Epoxy Adhesive Glue
In an era of heightened environmental awareness, industries continually seek sustainable alternatives to conventional practices. One such innovation gaining traction is using epoxy adhesive glue as a means of sustainable joining. Epoxy adhesive glue offers remarkable bonding capabilities and presents a range of environmental benefits. From reducing carbon footprint to minimizing waste, this adhesive solution holds the potential to revolutionize the way we approach joining processes across various industries.
This article explores the diverse environmental advantages of epoxy adhesive glue and its contribution to a more sustainable future.
What is Epoxy Adhesive Glue?
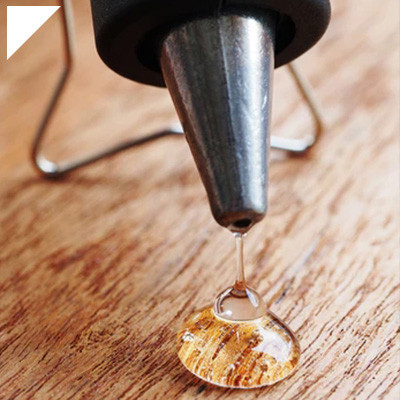
Epoxy adhesive glue, commonly called epoxy glue, is a type of adhesive formulated from epoxy resins. Epoxy resins are a class of synthetic thermosetting polymers that undergo a chemical reaction known as curing or polymerization when mixed with a curing agent or hardener. This reaction transforms the liquid resin mixture into a strong, durable, rigid solid material.
Epoxy adhesive glue is known for its exceptional bonding properties, high strength, and resistance to various environmental factors, including temperature, moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. It is widely used in multiple industries and applications due to its versatility and reliability.
How Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Work?
Epoxy adhesive glue is a versatile and robust bonding material used in various applications, from construction and manufacturing to crafts and DIY projects. Its effectiveness is attributed to its unique chemical composition and curing process. Here’s how epoxy adhesive glue works:
- Components: Epoxy adhesive typically comprises two main parts: the epoxy resin and the curing agent (also known as hardener). These two components are stored separately to prevent premature curing.
- Mixing: The epoxy resin and curing agent must be thoroughly mixed in the correct proportions before application. This mixing initiates a chemical reaction between the two components, forming a cross-linked polymer structure, creating a strong adhesive bond.
- Chemical Reaction: The chemical reaction between the epoxy resin and curing agent is exothermic, meaning it releases heat. This reaction can be fast, so applying the adhesive immediately after mixing is essential.
- Cross-Linking: Mixing epoxy resin and curing agent causes the molecules in both components to react and cross-link. This forms a highly durable and rigid three-dimensional network of interconnected polymer chains. As this network develops, it creates the adhesive’s solid structure.
- Curing Process: Once the epoxy adhesive is applied to the surfaces to be bonded, the curing process begins. The cross-linking reaction continues, gradually transforming the initially liquid mixture into a solid, hardened material. The curing time can vary depending on temperature, humidity, and epoxy formulation.
- Bonding Mechanism: The solid adhesive bond is achieved through mechanical and chemical interlocking of the cured epoxy with the surfaces being bonded. The epoxy’s cross-linked polymer structure creates a strong and resilient connection that can withstand various forces, including tension, compression, shear, and more.
- Substrate Compatibility: Epoxy adhesive can bond to various substrates, including metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, wood, and fabrics. The compatibility of the epoxy with the substrates is influenced by surface preparation, cleanliness, and the nature of the materials being bonded.
- Strength and Properties: Epoxy adhesive bonds are known for their high strength, resistance to impact, and durability. The cured epoxy is also resistant to chemicals, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor applications.
It’s important to note that epoxy adhesives come in various formulations designed for specific applications, so choosing the right type of epoxy for your intended use is essential. Proper surface preparation, mixing ratios, and curing conditions are crucial for achieving optimal bond strength and performance.
When Did Epoxy Adhesive Glue Gain Prominence?
Epoxy adhesive glue gained prominence in the mid-20th century due to significant advancements in polymer chemistry and industrial applications. The development and adoption of epoxy adhesive glue can be traced back to several key milestones:
- Early Developments:The foundations of epoxy chemistry were laid in the 1930s when researchers began investigating the polymerization of epoxide compounds. However, it was in the 1940s that more practical and helpful epoxy resins were developed. These early formulations were used primarily for coatings, laminates, and encapsulation in various industrial applications.
- World War II and Aerospace Applications:During World War II, epoxy resins gained attention for their potential use in aircraft manufacturing. Epoxy-based adhesives and coatings offer excellent bonding strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, making them ideal for aerospace applications.
- Post-War Industrial Growth:After World War II, there was a significant surge in industrial growth and innovation. Due to their versatile bonding properties, epoxy adhesives began to find their way into various industries, such as automotive, construction, electronics, and consumer products. The ability of epoxy to bond with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and composites, contributed to its growing popularity.
- Advanced Formulations and Research:Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, researchers and chemists worked on refining epoxy formulations and exploring various curing agents to optimize performance characteristics, and developing new curing agents that allowed for tailored properties such as cure speed, flexibility, and thermal resistance.
- The 1970s and Beyond:By the 1970s, epoxy adhesive glues had become essential components in many industries. Their high strength, durability, and resistance to chemicals and temperature extremes made them indispensable for applications ranging from structural bonding to electronic encapsulation. The continued research and development in epoxy chemistry led to even more specialized formulations, expanding their applications further.
- Advancements in Composite Materials:Epoxy resins played a crucial role in the growth of composite materials, particularly in sectors like aerospace and sports equipment. Carbon fiber-reinforced composites, for example, often use epoxy resins as the matrix material due to their ability to provide strong adhesion between the fibers and the matrix.
- Modern Applications:In recent decades, epoxy adhesive glues have continued to evolve and find new applications. They are commonly used in woodworking, jewelry making, automotive repair, marine construction, and medical devices.
Overall, the prominence of epoxy adhesive glue can be attributed to its versatile properties, ongoing research and development, and its ability to meet the demands of various industries and the mid-20th century marked the turning point when epoxy adhesives transitioned from experimental materials to indispensable components in modern manufacturing and construction processes.
Why is Sustainable Joining Important?
Sustainable joining, often referred to in the context of manufacturing and engineering, involves joining or assembling materials to minimize negative environmental, social, and economic impacts while ensuring the long-term functionality and durability of the final product. This concept is gaining importance due to several interconnected reasons:
- Environmental Conservation:Sustainable joining methods aim to reduce the consumption of raw materials, energy, and resources. Traditional joining techniques, such as welding, brazing, or adhesive bonding, can generate significant waste, energy consumption, and emissions. By adopting sustainable joining methods, manufacturers can minimize these negative environmental impacts.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint:Many conventional joining processes involve high energy inputs, often from non-renewable sources, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable joining methods, such as mechanical joining, cold welding, or bio-based adhesives, can substantially lower the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing.
- Waste Minimization:Traditional joining processes may produce hazardous waste, excess materials, or by-products that pose disposal challenges and potential environmental harm. Sustainable joining methods aim to minimize waste generation and promote the efficient use of materials.
- Energy Efficiency:Sustainable joining techniques typically require lower energy inputs than traditional methods. For instance, mechanical joining methods like riveting or fastening often require less energy than welding or soldering, contributing to overall energy efficiency.
- Resource Conservation:Sustainable joining methods often focus on using materials more efficiently, extending product lifespan, and reducing the demand for virgin resources. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where products are designed for longevity and recyclability.
- Human Health and Safety:Some conventional joining techniques involve using hazardous materials or producing harmful fumes and by-products. Sustainable joining methods prioritize worker safety and the well-being of those exposed to the manufacturing processes.
- Product Performance and Longevity:Properly joined components contribute to the durability and performance of products. Sustainable joining methods ensure that products are built to last, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering overall environmental impacts.
- Regulatory Compliance:As governments and international bodies enact stricter environmental protection and sustainability regulations, manufacturers are incentivized to adopt sustainable practices, including in joining processes.
- Consumer Demand:Increasingly, consumers are becoming more conscious of their products’ environmental and social impacts. Sustainable products often enjoy a competitive advantage in the market, driving manufacturers to adopt more environmentally friendly practices, including sustainable joining methods.
- Innovation and Research:The push towards sustainability encourages research and innovation in manufacturing techniques. New and improved joining methods that are more eco-friendly and resource-efficient are continually being developed.
What Makes Epoxy Adhesive Glue Environmentally Friendly?
Epoxy adhesive glue can be considered environmentally friendly in specific contexts due to several factors:
- Low VOC Emissions:Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are chemicals that can vaporize into the air and contribute to air pollution. Environmentally friendly epoxy adhesives are formulated to have low or zero VOC emissions, minimizing their impact on indoor and outdoor air quality.
- Biodegradability and Low Toxicity:Some epoxy formulations are designed to be biodegradable, meaning they can break down over time into harmless substances through natural processes. Additionally, eco-friendly epoxies often contain lower levels of toxic or harmful components, making them less damaging to ecosystems when they eventually degrade.
- Renewable and Sustainable Materials:Manufacturers increasingly use renewable and sustainable raw materials to create epoxy adhesives. This reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and non-renewable resources, making the production process more environmentally friendly.
- Reduced Energy Consumption:Environmentally conscious epoxy manufacturers may implement energy-efficient production processes, reducing the energy consumption.
- Water-Based Formulations:Water-based epoxy adhesives have gained popularity due to their reduced environmental impact compared to solvent-based counterparts. Water-based formulations typically have lower VOC emissions and are easier to clean up, reducing the potential for environmental contamination.
- Recyclability:Some epoxy adhesives are designed to be easily recyclable, allowing for the separation and reprocessing of materials at the end of their useful life. This reduces waste and conserves resources.
- Longevity and Durability:High-quality epoxy adhesives can contribute to the longevity and durability of products used to bond. This can reduce the need for frequent replacements, lowering overall resource consumption and waste generation.
- Environmental Certifications:Some epoxy adhesive products may carry certifications from third-party organizations that validate their environmentally friendly attributes. Look for certifications such as Green Seal, EcoLogo, or Cradle to Cradle.
It’s important to note that the environmental friendliness of an epoxy adhesive depends on the specific formulation, manufacturing processes, and intended use. Before labeling a product as environmentally friendly, reviewing its specifications, certifications, and potential impacts on human health and the environment is recommended.
How Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Reduce Carbon Footprint?
Epoxy adhesive glue can contribute to reducing carbon footprint in several ways:
- Lower Energy Consumption in Production:Epoxy adhesive glue manufacturing typically consumes less energy than traditional mechanical fastening methods. For example, welding or using screws can require significant energy input, while producing epoxy adhesive might require less power, especially if it involves a solvent-free or low-energy curing process.
- Reduced Material Waste:Traditional fastening methods often generate more waste due to the need for additional materials like screws, bolts, or rivets. Epoxy adhesive eliminates the need for these extra materials, which can lead to reduced waste generation.
- Lightweight Design:Epoxy adhesive can be used to bond lightweight materials, which can lead to weight reduction in the final product. Lighter products require less transportation energy and can contribute to overall energy savings, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace.
- Improved Structural Integrity:Epoxy adhesives can distribute stress more evenly across bonded surfaces, improving structural integrity. This can result in longer-lasting products with reduced maintenance needs, thus minimizing the energy and resources required for repairs or replacements.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility:Epoxy adhesives enable more creative and flexible design options due to their ability to bond dissimilar materials. This can lead to innovative product designs that optimize material usage and reduce environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency in Applications:Epoxy adhesives can offer insulation and corrosion-resistant properties, contributing to energy efficiency in various applications. For instance, using epoxy adhesive to seal gaps can prevent heat loss, ultimately reducing energy consumption for heating or cooling.
- Reduced Emissions during Use:Depending on the specific application, the epoxy adhesive can replace mechanical fastening methods that involve welding, which can produce harmful emissions and fumes. Epoxy adhesives contribute to improved air quality and a healthier working environment by avoiding these emissions.
- Extended Product Lifespan:Epoxy adhesive bonding can create strong, durable connections that help extend the lifespan of products. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, reducing the resources, energy, and emissions associated with manufacturing and disposal.
- Lower Transportation Emissions:The lighter weight of epoxy-bonded products can reduce fuel consumption during transportation. This is particularly important in industries where transportation-related emissions significantly contribute to the carbon footprint.
- Lower Embodied Energy:The manufacturing and transportation of epoxy adhesives often require less energy and resources than alternative fastening methods like producing metal fasteners or welding equipment.
However, it’s important to note that the carbon footprint reduction achieved through epoxy adhesive use depends on various factors, including the specific application, the type of epoxy used, and the overall product design. While epoxy adhesives offer many environmental advantages, it’s also crucial to consider the complete life cycle of a product to assess its overall sustainability impact accurately.
What Industries Can Benefit from Epoxy Adhesive Glue?
Epoxy adhesive glue is a versatile and robust bonding material that can benefit many industries due to its excellent adhesive properties, durability, and versatility. Here are some sectors that can benefit from using epoxy adhesive glue:
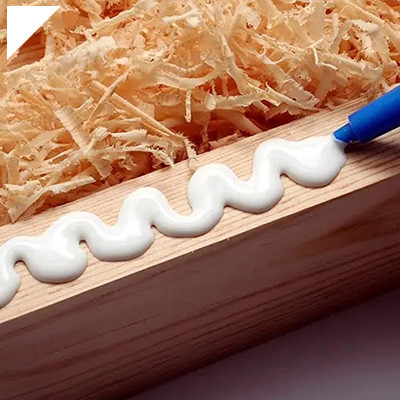
1.Construction and Building:Epoxy adhesives are used for various construction applications such as bonding concrete, stone, metal, wood, and ceramics. They provide strong bonds that can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for structural repairs and joining different materials.

2.Automotive and Aerospace:Epoxy adhesives are used to manufacture and repair vehicles, aircraft, and spacecraft. They can bond lightweight materials like carbon fiber composites, plastics, and metals, offering high strength and resistance to temperature variations.
3.Electronics:Epoxy adhesives are used in electronics assembly and packaging due to their excellent insulation properties, chemical resistance, and ability to bond different materials found in electronic components and circuitry.
4.Marine and Shipbuilding:Epoxy adhesives are resistant to water, chemicals, and salt, making them suitable for bonding and repairing materials in marine environments. They are used in boat construction, ship repair, and underwater infrastructure.
5.Woodworking:Epoxy adhesives are often used to bond wood pieces, fill cracks and gaps, and create solid and durable joints. They can also be used for creating decorative elements and laminates.
6.Medical Devices:Epoxy adhesives are utilized in the medical industry for bonding and encapsulating medical devices, such as catheters, pacemakers, and dental appliances. Their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization methods are beneficial in medical applications.
7.Packaging and Labeling:Epoxy adhesives can be used for bonding labels, seals, and other packaging materials due to their high tackiness and ability to adhere to various substrates.
8.Jewelry and Crafts:Epoxy adhesives are popular in the crafting and jewelry-making industry for their ability to bond various materials, including metals, gemstones, and plastics.
9.Textiles and Footwear:Epoxy adhesives can bond fabrics, leather, rubber, and other materials commonly found in textile and footwear manufacturing.
10.Renewable Energy:Epoxy adhesives are used in producing and maintaining wind turbine blades, solar panels, and other renewable energy components due to their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
11.Sporting Goods:Epoxy adhesives produce sporting goods such as skis, snowboards, surfboards, and bicycles to bond materials like composites and metals.
12.Art and Sculpture:Epoxy adhesives can be used by artists and sculptors to create strong bonds between different materials used in their creations.
These are just a few examples of industries that can benefit from using epoxy adhesive glue. Epoxy’s versatility, strong bonding properties, and resistance to various environmental factors make it a valuable tool in many applications.
How Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Contribute to Energy Conservation?
Epoxy adhesive glue can contribute to energy conservation in various ways due to its unique properties and applications. Here are some ways in which epoxy adhesive glue can help conserve energy:
- Bonding and Repair: Epoxy adhesive glue is known for its strong bonding capabilities, which can be used to repair and extend the life of various objects. By effectively improving items, such as appliances, tools, and machinery, epoxy can help prevent the need for manufacturing new replacements. This reduces the energy and resources required for manufacturing, as well as the energy needed for transporting and disposing of old items.
- Weight Reduction: Epoxy adhesive glues are often used in industries where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. By creating strong bonds with lightweight materials, epoxy adhesive glue can contribute to producing lighter vehicles and aircraft. Lighter vehicles require less energy to operate, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Enhanced Insulation: Epoxy adhesive glue can create insulated barriers in various applications. For example, it can bond insulation materials in buildings, electronic devices, and industrial equipment. Proper insulation reduces heat transfer, leading to more energy-efficient temperature control. This can lower the demand for heating and cooling systems, thereby saving energy.
- Efficient Construction: Epoxy adhesive glues are used in the construction industry for various purposes, including bonding structural components and joining dissimilar materials. These adhesives can provide structural integrity while requiring less energy-intensive processes than traditional methods like welding or mechanical fastening. This can result in faster construction times and reduced energy consumption during the building process.
- Extended Equipment Life: Epoxy adhesive glue can help extend the lifespan of equipment by providing corrosion protection and preventing wear and tear. When equipment lasts longer, the need for replacements is reduced, leading to energy savings associated with manufacturing and disposing of new equipment.
- Energy-Efficient Electronics: In the electronics industry, epoxy adhesive glue encapsulates and protects delicate components. Epoxy adhesives can reduce the frequency of replacements and the associated energy consumption in manufacturing, transportation, and disposal by ensuring the longevity of electronic devices.
- Renewable Energy Applications: Epoxy adhesives are used to manufacture and install renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines and solar panels. By providing reliable bonds in harsh environments, epoxy adhesives contribute to the durability and efficiency of these systems, which generate clean energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Reduced Energy in Packaging: Epoxy adhesives are often used in packaging materials, ensuring that products are securely placed during shipping. This reduces the need for excessive packaging materials, contributing to energy savings in manufacturing and transportation.
While epoxy adhesive glue does offer various energy-saving benefits, it’s essential to consider the overall lifecycle impact of its production, use, and disposal. Careful consideration of materials, application techniques, and end-of-life scenarios is crucial to maximize its positive environmental contributions.
What Are the Longevity and Durability of Epoxy Adhesive Joints?
The longevity and durability of epoxy adhesive joints can vary based on several factors, including the type of epoxy used, the materials being bonded, the application conditions, and the quality of the bonding process. In general, epoxy adhesive joints are known for their excellent durability and long service life, but there are specific considerations to keep in mind:
- Epoxy Type: Various types of epoxy adhesives are available, each with different formulations designed for specific applications. Some epoxies are more flexible, while others are more rigid. The choice of epoxy type should be based on the materials being bonded and the intended use of the joint.
- Materials Being Bonded: The materials being bonded play a significant role in the longevity of epoxy adhesive joints. Epoxies can bond various materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. However, the compatibility of the epoxy with the specific materials will impact the joint’s durability.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving robust, long-lasting epoxy adhesive joints. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from contaminants such as oils, dirt, and oxidation. Proper surface preparation ensures optimal adhesion between the epoxy and the substrates.
- Bonding Process: The application process, including mixing the epoxy components in the correct proportions and applying the adhesive evenly, affects the quality of the bond. Follow the manufacturer’s mixing, application, and curing guidelines to ensure the best results.
- Curing Time and Conditions: Epoxy adhesive joints require sufficient curing time and appropriate conditions to achieve maximum strength. Healing at the recommended temperature and humidity levels ensures the epoxy reaches its complete mechanical properties.
- Environmental Factors: The environment in which the epoxy adhesive joint will be used can influence its durability. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, exposure to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation can impact the performance of the adhesive over time.
- Load and Stress: The level of burden or stress that the adhesive joint will experience affects its longevity. Proper design and load analysis are essential to ensure the joint can withstand the intended application conditions.
- Vibration and Dynamic Loads: Epoxy adhesive joints can perform well under dynamic loads and beats, but special considerations might be needed for applications subject to frequent movement or mechanical stress.
- Age and Degradation: Over time, all materials undergo aging and degradation to some extent. The rate of aging for epoxy adhesive joints can vary based on the abovementioned factors. Regular inspection and maintenance can help detect any signs of degradation and prevent failures.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality in the manufacturing of epoxy adhesive joints is essential. Using reputable epoxy brands and following established quality control procedures can lead to more reliable and durable joints.
When properly applied and used within their intended conditions, epoxy adhesive joints can provide long-lasting, durable bonds that contribute to the longevity and reliability of various products and structures. It’s recommended to consult with epoxy adhesive manufacturers or industry experts to select the appropriate epoxy formulation and to ensure proper application for specific bonding needs.
How Can Epoxy Adhesive Glue Enhance Design Flexibility?
Epoxy adhesive glue offers several ways to enhance design flexibility in various applications. Here are some ways in which epoxy adhesive glue can contribute to increased design flexibility:
- Bonding Versatility:Epoxy adhesive glues can bond a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, wood, and more. This versatility allows designers to combine different materials to achieve their designs’ desired functionality and aesthetics.
- Reduced Mechanical Fasteners:Epoxy adhesive glues can eliminate the need for traditional mechanical fasteners like screws, bolts, and rivets. This creates a cleaner, more streamlined appearance and provides more design freedom by allowing for seamless and hidden connections.
- Complex Shapes:Epoxy adhesives can bond irregular or complex shapes that might be difficult to achieve using traditional fasteners. This enables designers to create intricate and innovative designs that might not be feasible with conventional assembly methods.
- Improved Stress Distribution:Epoxy adhesive glues form a strong and uniform bond between surfaces. This helps distribute stress and loads evenly across the bonded area, enhancing the design’s structural integrity. As a result, designers can explore new forms and load-bearing capabilities.
- Joining Dissimilar Materials:Epoxy adhesive glues can successfully bond materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion, which can be challenging with mechanical fasteners. This capability enables designers to combine materials with varying properties to optimize performance and design outcomes.
- Weight Reduction:Epoxy adhesive glues are lightweight compared to many traditional fasteners. By using adhesives, designers can reduce the weight of assemblies, which is particularly advantageous in applications where weight savings are critical, such as aerospace and automotive design.
- Seamless Surfaces:Epoxy adhesive bonds create seamless joints, which can result in a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing surface. This is especially important in design applications where appearance is a significant factor.
- Improved Stress Concentration:Epoxy adhesive bonds can help reduce stress concentration points familiar to traditional fasteners. This allows designers to distribute stress more evenly, enhancing the overall durability of the design.
- Enhanced Water and Chemical Resistance:Epoxy adhesive glues often resist water, chemicals, and environmental factors. This makes them suitable for designs exposed to challenging conditions, expanding the range of potential applications.
- Design Innovation:The elimination of traditional fasteners and the ability to bond dissimilar materials can open up new possibilities for design innovation. Designers can think outside the box and explore novel design concepts previously limited by assembly constraints.
Incorporating epoxy adhesive glues into your design process can significantly broaden your options and empower you to create more versatile, durable, and aesthetically pleasing products. However, selecting the correct type of epoxy adhesive for your specific application is essential, and following proper bonding techniques ensures the best results.
What Safety Benefits Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Offer?
Epoxy adhesive glue offers several safety benefits, making it a popular choice for various applications. Some of the critical safety benefits of epoxy adhesive glue include:
- Chemical Resistance:Epoxy adhesives resist various chemicals, including solvents, acids, bases, and other corrosive substances. This property ensures that the bond remains stable and effective in multiple environments, reducing the risk of failure due to chemical exposure.
- High Bond Strength:Epoxy adhesives provide powerful bonds, capable of withstanding significant loads and stress. This high bond strength contributes to the overall safety of structures and assemblies, preventing failures that could lead to accidents or injuries.
- Durability and Longevity:Epoxy adhesives are highly durable and can withstand harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and mechanical vibrations. Their ability to maintain their performance over time reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements, enhancing overall safety and reliability.
- Non-Toxic Formulations:Many modern epoxy adhesive formulations are designed to be non-toxic, making them safe for use in various applications, including those involving food contact, medical devices, and consumer products. These formulations adhere to strict health and safety regulations, minimizing potential risks to human health.
- Low Volatility:Epoxy adhesives typically have soft volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which helps maintain air quality and reduces the potential for health concerns associated with inhaling explosive fumes.
- Gap-Filling Ability:Epoxy adhesives have excellent gap-filling properties, allowing them to bond irregular or uneven surfaces effectively. This feature ensures that joints are securely connected, reducing the risk of weak points that could compromise safety.
- Electrical Insulation:Epoxy adhesives are excellent insulators, making them suitable for applications where electrical components must be securely bonded without the risk of short circuits or electrical leakage.
- Fire Resistance:Epoxy adhesives often have good fire-resistant properties, which can be crucial in applications where fire safety is a concern.
- Easy Dispensing and Application:Epoxy adhesives are available in various forms, including liquid, paste, and putty-like. This versatility allows for easy dispensing and precise application, reducing the likelihood of accidental spills or mishaps.
- Minimal Shrinkage:Epoxy adhesives typically exhibit minimal shrinkage during curing, ensuring the bonded materials stay in their intended positions and maintain their structural integrity.
While epoxy adhesives offer these safety benefits, it’s important to note that proper handling, storage, and application are essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. Users should always follow manufacturer guidelines and take appropriate safety precautions when working with epoxy adhesives.
How Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Enable Lightweighting of Products?
Epoxy adhesive glue plays a significant role in enabling the lightweight of products primarily due to its exceptional bonding properties and versatility in joining different materials. Lightweighting refers to reducing the overall weight of a product without compromising its structural integrity or functionality. This is especially important in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods industries, where the demand for more fuel-efficient vehicles, increased energy efficiency, and improved performance drives the need for lighter materials and designs.
Here’s how epoxy adhesive glue contributes to lightweight:

- Strong Bonding: Epoxy adhesive glue forms a solid and durable bond between various materials, including metals, composites, plastics, and dissimilar materials. This eliminates the need for heavy mechanical fasteners like screws, bolts, and rivets, which can add significant weight to a product.
- Reduced Material Thickness: Epoxy adhesives allow for the use of thinner materials while maintaining structural integrity. Traditional welding or mechanical fastening methods often require thicker materials to withstand the stress and load. Epoxy adhesive bonds distribute pressure evenly across the joint, enabling the use of thinner materials without sacrificing strength.
- Stress Distribution: Epoxy adhesive glues have a higher load-carrying capacity than mechanical fasteners. They distribute stress more evenly across the joint, reducing stress concentration points and the potential for fatigue failure. This enables using lighter, more delicate materials prone to cracking or breaking under stress.
- Corrosion Prevention: Some lightweight materials, such as aluminum and carbon fiber composites, can be vulnerable to corrosion when exposed to specific environments. The epoxy adhesive acts as a barrier, protecting the joined surfaces from environmental factors that could cause decay, thus extending the product’s lifespan.
- Design Flexibility: Epoxy adhesives can be applied in various forms, including liquids, films, and pastes. This versatility allows manufacturers to create complex and innovative designs, including bonding irregular shapes and joining dissimilar materials that might not be possible with traditional fastening methods.
- Vibration Damping: Epoxy adhesive bonds can also provide vibration-damping properties, which can be especially beneficial in applications such as aerospace and automotive, where reducing vibrations can improve overall performance and comfort.
- Reduced Assembly Time: Epoxy adhesive glues often cure quickly, reducing assembly time compared to traditional methods that involve drilling, screwing, or welding. This can lead to cost savings and increased production efficiency.
- Weight Distribution: Epoxy adhesive bonds distribute loads and stress more uniformly, enabling manufacturers to optimize the weight distribution within a product. This can lead to improved balance, stability, and overall performance.
- Seamless Appearance: Epoxy adhesives can create nearly invisible joints, providing a cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing finish than visible mechanical fasteners.
Overall, epoxy adhesive glue enables lightweight by providing robust, durable, and lightweight bonding solutions that reduce the need for heavy fasteners and allow for the use of thinner, lighter materials. This positively impacts product performance, energy efficiency, and manufacturing processes in various industries.
What Challenges Are Associated with Epoxy Adhesive Glue’s Sustainability?
Epoxy adhesive glues have gained popularity due to their strong bonding properties and versatility across various industries. However, like many products, they have sustainability challenges that must be addressed. Some of the critical challenges associated with epoxy adhesive glue’s sustainability include:
- Raw Material Sourcing:Epoxy adhesives are typically derived from petroleum-based chemicals, which are non-renewable resources. These materials’ extraction, processing, and transportation can contribute to environmental degradation and carbon emissions.
- Energy Intensive Production:The manufacturing process of epoxy adhesives involves high-energy consumption and emissions. The curing process often requires heat or chemical catalysts, which can contribute to a significant carbon footprint.
- Toxicity and Health Concerns:Many epoxy adhesives contain hazardous chemicals, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and formaldehyde, which can harm human health and the environment. Exposure to these chemicals during production, application, and disposal can pose risks.
- Waste Generation:Improper disposal of epoxy adhesive residues can lead to environmental pollution. Additionally, epoxy adhesives can be challenging to recycle due to their complex chemical composition and curing mechanisms.
- Durability and End-of-Life Issues:While epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonds, this durability can pose challenges during the end-of-life phase. Disassembling bonded materials can be complex, leading to increased waste and resource consumption when separating components for recycling or reusing.
- Limited Biodegradability:Epoxy adhesives are generally not biodegradable, which means they persist in the environment long after disposal. This can contribute to litter and pollution in ecosystems.
- Lack of Circular Economy:The linear nature of epoxy adhesive production and consumption, where materials are extracted, used, and discarded, contrasts with the principles of a circular economy that promotes resource efficiency and reduces waste.
- Alternative Material Development:Finding sustainable alternatives to traditional epoxy adhesive formulations is challenging. While some bio-based and water-based epoxy adhesives have been developed, they may still need improvement in performance and cost.
- Consumer Awareness and Behavior:Lack of awareness among consumers about the environmental impacts of epoxy adhesives can hinder the demand for more sustainable options. Educating consumers about their choices and encouraging responsible use and disposal is essential for promoting sustainability.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technological advancements, regulatory measures, and changes in industry practices. Research and development efforts are ongoing to create epoxy adhesive formulations with reduced environmental impact, improved biodegradability, and better end-of-life options. Additionally, promoting sustainable adhesive application techniques, such as using the right amount of adhesive and ensuring proper disposal, can contribute to minimizing the adverse effects of epoxy adhesive glue on the environment.
How Can Manufacturers Transition to Using Epoxy Adhesive Glue?
Transitioning to using epoxy adhesive glue in manufacturing can offer numerous benefits, including improved bonding strength, durability, and versatility. However, this transition requires careful planning and implementation to ensure a smooth integration of epoxy adhesive into your manufacturing processes. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how manufacturers can transition to using epoxy adhesive glue:
- Assessment and Planning:
- Identify the specific applications and processes where epoxy adhesive will be used. Determine if epoxy is the right choice for the intended materials and bonding requirements.
- Assess the current adhesive or bonding methods and evaluate their limitations and drawbacks.
- Set clear objectives for the transition, such as improved bond strength, reduced assembly time, or increased product lifespan.
- Material Compatibility and Testing:
- Verify the compatibility of epoxy adhesive with the materials you are bonding. Conduct compatibility tests to ensure the epoxy does not react negatively with the substrates.
- Perform bond strength tests under various conditions (temperature, humidity, stress) to determine your specific application’s optimal epoxy formulation and curing conditions.
- Supplier Selection:
- Choose a reputable epoxy adhesive supplier that provides high-quality products and technical support.
- Collaborate with the supplier to select the epoxy formulation that best meets your requirements.
- Training and Skill Development:
- Train your personnel on handling, mixing, and application of epoxy adhesive. Provide guidelines on safety precautions and protective equipment.
- Ensure your employees know the epoxy’s pot life (when it remains workable) and curing times.
- Equipment and Facilities:
- Verify that your manufacturing equipment and facilities are suitable for epoxy adhesive application. Epoxy adhesives require different dispensing equipment or curing mechanisms than previous adhesive methods.
- Ensure proper ventilation and environmental controls to maintain the recommended curing conditions.
- Process Integration:
- Develop new processes or modify existing ones to accommodate epoxy adhesive. Consider surface preparation, adhesive application, clamping, and curing methods.
- Implement quality control measures to monitor and verify adhesive application and curing consistency.
- Prototyping and Testing:
- Before full-scale implementation, conduct small-scale prototyping and testing to identify potential issues or challenges during the transition.
- Pilot Implementation:
- Begin with a limited-scale transition in specific areas or products to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of using epoxy adhesive on a larger scale.
- Feedback and Iteration:
- Gather feedback regarding the transition process from production teams, quality control, and other relevant stakeholders. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
- Full-Scale Implementation:
- Once the pilot phase is successful and any issues have been addressed, proceed with a broader implementation of epoxy adhesive across your manufacturing processes.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Continuously monitor the performance of epoxy adhesive in your manufacturing processes and make adjustments as needed to optimize efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Remember that a successful transition to epoxy adhesive glue requires careful planning, collaboration, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Regular communication with suppliers, employees, and stakeholders will help ensure a smooth and successful integration.
What Innovations Are Being Explored in Epoxy Adhesive Glue Development?
There may have been further developments since then. Some of the innovations being explored include:
1.Bio-Based and Sustainable Epoxies:There has been a growing emphasis on developing epoxy adhesives using bio-based materials, such as plant-derived resins or renewable feedstocks. This trend is driven by the desire to reduce the environmental impact of adhesive production and disposal.

2.Nanotechnology Enhancements:Researchers are investigating incorporating nanoparticles into epoxy adhesive formulations to enhance their mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to various environmental conditions. These nanoparticles can include graphene, carbon nanotubes, and nanoclays.
3.Self-Healing Epoxies:Self-healing epoxy adhesives are designed to repair microcracks and damage that may occur over time, extending the service life of bonded materials. This innovation could be beneficial in industries where maintenance and durability are critical.
4.UV-Curable Epoxies:Traditional epoxy adhesives cure through a chemical reaction between the resin and hardener. On the other hand, UV-curable epoxies cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This allows for faster curing times and reduced energy consumption.
5.Flexible and Tough Epoxies:Developing epoxy adhesives with improved flexibility and toughness while maintaining high bonding strength is an active research area. This is especially important for applications where the bonded materials experience dynamic stress or impact.
6.Smart Epoxiesare epoxy adhesives that respond to environmental changes or external stimuli. For example, intelligent epoxy adhesives could change color when exposed to specific conditions, providing visual cues for quality control.
7.Improved Bonding to Challenging Substrates:Researchers are working to develop epoxy adhesives that can effectively bond to substrates that are traditionally difficult to adhere to, such as plastics, composites, and low-energy surfaces.
8.Adhesives for Electronics:Epoxy adhesives are widely used in assembly and packaging. Ongoing research aims to develop adhesives that offer excellent electrical conductivity, thermal management, and durability for bonding electronic components.
9.Biocompatible Epoxies:In medical and healthcare applications, there is a need for epoxy adhesives that are biocompatible and safe for use in contact with living tissues. Developing such bonds can enable advancements in medical devices and implantable technologies.
10.Advanced Curing Techniques:Researchers are exploring innovative curing methods, such as microwave curing, induction heating, and pressure-assisted curing, to improve the efficiency and performance of epoxy adhesives.
These innovations highlight the diverse applications and challenges that epoxy adhesives are being developed for. It’s essential to consult recent literature and industry sources for the latest information on epoxy adhesive glue development and advancements.
How Does Epoxy Adhesive Glue Align with Circular Economy Principles?
Epoxy adhesive glue can align with circular economy principles in several ways. However, it’s important to note that the extent of alignment can vary based on product design, usage, and disposal factors. The circular economy is an economic model focused on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency throughout a product’s lifecycle. Here’s how epoxy adhesive glue can align with these principles:
- Resource Efficiency and Longevity: Epoxy adhesive glue is known for its strong bonding properties, which can extend the lifespan of products. By effectively repairing and bonding materials, epoxy glue can help extend the useful life of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving resources.
- Repairability: Epoxy adhesive glue can be used to repair various materials, including plastics, metals, and wood. By enabling repairs, the glue contributes to the circular economy by reducing the demand for new products and minimizing waste. This aligns with the circular economy principle of promoting repair and maintenance over disposal.
- Modularity and Design for Disassembly: If products are designed to be easily disassembled and repaired, the epoxy adhesive can aid in this process. Repairs and component replacements become more feasible when modular products can be removed without significant damage. This reduces the overall waste generated and contributes to a more circular system.
- Reduced Waste: By allowing for repairs, epoxy adhesive glue can help reduce the amount of waste generated from discarded products. Broken items that might otherwise be thrown away can be fixed and put back into use, thereby minimizing the environmental impact of disposal.
- End-of-Life Considerations: While epoxy adhesive glue can prolong product life, it’s essential to consider its impact on recyclability and degradation. Some epoxy adhesives can make recycling more difficult due to the strong bonds they create. Manufacturers and designers must carefully consider the adhesive type used and its potential impact on the product’s recyclability.
- Material Compatibility: Epoxy adhesive glue can bond various materials, including dissimilar ones. This can enable the repurposing of materials that might otherwise be considered waste. For example, combining different epoxy materials can create innovative products, minimizing the need for virgin resources.
- Localized Production and Consumption: Epoxy adhesive glue is widely available and can be used in various industrial and domestic applications. Its accessibility encourages localized repair and production, which can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and distribution.
However, it’s essential to be mindful of potential downsides. Some epoxy adhesives may contain hazardous chemicals, and the environmental impact of their production and disposal should be considered. If not used and disposed of properly, epoxy residues could contaminate recycling streams.
What Environmental Regulations Support the Use of Epoxy Adhesive Glue?
The environmental regulations that support the use of epoxy adhesive glue can vary depending on the jurisdiction, application, and specific formulation of the adhesive. Some general ecological rules that might be relevant to the use of epoxy adhesive glue include:
- VOC Regulations: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are chemicals that can contribute to air pollution and have potential health and environmental impacts. Many environmental regulations, especially air quality, restrict the VOC content in adhesive products, including epoxy adhesives. Low-VOC or zero-VOC epoxy adhesives are likely to comply with these regulations.
- REACH: The European Union’s Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation aims to ensure the safe use of chemicals while protecting human health and the environment. Epoxy adhesive manufacturers and users must comply with REACH requirements by registering substances, using authorized chemicals, and following applicable restrictions.
- RoHS: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive restricts using certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products. While RoHS primarily applies to electronics, it might influence the choice of epoxy adhesives to assemble electronic components.
- Waste Disposal Regulations: The disposal of waste materials, including epoxy adhesives and related containers, is subject to waste disposal regulations. Epoxy adhesive waste might be classified as hazardous waste depending on its composition. Proper disposal methods need to be followed to prevent environmental contamination.
- Product Labeling and Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Many environmental regulations require manufacturers to provide accurate labeling and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for their products. This includes information about the product’s composition, handling procedures, potential hazards, and disposal instructions.
- Water Pollution Regulations: Epoxy adhesive residues and waste might contain chemicals that could harm aquatic ecosystems. Regulations related to wastewater discharge and releasing hazardous substances into water bodies might apply.
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations: While not exclusively environmental, occupational health and safety regulations often have ecological implications. Proper handling and use of epoxy adhesives, including personal protective equipment and ventilation, might be required to ensure worker safety and prevent environmental exposure.
It’s important to note that regulations can change over time and vary by region, so it’s crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest local, national, and international rules that apply to the use of epoxy adhesive glues in your specific context. Additionally, the particular formulation and intended use of the epoxy adhesive can impact which regulations are most relevant. Always consult with regulatory authorities or experts in the field to ensure compliance.
How Does the Cost of Epoxy Adhesive Glue Compare to Traditional Joining Techniques?
The cost of epoxy adhesive glue compared to traditional joining techniques can vary based on several factors, including the specific application, the materials being joined, labor costs, and the scale of the project. Here’s a general overview of how the cost of epoxy adhesive glue compares to traditional joining techniques:
Epoxy Adhesive Glue:
- Material Cost:Epoxy adhesive glues can vary in cost depending on the brand, quality, and specific formulation. Generally, high-quality epoxy adhesives tend to be more expensive.
- Labor Cost:Using epoxy adhesive glue typically requires less skilled labor compared to some traditional joining techniques, which can reduce labor costs. However, the surface preparation, application, and curing processes must be followed correctly for optimal results.
- Equipment Cost:The equipment required for epoxy adhesive glue is often minimal. You might need tools for mixing and applying the adhesive, but these are generally affordable.
- Speed of Application:Epoxy adhesives can often provide quicker bonding times than traditional welding or soldering methods. This can lead to time savings in production.
Traditional Joining Techniques (Welding, Soldering, etc.):
- Material Cost:Traditional joining techniques may require consumable materials such as welding rods or solder, contributing to material costs. The cost of these materials can vary depending on the type of joint and the materials being joined.
- Labor Cost:Skilled labor is often required for traditional joining techniques like welding or soldering, which can lead to higher labor costs. Welding may necessitate trained and certified welders.
- Equipment Cost:Traditional joining techniques often require specialized equipment such as welding machines, torches, soldering irons, and safety gear. These equipment costs can be significant, especially for large-scale operations.
- Speed of Application:Traditional joining techniques can sometimes be slower than epoxy adhesives, especially if complex joints or multiple steps are involved.
Considerations:
- For small-scale projects or applications where precision and minimal heat impact are essential, epoxy adhesive glues might be a more cost-effective choice.
- In high-production environments, epoxy adhesive glues speed up assembly processes, potentially offsetting the slightly higher material cost.
- Traditional joining techniques might be preferred when extreme strength and durability are required, as they can provide stronger joints, particularly in metals.
- The type of materials being joined plays a crucial role. Some materials might not be suitable for specific joining techniques, making one option more viable.
Ultimately, the cost comparison between epoxy adhesive glue and traditional joining techniques will depend on the specific project’s requirements, including material properties, required strength, production volume, and available labor skills. Conducting a cost analysis considering all these variables before deciding is advisable.