Plastic Bonding Adhesive

In the world of modern manufacturing, the ability to bond plastics reliably and effectively is a critical component of producing durable and functional products. Plastic bonding adhesive has emerged as a versatile solution, revolutionizing the way various types of plastic materials are joined together. Whether it’s in automotive, electronics, healthcare, or consumer goods, plastic bonding adhesive offers a way to create robust and long-lasting connections, overcoming the challenges posed by the unique characteristics of plastics. This comprehensive exploration delves into the realm of plastic bonding adhesive, uncovering its types, mechanisms, applications, advantages, and its pivotal role in shaping the landscape of contemporary manufacturing.
Exploring Plastic Bonding Adhesive
In modern manufacturing, plastic bonding adhesives are essential for joining diverse plastic substrates, offering versatility, efficiency, and improved aesthetics. These adhesives have witnessed remarkable advancements, addressing material compatibility, bond strength, and durability challenges.
Advantages and Applications
- Versatility and Compatibility:Plastic bonding adhesives exhibit exceptional compatibility with a wide array of plastic materials, including polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, and polycarbonate, enabling seamless joining of dissimilar plastics.
- Enhanced Aesthetics:Unlike traditional fastening methods, adhesives create smooth, seamless bonds without visible mechanical fixtures, enhancing aesthetics in various applications.
- Lightweight Design:Adhesive bonds contribute to lightweight designs, which are critical in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where reducing weight without compromising structural integrity is paramount.
Innovations in Adhesive Formulations
- Structural Plastic Adhesives:Advancements in adhesive formulations have led to the development of structural plastic adhesives that offer high bond strength, exceptional impact resistance, and durability, suitable for load-bearing applications.
- Flexible and Tough Adhesives:New adhesive formulations are engineered to withstand dynamic stresses and offer flexibility and toughness, making them suitable for applications subjected to vibrations, impacts, and thermal cycling.
Challenges and Considerations
- Surface Preparation:Ensuring proper surface preparation, including cleaning, roughening, and activation, is critical for achieving solid and durable adhesive bonds on plastic substrates.
- Temperature and Environmental Resistance:Adhesives must exhibit reliable performance across various temperatures and environmental conditions, maintaining their integrity in challenging settings.
- Long-Term Durability:For applications with extended lifetimes, ensuring the adhesive’s resistance to degradation, UV exposure, and chemical agents is crucial.
Future Directions and Industry Trends
- Biocompatible Adhesives:The growing demand for medical devices and healthcare applications drives research into biocompatible plastic bonding adhesives that meet stringent regulatory requirements.
- Innovative Adhesives:Researchers are exploring adhesive technologies that integrate functionalities such as conductivity, sensing, and self-healing, opening doors to innovative applications in electronics and beyond.
The realm of plastic bonding adhesives continues to evolve, offering a diverse range of benefits and solutions for modern manufacturing challenges. With ongoing innovations in adhesive formulations, improved compatibility, and expanding application areas, industries increasingly rely on these adhesives to play a pivotal role in creating robust, lightweight, and aesthetically pleasing products. Proper consideration of material properties, surface preparation, and adhesive characteristics will be essential in harnessing the full potential of plastic bonding adhesives for diverse applications.
Challenges in Bonding Plastics
Bonding plastics presents a unique set of challenges due to plastic materials’ diverse nature and inherent properties. Achieving strong, reliable, and durable adhesive bonds requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Surface Energy Variation:Plastics exhibit varying surface energies, making finding a single adhesive that can effectively bond different plastics challenging. An adhesive selection must account for these variations to ensure optimal adhesion.
- Material Compatibility:Not all adhesives are compatible with every type of plastic. Selecting an adhesive that forms strong bonds with the specific plastic substrates is crucial to avoid bond failure.
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation, including cleaning, roughening, and activation, is essential to promote adhesion. Plastics’ low surface energy often necessitates additional steps to improve bonding, which can increase processing time and complexity.
- Thermal Expansion Mismatch:Plastics have varying coefficients of thermal expansion, which can lead to stress buildup and bond failure when exposed to temperature changes. Managing this thermal expansion mismatch is critical for maintaining bond integrity.
- Chemical Resistance:Adhesive bonds must withstand exposure to various chemicals, solvents, and environmental conditions. Ensuring the adhesive’s resistance to these factors is vital for long-term bond durability.
- UV Degradation:Many plastics are sensitive to UV radiation, which can cause degradation over time. Adhesives used for outdoor or UV-exposed applications must possess UV-resistant properties to maintain bond strength.
- Joint Design and Load Distribution:Designing the joint geometry and load distribution is essential to prevent stress concentration points and ensure even force distribution across the adhesive bond area.
- Testing and Quality Control:Proper testing protocols are necessary to validate the strength and reliability of adhesive bonds. Establishing quality control measures and testing procedures ensures consistent bond performance.
- Environmental Considerations:As industries prioritize sustainability, selecting adhesives that align with environmental standards and regulations is becoming increasingly important.
Bonding plastics requires a comprehensive understanding of material properties, adhesive selection, surface preparation, and design considerations. Overcoming challenges related to material compatibility, surface energy, thermal expansion, and environmental factors demands a systematic approach and the utilization of appropriate adhesive technologies to achieve robust and enduring bonds in various applications.
Mechanisms of Adhesion to Plastics
Adhesion to plastics involves intricate interactions between adhesive materials and the often low-energy surfaces of plastic substrates. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for designing effective bonding strategies:
- Mechanical Interlocking:Some adhesives penetrate surface irregularities on plastics, creating a mechanical interlock that enhances bond strength.
- Chemical Bonding:Certain plastics, like polyesters and nylons, possess functional groups that can form chemical bonds with adhesive molecules, ensuring strong adhesion.
- Polar and Non-Polar Interactions:Plastics exhibit varying degrees of polarity. Polar adhesives can bond to polar plastics through dipole-dipole interactions, while non-polar adhesives are effective on non-polar plastics via dispersion forces.
- Wetting and Spreading:Good wetting of the adhesive on the plastic surface is crucial. High surface energy plastics facilitate better wetting, leading to improved adhesion.
- Surface Activation:Some plastics have inherently low surface energy, necessitating surface activation techniques like corona treatment or plasma etching to increase adhesion.
- Adhesive Selection:An adhesive with complementary properties to the plastic substrate, such as surface energy and chemical compatibility, is vital for solid adhesion.
- Priming and Pre-Treatment:Primers and pre-treatments can modify the plastic surface, enhancing adhesion and promoting better bonding.
- Microscopic Interactions:At the microscale, adhesive molecules can physically interact with plastic surface features, creating intimate contact and enhancing adhesion.
Understanding the mechanisms of adhesion to plastics allows engineers and manufacturers to tailor their bonding processes to specific materials and applications. Successful adhesion involves a combination of adhesive material selection, surface preparation, and process optimization to achieve reliable and durable bonds on plastic substrates.
Surface Preparation and Activation
Achieving solid and lasting adhesive bonds requires meticulous surface preparation and activation techniques that enhance the adhesion-promoting properties of plastic substrates:
- Cleaning:Thorough cleaning removes contaminants like dust, grease, oils, and residues that could hinder adhesion. Commonly used methods include solvent cleaning or aqueous solutions.
- Mechanical Roughening:Abrasive methods, such as sanding or grit blasting, create micro-roughness on the plastic surface, facilitating mechanical interlocking with the adhesive.
- Plasma Treatment:Plasma exposure alters the plastic’s surface energy and introduces functional groups, enhancing wettability and promoting adhesive spread.
- Corona Treatment:This electrical discharge treatment generates ozone, which oxidizes the plastic surface, raising its surface energy and making it more receptive to adhesion.
- Flame Treatment: Controlled exposure to an open flame creates localized oxidation, increasing surface energy and creating polar sites for adhesion.
- Chemical Primers:Applying primers involves placing a thin layer on the plastic surface. They enhance chemical interactions and provide a bridge between the plastic and the adhesive.
- Silane Coupling Agents: These molecules contain functional groups that react with the plastic surface and the adhesive, promoting a strong bond.
- UV/Ozone Treatment:Ultraviolet (UV) light combined with ozone alters the plastic’s surface, increasing its reactivity and adhesive affinity.
- Adhesion Promoters:Specialty adhesion promoter compounds enhance the interaction between adhesive and plastic, often improving long-term bond durability.
Adequate surface preparation and activation techniques depend on the specific plastic-type, adhesive, and application requirements. Implementing the right combination of these methods ensures successful bonding using adhesives for plastics with inherently low surface energy or non-reactive surfaces. This results in durable and reliable bonds across various industries and applications.
Types of Plastic Bonding Adhesives
Plastic bonding adhesives are pivotal in various industries, offering versatile solutions for joining different plastic materials. These adhesives leverage distinct formulations to ensure adequate bonding, catering to diverse application requirements. Here’s an overview of some key types of plastic bonding adhesives:
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (CA)
- Commonly known as super glue, CA adhesives offer rapid bonding for plastics.
- Ideal for bonding small plastic parts, they provide quick and intense bonds.
- It is suited for applications requiring high clarity and minimal gap filling.
Epoxy Adhesives
- Epoxy adhesives provide exceptional strength and durability for plastic-to-plastic bonding.
- They resist chemicals, moisture, and heat, making them suitable for demanding environments.
- Their robust nature makes them a frequent choice for structural bonding applications.
Polyurethane Adhesives
- Polyurethane adhesives offer flexibility and impact resistance when bonding plastics.
- They can handle varying degrees of expansion and contraction, making them suitable for materials with different thermal coefficients.
- People use them in applications where they expect some degree of movement.
Acrylic Adhesives
- Acrylic adhesives provide a balance between strength and flexibility.
- They offer excellent UV and weather resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
- People often use them to bond transparent plastics because of their optical clarity.
Structural Adhesives
- These adhesives are designed for load-bearing applications, providing high-strength bonds.
- Industries such as automotive and aerospace commonly use them to bond plastic components.
Thermoplastic Adhesives
- You can melt and reactivate thermoplastic adhesives, making repositioning them quickly before the final bonding.
- They are well-suited for bonding thermoplastic materials, providing a strong bond upon cooling.Specialty Adhesives
- Manufacturers formulate some adhesives specifically for plastic types like polyethylene or polypropylene.
- Specialty adhesives address the challenges associated with bonding these difficult-to-adhere plastics.
The choice of plastic bonding adhesive depends on factors like the type of plastic, application conditions, required bond strength, and flexibility. Manufacturers and engineers select from this array of adhesive styles to achieve optimal bonding solutions for various plastic materials and industries.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives for Plastics
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives for Plastics, commonly called Plastic Bonding Adhesives or super glues, have emerged as a transformative solution for joining plastic materials. These adhesives offer a host of advantages that make them a preferred choice in diverse applications:
1.Rapid Bonding:Cyanoacrylate adhesives ensure swift and efficient bonding, reducing assembly time and increasing overall productivity.
2.Broad Compatibility:These adhesives exhibit exceptional adhesion to various plastic substrates, including ABS, PVC, polycarbonate, acrylic, and more.
3.Robust Strength:Despite their quick curing time, these adhesives establish sturdy and enduring bonds, capable of withstanding various environmental stresses.
4.Minimal Preparatory Steps:People often require minimal surface cleaning or priming, simplifying the bonding process and saving valuable time.
5.Precise Application:Cyanoacrylate Adhesives enable meticulous application in different viscosities, ensuring controlled dispensing even in intricate bonding scenarios.
6.Chemical Resistance:Once cured, these adhesives demonstrate chemical resistance, enhancing the bond’s durability and resilience.
7.Enhanced Design Flexibility:The reliable bonding provided by Cyanoacrylate Adhesives often obviates the need for traditional mechanical fasteners, enabling more streamlined designs and reducing material costs.
8.Aesthetic Excellence:Clear formulations are accessible for applications where aesthetics are paramount, ensuring a discreet and aesthetically pleasing bond line.
The exceptional attributes of Cyanoacrylate Adhesives for Plastics have revolutionized the realm of Plastic Bonding Adhesives, offering a potent combination of speed, strength, and versatility that meets the demands of various industrial and do-it-yourself projects. Whether joining plastic components in manufacturing processes or executing intricate plastic repairs at home, these adhesives have proven their prowess in creating enduring and resilient bonds across the plastic spectrum.
Epoxy Resins for Plastic Bonding
Epoxy resins have established themselves as indispensable Plastic Bonding Adhesives, showcasing remarkable properties that ensure solid and enduring bonds for a wide range of plastic materials. We can summarize the versatility and effectiveness of Epoxy Resins for Plastic Bonding through the following key points:
- Exceptional Adhesion:Epoxy resins exhibit outstanding adhesion to various plastic substrates, such as ABS, polycarbonate, acrylic, and more, fostering reliable connections that endure multiple stressors.
- Customizable Formulations:These adhesives come in diverse formulations with varying viscosities and curing times, allowing for tailored applications depending on the specific bonding requirements.
- Chemical and Temperature Resistance:Once cured, epoxy bonds offer resistance to chemicals, solvents, and elevated temperatures, enhancing the longevity of the bonded plastic components.
- Structural Integrity:Epoxy adhesives provide adhesive strength and contribute to structural integrity, making them suitable for applications where load-bearing capability is crucial.
- Gap-Filling Abilities:The thixotropic nature of specific epoxy formulations enables effective gap-filling, accommodating irregularities in plastic surfaces and ensuring a uniform bond line.
- Versatility in Application:You can use epoxy resins for various plastic bonding tasks, including fabricating composite materials, encapsulating components, and repairing plastic objects.
- Mechanical and Electrical Properties:Epoxy bonds often possess desirable mechanical and electrical properties, making them suitable for applications requiring adhesive strength and functional attributes.
- Surface Preparation Flexibility:While some cases may require proper surface cleaning and preparation, epoxy resins generally exhibit good adhesion, even on less prepared plastic surfaces.
Epoxy resins have cemented their position as a versatile and robust choice for Plastic Bonding Adhesives, offering a combination of adhesion strength, durability, and customization that suits various industrial, commercial, and DIY applications. Whether it’s reinforcing plastic components in manufacturing or mending broken plastic objects, epoxy adhesives have consistently demonstrated their ability to form enduring bonds that withstand the test of time and usage.
Polyurethane Adhesives and Plastics
Polyurethane adhesives have emerged as a dynamic and versatile solution for Plastic Bonding, offering a unique blend of robust bonding strength and flexibility. These adhesives have proven their efficacy across a spectrum of plastic materials, exhibiting a range of benefits that make them an ideal choice for various applications.
Key Advantages
- Strong Adhesion:Polyurethane adhesives form strong bonds with diverse plastic substrates, including but not limited to ABS, PVC, polycarbonate, and more.
- Flexibility and Resilience:Their inherent flexibility ensures that bonded plastics can withstand stresses and strains without compromising the integrity of the adhesive joint.
- Bonding Dissimilar Plastics:Polyurethane adhesives can bond different types of plastics together, expanding their application potential.
- Impact Resistance:The flexibility of polyurethane bonds contributes to enhanced impact resistance, which is crucial in applications prone to sudden forces.
- Environmental Resistance:These adhesives resist moisture, chemicals, and varying temperatures, safeguarding the bond’s durability.
Versatile Applications
Polyurethane adhesives find wide application across various sectors, including automotive, construction, electronics, and more. They excel in scenarios where strength and flexibility are essential, such as adhering to plastic components subject to vibrations or varying temperatures. Moreover, their ability to bond dissimilar plastics facilitates composite fabrication, enabling innovative designs and material combinations.
Surface Preparation and Application
While we generally recommend surface preparation for optimal bonding, polyurethane adhesives offer good adhesion even on adequately cleaned plastics. Their formulations cater to different bonding scenarios with options for fast-curing or more flexible variants, enabling precise adhesive selection.
Polyurethane adhesives have carved a niche in Plastic Bonding Adhesives, providing a balance between strength and flexibility that complements the requirements of modern plastic-based applications. Whether in constructing resilient plastic assemblies or bonding plastic components with varying properties, these adhesives are a reliable choice, creating enduring connections that adapt to the dynamic demands of the materials they bond.
Acrylic Adhesives for Plastic Applications
In the realm of plastic bonding solutions, Acrylic Adhesives stand out as versatile and highly effective options. These adhesives have gained widespread recognition for their remarkable bonding capabilities across various plastic substrates. With their exceptional properties, acrylic adhesives offer an ideal solution for many plastic applications, ensuring strong, durable, and long-lasting bonds.
Advantages of Acrylic Adhesives
- Versatility:Acrylic adhesives exhibit excellent adhesion to a wide range of plastic materials, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, PET, PVC, and more.
- Durability:With high resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, acrylic-bonded plastics maintain their integrity even in challenging conditions.
- Fast Curing:Many acrylic adhesives cure rapidly, enhancing production efficiency and reducing assembly time, thus contributing to streamlined manufacturing processes.
- Strength:Acrylic adhesives create robust bonds that can withstand mechanical stress, offering reliability in load-bearing applications.
- Transparency:For applications where aesthetics matter, clear acrylic adhesives ensure a seamless, unobtrusive bond line, maintaining the visual appeal of the plastic components.
Plastic Bonding Adhesive Applications
- Automotive Industry:Acrylic adhesives are pivotal in bonding plastic components in vehicle interiors and exteriors, ensuring structural integrity, vibration resistance, and improved overall aesthetics.
- Electronics:These adhesives find use in assembling electronic devices, securely bonding plastic housings, connectors, and components while providing electrical insulation.
- Medical Devices:Acrylic adhesives meet stringent requirements for medical equipment, joining plastic parts without compromising biocompatibility or sterilization procedures.
- Packaging:In the packaging industry, acrylic adhesives are employed to bond plastic films, containers, and closures, contributing to the integrity and shelf life of packaged products.
- Construction:Acrylic adhesives facilitate the assembly of plastic elements in construction applications, offering reliable bonding for architectural panels, windows, and façade components.
The remarkable qualities of acrylic adhesives make them an invaluable resource in plastic bonding. Their versatility, durability, rapid curing, and exceptional strength have rendered them indispensable across various industries. Whether in the automotive sector, electronics manufacturing, medical device production, packaging, or construction, acrylic adhesives ensure plastic applications’ integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. As technology advances, acrylic adhesives are poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of plastic bonding solutions.
Thermoplastic and Thermoset Bonding
The art of Plastic Bonding Adhesive extends its reach to Thermoplastic and Thermoset materials, offering tailored solutions to harness the unique properties of each. This duality arises from the distinct characteristics of these plastic categories, necessitating specialized adhesive approaches to achieve optimal bonding results.
Thermoplastic Bonding
- Molecular Mobility:Thermoplastics can be repeatedly melted and solidified due to their molecular structure, allowing for repositioning and stress relief during bonding.
- Adhesive Compatibility:Selecting the suitable adhesive is critical, as thermoplastics can vary widely in surface energy and chemical composition.
- Heat Sensitivity: Careful consideration of curing temperatures is essential to prevent distortion or degradation of thermoplastic components.
- Bond Strength:Proper adhesive selection and surface preparation lead to solid and durable bonds, which are crucial for load-bearing applications.
Thermoset Bonding
- Irreversible Curing:Thermosets undergo a chemical transformation during curing, becoming rigid and resistant to further melting, requiring careful adhesive selection.
- Adhesive Selection:Compatibility between adhesive and thermoset resin is pivotal to ensure adequate bonding, often necessitating specialized formulations.
- Curing Conditions:Precise control of temperature and curing time is imperative to trigger the irreversible curing process and achieve optimal bond strength.
- Chemical Resistance:Thermoset adhesives provide excellent resistance to chemicals and environmental stressors, enhancing the durability of bonded components.
Applications of Thermoplastic and Thermoset Bonding
- Thermoplastic Applications:Automotive interiors, consumer goods, and flexible packaging utilize thermoplastic bonding for its repositioning flexibility and diverse material compatibility.
- Thermoset Applications:Aerospace, electronics, and composite manufacturing rely on thermoset bonding for its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and durability.
Challenges and Advances
The dynamic field of plastic bonding continually evolves with advancements in adhesive technology, addressing challenges unique to thermoplastic and thermoset bonding. Engineers and manufacturers now benefit from innovative adhesive formulations designed to overcome the complexities of these diverse materials. As industries demand higher performance and versatility from plastic bonded structures, ongoing research and development pave the way for optimized adhesive solutions, ensuring reliable, durable, and resilient bonds in thermoplastic and thermoset applications.
Engineering Plastics and Specialty Adhesives
The realm of Plastic Bonding Adhesive reaches a new dimension with the bonding of Engineering Plastics and the application of Specialty Adhesives. The amalgamation of these two domains leads to innovative solutions that cater to the unique challenges posed by high-performance plastics and specialized bonding requirements.
Engineering Plastics:
1.High-Performance Materials:Engineering plastics such as PEEK, ABS, PA, and PPS exhibit exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, demanding adhesives that can match their performance.

2.Surface Energy Variation:These plastics can possess varying surface energies and chemical compositions, necessitating tailored adhesive formulations for reliable bonding.
3.Extreme Environments:Engineering plastics often find use in harsh environments, requiring adhesives with resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
4.Precision Bonding:Applications in aerospace, medical devices, and automotive industries demand precise and strong bonds to ensure safety, reliability, and functionality.
Specialty Adhesives
- Flexible Formulations:We formulate specialty adhesives to address the specific requirements of bonding engineering plastics, providing optimal adhesion and compatibility.
- Enhanced Compatibility:Designers formulate these adhesives to create strong bonds even on low-energy surfaces and challenging substrates like filled or reinforced plastics.
- Thermal Resistance:Specialty adhesives exhibit remarkable resistance to extreme temperatures, maintaining bond integrity in demanding thermal environments.
- Chemical Compatibility:In industries like electronics and medical devices, specialty adhesives offer chemical resistance, preventing deterioration due to exposure to harsh substances.
Applications of Engineering Plastics and Specialty Adhesives:
- Aerospace:Specialty adhesives ensure the integrity of components in aircraft interiors and exteriors, where engineers choose engineering plastics for their lightweight and durable attributes.
- Medical Devices:Bonding engineering plastics in medical equipment demands adherence to stringent regulatory standards, where specialty adhesives are crucial in maintaining biocompatibility and device functionality.
- Electronics:In electronics manufacturing, engineering plastics like polycarbonate and ABS are common for housings, and specialty adhesives provide reliable bonds while meeting electrical insulation requirements.
- Automotive:As engineering plastics become more prevalent in automotive design, specialty adhesives support the assembly of components for structural stability and safety.
Innovation and Collaboration
The synergy between engineering plastics and specialty adhesives represents an exciting frontier in plastic bonding. As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance and design complexity, collaborative efforts between material scientists, adhesive engineers, and manufacturers lead to the developing of advanced adhesive formulations tailored to the unique demands of engineering plastics. This ongoing innovation ensures that even in the most challenging applications, we achieve strong, durable, and reliable bonds, propelling the capabilities of modern plastic-bonded structures.
Medical Device Assembly
Medical Device Assembly integrates various components to create essential medical devices that ensure patient well-being. The success of this assembly heavily relies on the quality of adhesives used, particularly Plastic Bonding Adhesives, which play a pivotal role in securely joining plastic parts to form a cohesive and robust device. Key points to consider in this process include:
- Material Compatibility:We design Plastic Bonding Adhesives to adhere effectively to various types of medical-grade plastics commonly used in device construction, ensuring a strong and lasting bond that can withstand the rigors of real-world usage.
- Biocompatibility:Medical devices come into direct or indirect contact with the human body. We must thoroughly test Plastic Bonding Adhesives to ensure they are biocompatible, meaning they won’t cause adverse reactions when in contact with bodily tissues or fluids.
- Sterilization Resistance:Medical devices must undergo stringent procedures to maintain aseptic conditions. The adhesive should withstand these sterilization methods, such as autoclaving, without compromising its integrity.
- Precision Application:The assembly of medical devices often involves small and intricate parts. Plastic Bonding Adhesives should allow for precise application, minimizing the risk of excess adhesive interfering with device functionality or appearance.
- Chemical and Environmental Resistance:During their lifespan, medical devices can experience exposure to various chemicals and environmental factors. The adhesive should resist degradation and maintain its bonding strength even when exposed to such conditions.
- Mechanical Strength:The adhesive bond must provide the necessary mechanical strength to ensure the device remains intact. This aspect is significant for devices that may undergo pressure, like medical wearables.
- Ease of Quality Control:Adhesive applications should be consistent and easily assessable during quality control procedures. Uniform adhesive application is crucial to ensure the reliability and safety of the final product.
- Regulatory Compliance:The medical device industry is tightly regulated to ensure patient safety. Plastic Bonding Adhesives used in device assembly must comply with relevant regulations and standards to gain necessary approvals for commercialization.
- Longevity and Durability:Many manufacturers design medical devices for long-term use. The adhesive bond should retain strength and stability over the device’s expected lifespan, reducing the risk of component detachment or failure.
Automotive Interior and Exterior Bonding
The realm of Automotive Interior and Exterior Bonding relies on advanced technologies to create aesthetically pleasing, safe, and durable vehicles. In this intricate process, Plastic Bonding Adhesives take center stage as essential components for securely joining various plastic parts, both inside and outside the vehicle. The following key points highlight the significance of Plastic Bonding Adhesives in this context:
- Structural Integrity:Plastic Bonding Adhesives contribute to the overall structural integrity of vehicles, ensuring that components such as bumpers, panels, and interior trims remain firmly attached even under the stress of daily use and potential collisions.
- Weight Reduction:Automotive manufacturers seek to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. By replacing traditional mechanical fastening methods with Plastic Bonding Adhesives, the weight of vehicles can be lowered, leading to improved fuel economy.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility:Adhesives enable the creation of sleek and seamless designs, both inside and outside the vehicle, by eliminating the need for visible mechanical fasteners. This improvement enhances the overall aesthetic appeal and can contribute to a sense of luxury in the interior.
- Vibration Dampening:Adhesives reduce vibrations and noise, providing a quieter and more comfortable driving experience. This consideration is essential for interior components exposed to the engine or road vibrations.
- Corrosion Resistance:Various environmental conditions subject automotive components. Plastic Bonding Adhesives can provide a barrier against moisture, salt, and other corrosive substances, helping to extend the lifespan of exterior and interior parts.
- Sealing and Weatherproofing:Adhesives provide adequate sealing and weatherproofing for exterior components, preventing water infiltration and enhancing the vehicle’s durability against the elements.
- High-Speed Manufacturing:Adhesive applications can be automated, enabling rapid assembly on production lines. This approach speeds up the manufacturing process while ensuring consistent and reliable bonding.
- Improved Safety:Plastic Bonding Adhesives can enhance the safety of vehicles by distributing forces during impacts more evenly across bonded components. This feature can contribute to better crash performance and occupant protection.
- Ease of Application:Adhesives offer easy application on complex shapes and contours, allowing for precise bonding even in hard-to-reach areas, which might be challenging with traditional fastening methods.
- Regulatory Compliance:The automotive industry is subject to stringent safety regulations. Plastic Bonding Adhesives must meet relevant standards to ensure that bonded components withstand real-world conditions and comply with safety requirements.
Electronics Encapsulation and Bonding
Electronics Encapsulation and Bonding are vital processes that rely on advanced Plastic Bonding Adhesives to ensure electronic devices’ integrity, functionality, and durability. In this intricate realm, Plastic Bonding Adhesives play a central role, offering numerous benefits and functionalities highlighted by key subheadings:
- Reliable Component Bonding:Plastic Bonding Adhesives securely bond diverse electronic components, creating a cohesive unit that withstands mechanical stress and ensures consistent electrical connectivity.
- Environmental Shielding:These adhesives encapsulate sensitive electronics, safeguarding them from moisture, dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, maintaining device performance under challenging conditions.
- Vibration and Shock Absorption:Plastic Bonding Adhesives dampen vibrations and absorb shocks, protecting delicate electronic components from damage, making them suitable for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
- Seamless Waterproofing:The waterproofing properties of these adhesives shield electronics from water and other liquids, making them crucial for devices exposed to wet or outdoor environments.
- Thermal Management Enhancement:Plastic Bonding Adhesives with excellent thermal conductivity dissipate heat effectively, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance of electronic components.
- Compact Design Enablement:These adhesives facilitate compact device designs by securely bonding miniaturized components, ensuring efficient use of space without compromising performance.
- Chemical and Corrosion Resistance:Plastic Bonding Adhesives that resist chemicals and corrosion protect electronics in industrial and corrosive environments, extending the longevity of devices.
- RF Shielding Integration:Adhesives can incorporate RF shielding materials, reducing electromagnetic interference and maintaining signal integrity in sensitive electronic systems.
- Customized Material Selection:Adhesive selection can be tailored based on material compatibility, cure time, and required properties, allowing for precise bonding solutions in diverse electronic applications.
- Stringent Reliability Testing:Comprehensive testing procedures, including accelerated aging and environmental exposure tests, verify the durability and performance of encapsulated and bonded electronics.
In the dynamic landscape of electronics manufacturing, Plastic Bonding Adhesives for Electronics Encapsulation and Bonding empowers manufacturers to create devices that are not only technologically advanced but also resilient in the face of various challenges. By combining connectivity and protection, these adhesives are driving innovation across industries, shaping the future of electronics.
Packaging and Consumer Goods
In the world of Packaging and Consumer Goods, the role of Plastic Bonding Adhesives has become paramount. These specialized adhesives offer a versatile and efficient solution for enhancing various plastic-based products’ durability, functionality, and sustainability. As the demand for innovative packaging solutions grows, Plastic Bonding Adhesives play a crucial role in creating products that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally friendly.
Benefits of Plastic Bonding Adhesives
- Strong Adhesion:Designers formulate Plastic Bonding Adhesives to create solid and reliable bonds between different types of plastics, overcoming the challenges posed by plastics’ inherent low surface energy.
- Enhanced Durability:By providing a robust bond, these adhesives improve the overall durability of plastic products, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of transportation, handling, and usage.
- Design Flexibility:Plastic Bonding Adhesives create intricate and complex designs, allowing manufacturers to explore creative packaging and consumer goods designs previously limited by traditional bonding methods.
- Sustainability:With an increasing focus on environmental consciousness, these adhesives enable the development of eco-friendly products by facilitating recyclable plastics and reducing the need for excessive material usage.
Applications in Packaging
- Food Packaging:Plastic Bonding Adhesives are FDA-approved and suitable for food packaging, ensuring safety and preventing leakage or contamination.
- Protective Packaging:These adhesives create durable seals in protective packaging, safeguarding products from moisture, dust, and other external factors.
- Luxury Packaging:High-end consumer goods benefit from the precision and aesthetic possibilities offered by Plastic Bonding Adhesives, enhancing the overall presentation and user experience.
Advancements in Adhesive Technology
- UV-Curable Adhesives:Rapid-curing UV adhesives have streamlined the bonding process, reducing production time and energy consumption.
- Low-VOC Formulations:Environmentally friendly adhesive options with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions contribute to sustainability efforts.
- High-Temperature Resistance:Adhesives that withstand high temperatures ensure the longevity of bonded plastics, making them suitable for products requiring exposure to heat.
- Improved Bonding with Diverse Plastics:Advancements in adhesive formulations have expanded compatibility, enabling adequate bonding between different types of plastics.
Adhesive Dispensing Techniques
Adhesive Dispensing Techniques are pivotal in ensuring the practical application of Plastic Bonding Adhesives, enabling precise bonding, enhanced product durability, and streamlined manufacturing processes. These techniques have revolutionized how Plastic Bonding Adhesives are utilized in various industries, facilitating the creation of durable and sustainable plastic-based products.
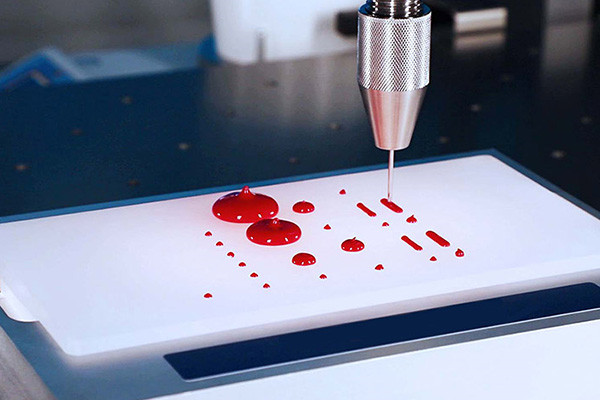
Key Dispensing Techniques
- Precision Jetting:Microscopic droplet deposition allows for accurate adhesive application, especially in intricate designs and small bonding areas.
- Spray Application:We achieve uniform adhesive coverage by using a fine mist of adhesive particles suitable for larger surface areas and high-speed production.
- Robotic Dispensing:Programmable robotic arms ensure consistent adhesive placement, reducing human error and enhancing production efficiency.
- Needle Dispensing:Controlled adhesive flow through a fine needle offers versatility in applying different adhesive volumes and patterns.
Advantages of Plastic Bonding
- Optimal Adhesive Distribution:Dispensing techniques ensure uniform adhesive distribution, minimizing the risk of weak bonds or uneven stress distribution.
- Reduced Waste:Precise application reduces adhesive wastage, contributing to cost savings and environmentally friendly practices.
- Enhanced Bond Strength:Accurate adhesive placement leads to more robust and reliable bonds, crucial for longevity in plastic-based products.
- Complex Bonding Scenarios:Dispensing techniques enable bonding in challenging scenarios, such as bonding dissimilar plastics or creating intricate 3D structures.
Technological Innovations
- Automated Control Systems:Advanced software controls offer real-time adjustments, ensuring consistent adhesive application even in complex geometries.
- Material Compatibility:Tailored dispensing techniques accommodate a wide range of Plastic Bonding Adhesives, adapting to the specific characteristics of each adhesive type.
- Inline Quality Monitoring:Incorporating monitoring systems provides immediate feedback, maintaining high bonding quality and minimizing defects.
- Nanotechnology Integration:Cutting-edge nano dispensing techniques allow ultra-precise adhesive application, ideal for microelectronics and medical devices.
- Sustainability Focus:Some dispensing methods promote eco-friendly practices by minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and enabling the use of recyclable plastics.
Testing and Quality Control
Testing and Quality Control are pivotal aspects in Plastic Bonding Adhesives, guaranteeing the integrity and performance of adhesive bonds in various applications. Through comprehensive testing methods and stringent quality checks, manufacturers can confidently deliver plastic-bonded products that meet the highest strength, durability, and safety standards.
Key Testing Methods
- Shear and Peel Tests:Evaluating adhesive strength and cohesion helps determine how well the adhesive withstands shear and peeling forces, mimicking real-world conditions.
- Environmental Simulation:Subjecting adhesive bonds to extreme temperatures, humidity, and UV exposure ensures reliability under diverse ecological conditions.
- Chemical Resistance Assessment:Testing adhesives against various chemicals ensures they maintain structural integrity when exposed to potentially corrosive substances.
- Aging Studies:Accelerated aging tests predict the long-term durability of adhesive bonds, aiding in estimating product lifespan.
Quality Control Measures
- Formulation Verification:Ensuring consistent adhesive formulation guarantees uniform bonding properties across production batches.
- Application Monitoring:Precise control over adhesive application parameters such as temperature, pressure, and curing time ensures uniformity and reliability.
- Non-Destructive Evaluation:Techniques like ultrasound and X-ray inspection allow for defect detection without compromising the integrity of the bonded product.
- Batch Consistency:Rigorous testing of adhesive batches maintains uniform performance, minimizing variations that could affect end-product quality.
- Real-time Inspection:Employing real-time monitoring during production enables prompt detection of deviations and potential defects.
Testing and Quality Control are the cornerstones of Plastic Bonding Adhesives’ success, guaranteeing that products meet stringent performance standards. Manufacturers can confidently provide plastic-bonded solutions that excel in strength, durability, and reliability across various applications through rigorous testing techniques and vigilant quality control measures.
Environmental Durability and Chemical Resistance
Regarding plastic bonding adhesives, we cannot overstate the significance of environmental durability and chemical resistance. These characteristics play a pivotal role in ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of adhesive bonds, particularly in applications involving plastics. Here are vital points highlighting their importance:
- Challenging Environments:Plastic bonding adhesives often find use in environments with fluctuating temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation. They must be resilient enough to withstand these conditions without weakening.
- Chemical Exposure:Plastics used in different industries can come into contact with various chemicals, including solvents, acids, and oils. Chemical resistance ensures that the adhesive bond remains stable and effective, preventing deterioration.
- Improved Product Reliability:Adhesive bonds in plastic assemblies need to endure stress, vibrations, and mechanical loads without failing. Environmental durability and chemical resistance enhance product reliability and reduce maintenance needs.
- Diverse Applications:Various sectors employ plastic bonding adhesives, from automotive and electronics to medical devices and packaging. Their ability to withstand environmental and chemical challenges ensures optimal performance in each application.
- Compatibility Consideration:Manufacturers must consider the compatibility between the adhesive and the specific types of bonded plastics. Environmental durability and chemical resistance help maintain this compatibility over time.
- Sustainable Solutions:Incorporating durable and chemically resistant adhesives extends the lifespan of plastic components, reduces waste, and promotes a more sustainable approach to production.
The success of plastic bonding adhesives hinges on their environmental durability and chemical resistance. These attributes ensure the longevity and reliability of bonds and support industries in achieving sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes.
Challenges in Bonding Different Plastic Types
Bonding different plastic types poses significant challenges due to chemical composition, surface properties, and compatibility variations. These challenges can affect the strength and longevity of adhesive bonds. Key points outlining the difficulties in bonding different plastic types are as follows:
- Diverse Surface Energies:Plastics exhibit varying surface energies, making it crucial to select adhesives that can effectively adhere to high-energy (polar) and low-energy (non-polar) surfaces.
- Chemical Compatibility:Different plastics are composed of distinct polymers, each with its chemical structure. One must carefully choose adhesives to ensure compatibility and avoid chemical interactions that could weaken the bond.
- Surface Pre-treatment:Many plastics have inert surfaces that resist adhesion. Surface pre-treatment methods such as plasma treatment, corona discharge, or chemical primers are often required to enhance surface wettability and adhesion.
- Thermal Expansion:Plastics have varying coefficients of thermal expansion, which can lead to differential expansion and contraction under temperature changes, potentially stressing adhesive bonds.
- Environmental Factors:Exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and harsh chemicals can weaken adhesive bonds over time, particularly if the adhesive and plastics have differing resistance levels.
- Mechanical Stress:Different plastics possess varying mechanical properties such as flexibility, hardness, and tensile strength. These differences can lead to uneven stress distribution within bonded assemblies, affecting bond integrity.
- Long-term Durability:The factors mentioned above can compromise the long-term performance of bonded plastic assemblies, necessitating thorough testing and evaluation.
Successfully bonding different plastic types requires a deep understanding of the materials involved, careful adhesive selection, proper surface preparation, and rigorous testing to ensure strong, durable, and reliable bonds. Addressing these challenges is essential for applications ranging from automotive and electronics to medical devices and consumer goods.
Future Trends in Plastic Bonding Technology
Plastic bonding adhesive is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and environmental considerations. Key future trends in plastic bonding technology include:
- Bio-Based Adhesives:Increasing emphasis on sustainability pushes the development of bio-based adhesives derived from renewable sources, reducing reliance on petrochemical-based materials.
- Nanotechnology Integration:Nanoadhesives with enhanced properties like improved strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors are on the horizon, enabling more reliable plastic bonding in diverse applications.
- Innovative Adhesive Systems:Integrating smart materials into adhesive formulations, such as self-healing adhesives and adhesives with built-in sensors, will offer innovative solutions for monitoring and maintaining bonded plastic structures.
- 3D Printing Adhesives:As 3D printing gains prominence, specialized adhesives tailored for bonding 3D-printed plastic parts will become essential, ensuring strong, precise, and functional connections.
- Digital Bonding Solutions:Using digital technologies like simulations and predictive modeling will optimize the adhesive selection and application processes, leading to more efficient and effective bonding outcomes.
- Multi-Material Bonding:With the trend towards light-weighting and multifunctional designs, adhesives capable of bonding different types of plastics and dissimilar materials will play a crucial role in various industries.
- Enhanced Surface Preparation:Advancements in surface modification techniques will enhance the bonding strength by providing better adhesion sites on plastic surfaces.
- Healthcare and Biomedical Applications:Developing biocompatible and sterilizable adhesives will open doors for innovative medical devices and wearable healthcare technologies.
These trends will revolutionize the plastic bonding adhesive landscape in the coming years, addressing both performance and environmental demands while enabling novel applications across industries.
Plastic bonding adhesive has redefined the possibilities of joining plastic materials, enabling industries to create products that are both functional and aesthetically appealing. Its role in overcoming the challenges posed by the diversity of plastic types and their inherent properties cannot be underestimated. As manufacturing processes continue to evolve, plastic bonding adhesive will remain a fundamental tool for achieving reliable connections in an array of applications. With ongoing advancements in adhesive formulations and techniques, the potential for innovation in plastic bonding is limitless, contributing to the creation of more durable, efficient, and sustainable products.