive performance can be influenced by temperature. Extremely low or high temperatures can affect the adhesive’s ability to cure and bond effectively.
- Flexibility: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can become brittle once cured. If the materials being bonded undergo frequent flexing or movement, the adhesive might be unable to maintain its bond over time.
- Chemical Compatibility:Some materials can react chemically with cyanoacrylate adhesive, leading to reduced bonding effectiveness or even degradation of the adhesive.
- Release Agents:Certain materials are coated with release agents or anti-adhesive substances to prevent sticking. These coatings can interfere with the adhesive’s ability to bond.
- Porous Surfaces:Highly porous surfaces can absorb the adhesive, preventing it from effectively bonding with the material’s surface.
In summary, the ability of cyanoacrylate adhesive to stick to a particular surface is influenced by a combination of factors, including surface cleanliness, roughness, energy, chemical composition, moisture content, temperature, flexibility, chemical compatibility, presence of release agents, and porosity. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful and reliable bonding with cyanoacrylate adhesives.
What are the Safety Precautions for Using Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue or instant glue, is a powerful adhesive that can bond quickly and strongly to various surfaces. To use it safely, you should follow these safety precautions:
- Ventilation: Always work in a well-ventilated area. Cyanoacrylate adhesives can release fumes that may irritate your eyes, nose, and throat.
- Protective Gear: Wear appropriate protective gear, such as safety goggles and gloves, to prevent contact with the adhesive. In case of accidental contact, you can minimize the risk of skin bonding.
- Skin Protection: Avoid skin contact with the adhesive. If it does get on your skin, do not try to pull it off. Instead, use acetone or nail polish remover to dissolve the adhesive gently. Wash the affected area with soap and water afterward.
- Eye Protection:Protect your eyes from accidental splashes by wearing safety goggles. If the adhesive does come into contact with your eyes, flush them with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention immediately.
- Clothing Protection: Wear old or disposable clothing to prevent accidental bonding of the adhesive to your clothes.
- Surface Preparation: Make sure the characters you are bonding are clean, dry, and free from grease or oil. This will ensure a stronger bond and reduce the chance of fumes being released due to incomplete curing.
- Avoid Inhalation: Do not inhale the fumes directly. If you’re working with large amounts of adhesive, consider wearing a mask or using an exhaust fan to reduce fume exposure.
- Application Control:Apply only a thin layer of adhesive. Excess adhesive can result in longer curing times and increased fume release.
- Keep Out of Reach: Keep cyanoacrylate adhesive out of reach of children and pets. It’s a strong adhesive and not suitable for unsupervised use by minors.
- Storage: Store the adhesive in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ensure the cap is tightly closed to prevent the adhesive from drying out.
- Emergency Preparedness: Keep acetone or nail polish remover on hand in case of accidental skin bonding. Know the location of the nearest eyewash station in your workspace.
- Read the Instructions:Carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions and warnings on the adhesive product. Different formulations might have slightly different handling instructions.
- Disposal: Dispose of unused or expired adhesive following local regulations. Do not pour it down the drain or throw it in the regular trash.
Remember, while cyanoacrylate adhesives are versatile and robust, they require careful handling to ensure your safety and achieve the best results. If you have any doubts or concerns, consult the product’s safety data sheet (SDS) and seek advice from professionals experienced in using such adhesives.
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Resist Temperature Extremes?
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as superglues, exhibit varying degrees of resistance to temperature extremes depending on the formulation and brand. Here’s how they generally respond to temperature:
- Low Temperatures: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can become brittle and lose their bond strength when exposed to extremely low temperatures. At sub-zero temperatures, the adhesive’s ability to flex and absorb stress is reduced, which can lead to cracking or debonding. However, some specialized formulations are designed to maintain their flexibility and bond strength at lower temperatures, making them suitable for applications in colder environments.
- High Temperatures: The heat resistance of cyanoacrylate adhesives is limited compared to other adhesive types. When exposed to high temperatures, such as those above 150°C (300°F), cyanoacrylates can break down, lose strength, and even evaporate, causing a reduction in bond performance. This is due to their relatively low molecular weight and the chemical structure of the adhesive.
- Specialized Formulations: Some specialized cyanoacrylate adhesive formulations are engineered to improve temperature resistance. These formulations might incorporate additives or modifications to the introductory cyanoacrylate chemistry to enhance the adhesive’s ability to withstand higher or lower temperatures. These specialized formulations are often labeled as “high-temperature” or “low-temperature” variants and can be used in specific applications where temperature extremes are a concern.
Considerations:
When using cyanoacrylate adhesives in applications that involve temperature extremes, it’s essential to:
- Check Product Specifications: Read the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for temperature resistance. Different brands and formulations can have varying tolerances to temperature extremes.
- Test Bond Strength: Conduct tests on a small-scale or non-critical application to assess the adhesive’s performance under the expected temperature conditions. This will give you a better understanding of how the adhesive will behave in your application.
- Choose the Right Formulation: If your application involves temperature variations, consider using a specialized formulation designed for the intended temperature range.
- Consider Alternatives:In cases where extreme temperature resistance is required, you should explore alternative adhesive types, such as epoxy adhesives or silicone-based adhesives, which often offer better resistance to both high and low temperatures.
Remember that cyanoacrylate adhesives can be a convenient choice for many applications, but their performance in extreme temperatures might be limited. Always make an informed decision based on the specific demands of your project and consult with adhesive manufacturers or industry experts for recommendations tailored to your needs.
Why Is Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Used in Medical Applications?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” is used in medical applications for wound closure and surgical procedures due to the unique properties that make it suitable. Here are some reasons why cyanoacrylate adhesive is used in medical applications:
- Quick and Strong Bonding: Cyanoacrylate adhesive forms a strong bond rapidly when it comes into contact with moisture, including the water on the skin. This property allows for quick and effective wound closure without sutures or staples. The adhesive creates a seal that helps prevent the entry of bacteria and contaminants, reducing the risk of infection.
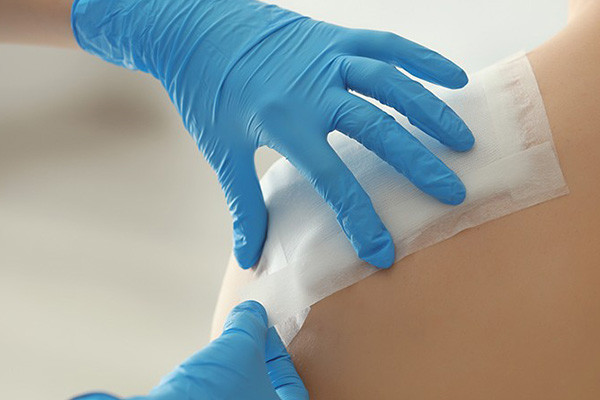
- Minimally Invasive: Cyanoacrylate adhesive can lead to more minimally invasive procedures than traditional sutures or staples. This can result in less tissue trauma, reduced scarring, and faster patient healing times.
- Waterproof and Bacteriostatic:Once cured, cyanoacrylate adhesive is waterproof and provides a barrier that helps protect wounds from external moisture, which can be particularly important in moist environments or during activities involving water exposure. Additionally, the adhesive’s bacteriostatic properties can help inhibit bacterial growth at the wound site.
- Ease of Application:Applying cyanoacrylate adhesive is relatively straightforward and doesn’t require extensive training or specialized equipment. This ease of application can make it a convenient option in various medical settings.
- Reduced Allergic Reactions:Traditional sutures or staples may cause allergic reactions in some patients due to the materials used. Cyanoacrylate adhesives are less likely to trigger allergies, making them suitable for a broader range of patients.
- Flexibility and Comfort:The cured adhesive moves with the skin, providing greater patient comfort than rigid staples or knots from sutures. This flexibility can also reduce the likelihood of wound dehiscence (wound opening).
- Hemostatic Properties: Some cyanoacrylate adhesives have hemostatic properties, meaning they can help control bleeding by sealing small blood vessels. This can be particularly useful during surgical procedures where achieving hemostasis is essential.
- Use in Specialized Surgical Applications: Cyanoacrylate adhesive can also be used in specialized surgical applications, such as in ophthalmic surgery for corneal wounds or neurosurgery for delicate tissue repair. In these cases, the precision and ease of application of cyanoacrylate adhesives can be highly advantageous.
It’s important to note that while cyanoacrylate adhesives offer various benefits for wound closure and specific surgical procedures, they are unsuitable for all types of wounds or surgical applications. The choice of wound closure method depends on the particular circumstances, the nature of the damage, and the medical professionals’ preferences.
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Aid in Electronics Manufacturing?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue, plays a significant role in manufacturing electronics by assembling intricate components. Its unique properties make it a valuable tool for bonding various materials and ensuring the reliable performance of electronic devices. Here’s how cyanoacrylate adhesive contributes to electronics manufacturing:
- Quick Bonding:Cyanoacrylate adhesive cures rapidly when exposed to moisture, creating solid bonds within seconds. This is advantageous in electronics manufacturing, where fast production cycles are essential. Components can be bonded quickly, allowing for efficient assembly processes.
- Precision Bonding:Electronics often involve small, delicate components requiring precise placement and bonding. Cyanoacrylate adhesive offers excellent control over application due to its low viscosity, ensuring that even tiny parts can be securely attached without excess adhesive interfering with the delicate circuitry.
- Versatile Substrate Compatibility:Cyanoacrylate adhesive adheres well to various materials commonly used in electronics manufacturing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, glass, and rubber. This versatility allows manufacturers to bond different components, regardless of the materials involved.
- Electrical Insulation:Cyanoacrylate adhesive is an insulator that does not conduct electricity. This property is crucial in preventing short circuits and maintaining the integrity of the electronic circuitry. Components can be bonded without the risk of unintentional electrical connections.
- Thermal Stability:Electronics can generate heat during operation, and the adhesive used in their assembly must withstand temperature variations. Cyanoacrylate adhesives offer good thermal stability, ensuring bonds remain intact even when exposed to moderate temperature changes.
- Mechanical Strength:Despite its rapid curing time, cyanoacrylate adhesive forms strong bonds that can withstand mechanical stress and vibrations. This durability is essential in electronic devices that might undergo handling, transport, and usage.
- Minimal Residue:Cyanoacrylate adhesives generally leave a minimal residue once cured. This is crucial in electronics manufacturing to ensure bonded components remain clean and free from contamination that could affect performance.
- Space-Saving:The small size of electronic components often requires efficient use of space within devices. Cyanoacrylate adhesive’s ability to create strong bonds in thin layers is advantageous in compact designs, where bulky mechanical fasteners are more practical.
- Optical Clarity:For electronics with transparent components like displays or optical sensors, cyanoacrylate adhesive’s optical clarity ensures that the adhesive does not interfere with the functionality or appearance of these components.
- Ease of Automation: Many electronics manufacturing processes are automated to enhance efficiency and precision. Cyanoacrylate adhesive can be dispensed automatically using robotic systems, enabling consistent and accurate application across a production line.
Cyanoacrylate adhesive plays a crucial role in electronics manufacturing by enabling efficient and reliable assembly of intricate components. Its quick curing, versatility, electrical insulation, thermal stability, and other properties make it an ideal choice for bonding a wide range of materials used in electronic devices.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue, is a fast-bonding adhesive widely used in various applications, including crafting, woodworking, electronics, and medical procedures. While it has numerous benefits, such as its quick drying time and strong bonding capabilities, it also has some environmental impacts to consider:
- Air Quality:Cyanoacrylate adhesives release fumes during curing, which can contribute to indoor air pollution. These fumes can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat and may exacerbate respiratory conditions in sensitive individuals.
- Hazardous Ingredients: Some cyanoacrylate adhesive formulations may contain dangerous chemicals such as formaldehyde, a known carcinogen that can negatively impact human health and the environment.
- Waste Generation: When using cyanoacrylate adhesive, excess glue may be produced, leading to waste generation. If not properly managed, this waste can end up in landfills, contributing to environmental pollution.
- Non-Biodegradability:Cyanoacrylate adhesives are generally not biodegradable, meaning they persist in the environment long after disposal. This can lead to accumulation in ecosystems and long-term impacts on wildlife.
- Energy Consumption:The production of cyanoacrylate adhesive requires energy and resources, contributing to the overall carbon footprint associated with its manufacturing process.
- Water Contamination:If cyanoacrylate adhesives enter water bodies, they can have adverse effects on aquatic life. They may not break down easily in water and can potentially contaminate the water supply.
- Packaging:The packaging of cyanoacrylate adhesive products, which often include plastic components, can contribute to plastic waste if not properly recycled.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, there are a few steps that can be taken:
- Proper Ventilation:When using cyanoacrylate adhesives, ensure adequate ventilation in the workspace to minimize fume exposure.
- Choosing Formulations: Opt for formulations free from hazardous chemicals like formaldehyde, and look for products labeled as more environmentally friendly.
- Reducing Waste: Minimize excess glue by applying the adhesive sparingly and using techniques that reduce waste.
- Recycling and Proper Disposal:Whenever possible, recycle the packaging materials, and dispose of used adhesive containers and waste appropriately according to local regulations.
- Considering Alternatives:In cases where environmental impact is a significant concern, consider alternative adhesive options with fewer adverse environmental effects.
- Awareness and Education:Educate yourself and others about the potential environmental impacts of cyanoacrylate adhesives and encourage responsible usage and disposal practices.
Remember that the specific environmental impact can vary depending on the formulation and intended use of the adhesive. Always check product labels and safety data sheets for information on potential environmental hazards and proper handling procedures.
How Can Artists and Craftsmen Utilize Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” is a versatile and fast-acting adhesive that artists and craftsmen can use to create innovative and unique projects. Its quick bonding properties make it suitable for various creative applications. Here are some ways artists and artisans can utilize cyanoacrylate adhesive in their art and creative projects:
- Mixed Media Collages: Artists can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to securely attach various materials, such as paper, fabric, metal, wood, and plastic, to create dynamic and textured mixed media collages. The adhesive’s quick-drying nature ensures the collage pieces stay in place and maintain a strong bond.
- Sculpture Assembly: Sculptors can assemble intricate sculptures from different materials using cyanoacrylate adhesive. Whether combining metal and wood elements or attaching delicate components, the adhesive’s precision, and rapid bonding can aid in creating stable and durable sculptures.
- Jewelry Making: In jewelry design, artists can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to bond gemstones, metal findings, and other decorative elements to various jewelry bases. Its clear and clean application ensures that no visible residue is left behind, enhancing the overall aesthetics of the piece.
- Woodworking and Inlay: Woodworkers can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to join intricate wood inlay pieces, such as marquetry or segmented wood designs. The adhesive’s ability to bond quickly and securely is beneficial for projects that involve minor and delicate wood components.
- Mosaic Art:Artists working with mosaic tiles can employ cyanoacrylate adhesive to attach tiles to various surfaces, such as vases, frames, and tabletops. The adhesive’s fast bonding time allows efficient progress in creating intricate mosaic patterns.
- Assembling Miniatures:Hobbyists creating miniature models, whether for tabletop gaming or dioramas, can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to make tiny parts with precision. Its quick-setting properties help ensure that delicate small components stay securely attached.
- Repair and Restoration: Artists and artisans specializing in restoration can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to repair and restore damaged artworks, ceramics, glass, and more. Its strong bond and ability to fill gaps can help bring damaged pieces back to their original state.
- Textile and Fabric Art: Fabric artists can use cyanoacrylate adhesive to create unique textures by bonding fabrics, lace, and fibers onto canvas or other surfaces. This technique can add depth and dimension to textile-based artworks.
- Paper Art: Paper artists can employ cyanoacrylate adhesive to create intricate and layered paper designs, such as pop-up cards, quilling, and paper sculptures. The adhesive’s quick drying time prevents paper components from shifting during assembly.
- Outdoor Art Installations: Cyanoacrylate adhesive formulated for outdoor use can create art installations in outdoor environments. It can help artists securely attach metal, stone, and glass to withstand weather conditions.
Remember to use cyanoacrylate adhesive in a well-ventilated area and follow safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and avoiding contact with skin. Reading and following the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and storage is essential. Experimenting with this adhesive can create innovative and exciting possibilities in your art and creative projects.
Why is Cyanoacrylate Adhesive a Preferred Choice in Aerospace Engineering?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” is preferred in aerospace engineering for bonding critical aircraft components due to several advantageous characteristics. Here are some reasons why it’s favored in this industry:
- Rapid Curing: Cyanoacrylate adhesives cure quickly, often within seconds to minutes, when exposed to moisture. This fast curing is crucial in aerospace applications where efficiency and reduced production time are essential.

- High Strength:Despite its quick curing time, cyanoacrylate adhesive forms strong bonds with high tensile and shear strength. This strength is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of aircraft components under various loads and stresses.
- Versatility: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond with various materials commonly used in aerospace engineering, including metals, plastics, composites, and rubber. This versatility is advantageous in assembling various aircraft components made from different materials.
- Low Volatility: These adhesives have soft volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, making them suitable in enclosed environments like aerospace manufacturing facilities where worker safety and air quality are paramount.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors:Cyanoacrylate adhesives exhibit good resistance to temperature extremes, moisture, chemicals, and vibration. This is particularly important in aerospace applications where aircraft components are subjected to varying environmental conditions.
- Compact and Lightweight: Since cyanoacrylate adhesives cure rapidly and form strong bonds, they can often replace mechanical fasteners like screws, rivets, and bolts. This can lead to weight savings and improved aerodynamics in aircraft design.
- Reduced Stress Concentrations: Adhesive bonding can distribute stress more evenly across the bonded area than traditional mechanical fasteners, creating stress concentrations at the attachment points. This helps enhance the overall structural integrity of aircraft components.
- Sealing and Gap-Filling Abilities:Cyanoacrylate adhesives can fill gaps and seal joints effectively, ensuring a more uniform distribution of forces and preventing the ingress of moisture or contaminants that could compromise the component’s integrity.
- Ease of Application:These adhesives are easy to apply manually or using automated processes, which helps streamline manufacturing processes and maintain consistent quality.
- Aesthetics and Smooth Surfaces: Adhesive bonding can lead to smoother surfaces and aesthetics than visible fasteners. This is particularly important for aircraft interiors and external exteriors.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to note that while cyanoacrylate adhesives have many benefits, their use should be carefully considered in aerospace applications. Adhesive selection should be based on a thorough understanding of the specific requirements, load conditions, and environmental factors the bonded components will face. Proper surface preparation and application techniques are critical to achieving optimal bond strength and reliability.
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Simplify Automotive Repairs?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as “super glue,” can simplify automotive repairs by offering quick, strong, and versatile bonding solutions for various vehicle parts. Here’s how it can be effective in fixing multiple components:
- Rapid Repairs:Cyanoacrylate adhesives cure rapidly, often within seconds to minutes, allowing quick repairs. This is especially useful for addressing minor damages or attaching small parts where waiting for traditional adhesives or mechanical fasteners might be time-consuming.
- Interior and Trim Components:Cyanoacrylate adhesives fix interior components like panels, trims, and upholstery. They provide strong bonds on materials commonly found in vehicles, such as plastic, leather, fabric, and rubber.
- Exterior Trim and Emblems:Exterior trim pieces and emblems can become loose or damaged over time. Cyanoacrylate adhesive can securely reattach these components without special tools or extensive disassembly.
- Mounting Rearview Mirrors: Rearview mirrors that have fallen off can be quickly reattached using cyanoacrylate adhesive. Its strong bonding properties ensure the mirror stays in place despite vibrations and road conditions.
- Headlight and Taillight Repairs: Minor cracks in the headlight and taillight lenses can be temporarily sealed with cyanoacrylate adhesive, preventing moisture from entering and potentially causing more extensive damage.
- Interior Console and Dashboard Repairs:If interior console or dashboard components are cracked or broken, cyanoacrylate adhesive can help create strong, nearly invisible bonds. This maintains the aesthetics of the vehicle’s interior.
- Weatherstripping and Rubber Seals:Automotive weatherstripping and rubber seals that have come loose can be effectively reattached using cyanoacrylate adhesive. This prevents leaks and maintains proper sealing.
- Plastic Components: Many automotive parts, such as bumper covers, grilles, and side mirrors, are malleable. Cyanoacrylate adhesive can bond these components securely, avoiding the need for replacement.
- Holding Small Parts in Place:Certain small parts might need to be temporarily stored during repairs. Cyanoacrylate adhesive can act as a temporary clamp, ensuring that components stay in the correct position while other repairs are carried out.
- Non-Structural Repairs:While cyanoacrylate adhesive is unsuitable for major structural repairs, it can quickly and effectively address a wide range of non-structural issues quickly and effectively.
It’s important to note that while cyanoacrylate adhesive can be incredibly helpful in simplifying certain automotive repairs, its application should be appropriate for the specific situation. Careful surface preparation, cleanliness, and proper bonding techniques are crucial to achieving the best results. Additionally, for more significant structural repairs, it’s recommended to consult professionals or follow manufacturer recommendations to ensure the safety and integrity of the vehicle.
What Future Developments Are Envisaged in Cyanoacrylate Technology?
While I don’t have access to real-time information beyond September 2021, I can speculate on potential developments and advancements in cyanoacrylate adhesive technology based on trends and possibilities that were emerging up until then. Keep in mind that actual results may have occurred since then. Here are some possible directions for advancement:
- Improved Strength and Durability:Researchers may continue to focus on enhancing the strength and durability of cyanoacrylate adhesives. This could involve the development of formulations that provide even higher bond strengths, especially for challenging materials and harsh environments.
- Enhanced Flexibility:Future cyanoacrylate adhesives might be engineered to have improved flexibility, allowing them to better accommodate movement, vibration, and thermal expansion/contraction without compromising the bond’s integrity.
- Temperature Resistance:Developing cyanoacrylate adhesives that can withstand extreme temperatures (both high and low) could expand their applications to industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where components experience diverse temperature conditions.
- Reduced Dependency on Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving strong bonds with cyanoacrylate adhesives. Future advancements involve adhesives less sensitive to surface cleanliness, potentially reducing the need for extensive pre-bonding treatments.
- Reduced Toxicity and Sensitization: Researchers might work on formulations that have reduced toxicity and are less likely to cause skin sensitization. This could improve the safety of handling and using cyanoacrylate adhesives.
- Biodegradable Formulations: As environmental concerns continue to grow, there could be efforts to develop biodegradable cyanoacrylate adhesives that minimize their impact on ecosystems and waste management.
- Adhesives with Self-Healing Properties: Future cyanoacrylate adhesives could be designed with self-healing capabilities, allowing them to repair minor damage or cracks that might occur over time.
- Advanced Bonding Techniques: Research might lead to developing new application techniques that enhance the effectiveness of cyanoacrylate adhesives. This could involve innovative curing methods or tools that optimize the bonding process.
- Electrical Conductivity and Insulation:Tailoring cyanoacrylate adhesives to exhibit specific electrical conductivity of insulating properties could open up new possibilities in electronics and electronic component assembly.
- Nanotechnology Integration: Incorporating nanomaterials into cyanoacrylate formulations could lead to adhesives with improved mechanical properties, better thermal stability, and enhanced resistance to environmental factors.
- Smart Adhesive Systems:Advancements involve the integration of sensors, indicators, or other responsive elements into the adhesive itself, enabling real-time monitoring of bond integrity or environmental conditions.
- Customizable Cure Times:Developing cyanoacrylate adhesives that offer adjustable curing times could provide greater flexibility in various applications, allowing for precise control over bond formation.
These are speculative ideas based on the trends and possibilities in adhesive technology until September 2021. I recommend checking recent scientific literature, industry reports, and news from adhesive manufacturers and research institutions to get the most accurate and up-to-date information on future developments in cyanoacrylate adhesive technology.
How Can Consumers Safely Remove Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Removing cyanoacrylate adhesive (commonly known as super glue) can be tricky, but you can safely detach bonded objects with the right approach and precautions. Here are some tips to help you safely remove cyanoacrylate adhesive:
- Safety Precautions:
Before attempting any removal, make sure to wear gloves and safety goggles and work in a well-ventilated area to protect your skin, eyes, and respiratory system from potential fumes and irritation.
- Patience is Key:
Removing cyanoacrylate adhesive may take some time, so be patient and avoid using excessive force, which could damage the objects you’re trying to detach.
- Warm, Soapy Water:
For skin contact, gently soak the bonded area in warm soapy water. Over time, the adhesive may soften, allowing you to peel or roll it off carefully. Please do not force it; it should come off naturally as it softens.
- Acetone-Based Nail Polish Remover:
You can try acetone-based nail polish remover for non-porous surfaces like glass, metal, or plastic. Apply a small amount to a cotton ball or soft cloth and gently rub the bonded area. Test a small, hidden area first to ensure the acetone won’t damage the surface. Avoid using acetone on painted surfaces or surfaces that might be sensitive to it.
- Warm Compress or Hair Dryer:
For objects that won’t be damaged by heat, try using a warm compress or a hair dryer on a low setting to warm the bonded area gently. This helps soften the adhesive, making peeling or scraping easier.
- Mechanical Methods:
Use a soft plastic scraper, such as an old credit card or plastic spatula, to gently scrape off the adhesive. Be careful not to scratch the surface. You can try a fine abrasive pad like a white eraser for more challenging spots.
- Specialized Adhesive Removers:
There are commercial adhesive removers available specifically designed to break down cyanoacrylate adhesive. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, and test on a small, inconspicuous area first.
- Natural Oils:
Some natural oils, like coconut or olive oil, can help loosen cyanoacrylate adhesive. Apply a small amount, let it sit for a while, and then gently work at the adhesive with a soft cloth or your fingernail.
Remember, each situation may differ, so cautiously assessing the material you’re working with is essential. If you’re dealing with a valuable or delicate item, consider seeking professional help to avoid causing damage. Always prioritize your safety and the preservation of the objects you’re working with.
Why is Cyanoacrylate Adhesive a Valuable Asset in Construction?
Due to its unique properties and applications, cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue or CA glue, has become a valuable asset in the construction industry. Here are some ways in which cyanoacrylate adhesive contributes to the construction field:
- Rapid Bonding:Cyanoacrylate adhesive cures quickly when exposed to moisture, forming strong bonds in seconds. This property is especially beneficial in construction projects where time is of the essence, as it allows for efficient assembly and installation of various components.

- Versatility:Cyanoacrylate adhesive works on a wide range of materials commonly used in construction, such as wood, metal, plastics, ceramics, and even some types of rubber. This versatility makes it an excellent choice for bonding different components together, whether similar or dissimilar materials.
- Reduced Need for Mechanical Fasteners: In many construction applications, cyanoacrylate adhesive can eliminate or reduce the need for traditional mechanical fasteners like nails, screws, or bolts. This saves time and enhances the aesthetic appeal of finished projects by minimizing visible fasteners.
- Precision and Accuracy:Cyanoacrylate adhesive can be applied in small amounts, allowing for precise bonding in tight spaces or delicate constructions. This makes it valuable for intricate architectural designs, detailed woodworking, and other precision-based applications.
- Strength and Durability: Cyanoacrylate adhesive creates robust and durable bonds despite its rapid curing time. These bonds can withstand various stresses and environmental conditions, contributing to constructed structures’ long-term stability and reliability.
- Sealing and Filling Capabilities:Cyanoacrylate adhesive can seal gaps and cracks, preventing the ingress of moisture, air, or other contaminants that could compromise the integrity of a construction project. It can also be used to fill voids, enhancing the structural integrity and appearance of the finished work.
- Reduced Vibration and Noise:When used to bond materials together, cyanoacrylate adhesive can help dampen vibrations and reduce noise transmission between components. This is particularly useful in construction projects such as residential and commercial buildings; minimizing beats and noise is a priority.
- Safety and Cleanliness: Cyanoacrylate adhesive is relatively easy to use and doesn’t require complex mixing or special equipment. This can help improve job site safety by reducing the risk of accidents associated with more hazardous adhesives or traditional mechanical fastening methods.
- Design Flexibility: The quick-curing nature of cyanoacrylate adhesive allows for faster assembly and modification of construction elements. This can facilitate adjustments during construction, leading to greater design flexibility and the ability to adapt to unexpected challenges.
- Reduced Weight:Traditional mechanical fasteners can add significant weight to a structure. Construction projects can achieve the desired strength and stability without unnecessary weight increase by using cyanoacrylate adhesive to bond lightweight materials.
Cyanoacrylate adhesive has become a valuable asset in the construction industry due to its rapid bonding, versatility, strength, precision, and other advantages. Its ability to efficiently bond different materials while reducing the reliance on mechanical fasteners makes it an indispensable tool for modern construction projects.
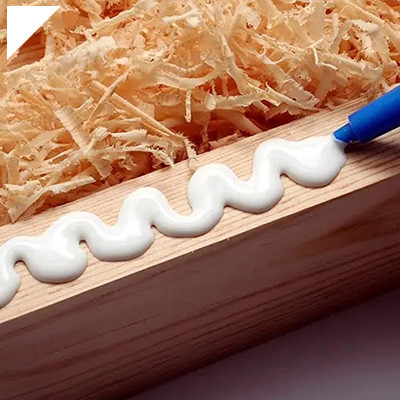
How Does Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Transform Woodworking Projects?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, commonly known as super glue or CA glue, can play a significant role in woodworking projects by providing robust and quick bonding for various wood-related applications. Its transformative impact on woodworking projects lies in its ability to create sturdy wooden structures through the following aspects:
- Quick Bonding:Cyanoacrylate adhesive cures rapidly, often within seconds to minutes, creating an almost instant bond between wood pieces. This rapid bonding is beneficial when assembling complex woodworking projects or when traditional woodworking glues require longer clamping.
- Precision and Accuracy: Cyanoacrylate adhesives are available in various viscosities, from thin to gel-like consistency. This allows woodworkers to choose the appropriate viscosity for the specific application, ensuring the adhesive reaches the desired areas without excessive dripping or running.
- No Clamping Required:In many cases, cyanoacrylate adhesives eliminate the need for clamping. The fast curing time means you can manually hold the pieces together for a short period while the adhesive sets free clamps for other tasks.
- Strong Bond:Cyanoacrylate adhesives form a strong bond between wood surfaces. They can create a bond often as vital, if not stronger, than the wood itself. This is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of woodworking projects.
- Versatile Application: Cyanoacrylate adhesives can be used for various woodworking applications, including joining small parts, filling gaps, repairing cracks, and even laminating thin wood veneers. Their versatility makes them a valuable addition to a woodworker’s toolkit.
- Minimal Disruption:Unlike traditional woodworking glues that might require extended drying times and clamping, cyanoacrylate adhesives allow you to proceed with the project relatively quickly. This minimizes disruptions to your workflow and accelerates project completion.
- Enhancing Aesthetics:Since cyanoacrylate adhesives can bond thin wood veneers, they can be employed to create visually appealing designs and patterns that would be challenging to achieve with traditional woodworking techniques.
- Less Invasive Repairs:When it comes to repairing minor damages or cracks in wooden structures, cyanoacrylate adhesives can be advantageous. They provide a seamless fix and can be used to reinforce weak areas.
- Reduced Material Waste:Due to its efficiency and fast curing time, cyanoacrylate adhesive can help reduce material waste. You’re less likely to end up with misaligned pieces that must be reworked.
Despite its advantages, it’s important to note that cyanoacrylate adhesive might only be suitable for some woodworking applications. Its quick curing time can be challenging if you need to make adjustments after joining, and it may not provide the same “open time” that traditional woodworking glues offer.
What Lies Ahead: Innovations and Possibilities for Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Cyanoacrylate adhesive, often called super glue, has already proven to be a versatile and reliable adhesive solution for various applications. As we look ahead, several innovations and possibilities could shape the evolution of cyanoacrylate adhesive technology:
- Improved Formulations:Researchers are constantly working on enhancing the properties of cyanoacrylate adhesives, such as increasing bond strength, flexibility, and resistance to various environmental factors like heat, moisture, and chemicals. Innovations in formulation could lead to adhesives that perform exceptionally well across a broader range of conditions.
- Biocompatible Variants: The development of cyanoacrylate adhesives with biocompatibility could open up new applications in the medical field. These adhesives could be used for wound closure, medical device assembly, and tissue engineering.
- Nanotechnology Integration:Incorporating nanoparticles into cyanoacrylate formulations could enhance its properties further. For instance, adding nanoparticles with specific functionalities could lead to adhesives with tailored electrical conductivity, thermal insulation, or UV resistance.
- Self-Healing Adhesives:Researchers are exploring ways to develop cyanoacrylate adhesives that have self-healing properties. This could revolutionize maintenance and repair applications by allowing bonded surfaces to repair themselves when damaged.
- Innovative Adhesives: The integration of sensors, indicators, or even microcapsules containing specific substances into cyanoacrylate adhesives could enable them to provide real-time information about the bonded surface, such as stress levels, temperature or the presence of harmful chemicals.
- Biodegradable Options: As environmental concerns grow, the development of biodegradable cyanoacrylate adhesives could become an important focus. These adhesives could find applications in temporary bonding or situations where eco-friendliness is paramount.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing:The adaptability of cyanoacrylate adhesives makes them a candidate for use in 3D printing or additive manufacturing processes. This could create complex structures by bonding layers of different materials together.
- Advanced Application Techniques: Innovations could emerge in how cyanoacrylate adhesives are applied. Automated, precise dispensing methods could become more prevalent, allowing for efficient and consistent industry bonding.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Applications: As cyanoacrylate adhesives continue to improve in strength and durability, they could find increased use in heavy-duty industrial applications, where traditional welding or mechanical fastening methods are currently dominant.
- Cross-Industry Collaborations: The evolution of cyanoacrylate adhesive technology could benefit from collaborations between adhesive manufacturers, material scientists, engineers, and experts from various industries. This interdisciplinary approach could lead to breakthroughs in both formulation and application techniques.
The future of cyanoacrylate adhesive lies in its ability to adapt to the changing needs of various industries and applications. Through continuous research, innovation, and collaboration, cyanoacrylate adhesives could become even more versatile, durable, and specialized, offering solutions to challenges we may not be fully aware of today.
Deepmaterial Adhesives
Shenzhen Deepmaterial Technologies Co., Ltd. is an electronic material enterprise with electronic packaging materials, optoelectronic display packaging materials, semiconductor protection and packaging materials as its main products. It focuses on providing electronic packaging, bonding and protection materials and other products and solutions for new display enterprises, consumer electronics enterprises, semiconductor sealing and testing enterprises and communication equipment manufacturers.
Adhesives
Deepmaterial adhesives primary focus is custom adhesive manufacturing and tailoring.
Applications
Adhesives Cover the main industrial, biomedical and pharmaceutical applications.
Technical Support
We will provide you with product application and technical guidance.
Products
Adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board-level adhe- sives, and adhesives for electronic products.
DeepMaterial Industrial Adhesive Pruducts
DeepMaterial has developed industrial adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board-level adhe- sives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
Blogs & News
DeepMaterial is consumer industrial adhesive glue manufacturer and supplier in china.
We are focus on the latest science and technology about adhesives, and we make them to industrial appliaction.