UV Adhesive Glue
In modern materials science, fascinating innovations continue to emerge, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. One such marvel is using light-activated magic through UV adhesive glue, showcasing its extraordinary bonding wonders. This revolutionary adhesive has transformed industries, from electronics to medicine, offering myriad applications that were once thought impossible.
This article delves into the captivating world of UV adhesive glue, dissecting its properties, applications, and the science behind its remarkable bonding capabilities.
What is UV Adhesive Glue?
UV adhesive glue, also known as ultraviolet-curing or UV-curable adhesive, is an adhesive that cures and hardens rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is commonly used in applications where quick bonding and curing times are required, and traditional adhesives may need to be more effective.
Composition and Nature of UV Adhesive Glue: UV adhesive glue consists of several components that work together to achieve its adhesive properties and rapid curing:
- Monomers and Oligomers: These are the primary building blocks of the adhesive. Monomers are small molecules with reactive groups, while oligomers are larger molecules that help provide the adhesive with its desired properties. These molecules remain in a liquid state until exposed to UV light.
- Photoinitiators: These compounds initiate the curing process when exposed to UV light. They absorb UV radiation and then release energy that triggers monomers’ and oligomers’ polymerization (curing).
- Additives: Various additives may be included to modify the adhesive’s properties, such as flexibility, viscosity, and color.
- Stabilizers: Stabilizers are added to prevent premature adhesive curing before UV exposure.
How UV Adhesive Differs from Traditional Adhesives:
- Curing Mechanism: The curing mechanism is the most significant difference between UV adhesive glue and traditional adhesives. Conventional adhesives use evaporation, solvent-based drying, or chemical reactions to bond and cure. In contrast, UV adhesive glue cures almost instantly when exposed to UV light, making it suitable for rapid assembly processes.
- Speed: UV adhesive glue cures within seconds to minutes, compared to traditional adhesives, which may require hours or even days to cure fully. This rapid curing time can significantly increase productivity in manufacturing processes.
- Bond Strength: UV adhesive glues can provide strong and durable bonds, similar to many traditional adhesives. However, the bond strength can vary based on the specific formulation and the bonded materials.
- Substrate Compatibility: UV adhesive glue is suitable for connecting a wide range of substrates, including plastics, glass, metals, and ceramics. Traditional adhesives can also bond diverse materials, but UV adhesives’ ability to connect dissimilar materials efficiently is one of their advantages.
- Environmental Considerations: UV adhesive glue is often considered more environmentally friendly than some traditional solvent-based adhesives, as it produces minimal or no volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during curing. This can contribute to safer working conditions and reduced environmental impact.
- Applications: UV adhesive glue is commonly used in electronics, medical devices, optics, and automotive manufacturing, where precise bonding, quick curing, and high bond strength are crucial.
How Does UV Adhesive Work?
UV adhesive, also known as ultraviolet or UV-curable adhesive, cures, and forms bonds when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. It has become widely used in various industries due to its rapid curing time, strong bond formation, and versatility. The key to its functionality lies in the chemical reactions UV light exposure triggers.
1.UV Adhesive Composition: UV adhesives are typically composed of several key components:
Monomers: These are the primary building blocks of the adhesive. They are low molecular weight compounds that have reactive double bonds.
Oligomers: These are larger molecules composed of multiple monomers. They provide the adhesive with mechanical properties, such as flexibility and toughness.
Initiators: These are chemical compounds that are sensitive to UV light. When exposed to UV light, initiators release free radicals or cations, highly reactive species that initiate the curing process.
Stabilizers and Additives: These are included to enhance the performance and stability of the adhesive, such as improving adhesion to different substrates or preventing premature curing.
2.Curing Process and Bond Formation: The curing process of UV adhesive involves a series of chemical reactions initiated by UV light exposure:
Initiation: When UV light hits the adhesive, the initiators absorb the energy from the light and become activated. This activation leads to the release of free radicals or cations.
Propagation: The released free radicals or cations react with the monomers and oligomers in the adhesive, causing them to polymerize. Polymerization is forming long chains of molecules by reacting to reactive sites on the monomers.
Cross-Linking: The polymer chains link together as polymerization proceeds, creating a three-dimensional network structure. This cross-linked network is what gives the adhesive its strength and durability.
Curing Completion: The adhesive solidifies and hardens as the cross-linking continues. This process is relatively rapid, often taking only a few seconds to minutes, depending on the specific adhesive composition and the intensity of the UV light.
- Advantages of UV Adhesive:UV adhesive offers several advantages over traditional adhesive methods:
Rapid Curing: UV adhesives cure quickly, reducing production time and increasing efficiency.
Bond Strength: The cross-linked network formed during curing produces solid and durable bonds.
Minimal Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Since UV adhesives cure through chemical reactions initiated by UV light, there is less reliance on solvent evaporation, leading to lower VOC emissions.
Precise Application: UV adhesives can be precisely applied and controlled before curing, as the process only starts when exposed to UV light.
When Was UV Adhesive First Developed?
Tracing the origins of UV adhesive technology:
They were using ultraviolet (UV) light to initiate adhesive bonding dates back to the mid-20th century. However, the practical application of UV adhesives took time to develop. The earliest experiments with UV-curable materials began in the 1950s, driven by the desire for faster and more efficient bonding methods. Researchers explored photoinitiators – substances that generate free radicals when exposed to UV light – to initiate polymerization and create bonds.
Evolution and advancements over the years:
- 1950s – 1960s:Initial experiments with UV adhesives involved simple formulations, often based on acrylic monomers. These early adhesives had limited applicability due to their low strength and susceptibility to environmental factors.
- 1970s – 1980s:Researchers made significant progress in developing more robust UV adhesives by enhancing photoinitiators and optimizing monomer structures. These adhesives found use in applications such as glass bonding and jewelry assembly.
- 1990s:Advancements in photopolymerization technology led to the development of UV-curable adhesives with improved performance characteristics, including higher strength, better resistance to temperature and moisture, and broader compatibility with different substrates.
- 2000s:UV adhesives gained traction in electronics, especially in assembling electronic components and displays. The demand for miniaturization and delicate bonding led to the refinement of UV adhesive formulations to meet stringent requirements.
- 2010s:UV adhesive technology continued to evolve, with innovations in curing techniques, such as LED-based UV curing systems. This decade saw broader medical device assembly, automotive applications, and aerospace engineering adoption.
- Present and Future:In recent years, UV adhesive technology has witnessed breakthroughs in sustainability, biocompatibility, and tailor-made formulations for specific industries. Advancements in curing speed, cure depth, and control mechanisms further expand the potential applications of UV adhesives.
The evolution of UV adhesive technology highlights a fascinating journey from its humble beginnings to its current status as a versatile and indispensable bonding solution across various sectors. Ongoing research and development promise even more exciting possibilities in the years to come as UV adhesives continue redefining how we bond materials.
Where is UV Adhesive Commonly Used?
UV adhesive, also known as ultraviolet-curing adhesive, is a type of adhesive that cures or solidifies when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This unique property makes it suitable for various applications across different industries due to its rapid curing process, strong bonding capabilities, and ability to adhere to various substrates. Here are some common uses of UV adhesive across sectors:
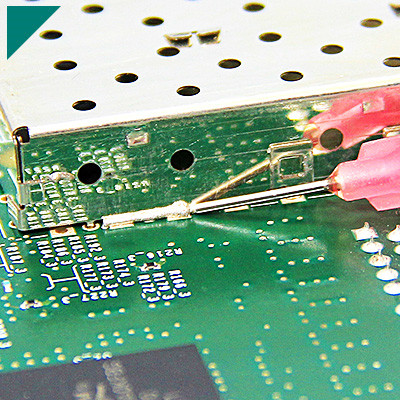
- Electronics: UV adhesives are widely used in electronics for bonding and sealing components. They are used to assemble microchips, semiconductor devices, and printed circuit boards (PCBs). Their ability to cure quickly with UV light allows for efficient production processes and the creation of compact electronic devices.
- Medical Devices: UV adhesives play a crucial role in the assembly and bonding of medical devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, syringes, and hearing aids. These adhesives are often biocompatible and can withstand sterilization, making them suitable for medical applications.
- Automotive: UV adhesives are used in the automotive industry for bonding and sealing applications. They assemble interior components, such as dashboard panels and touchscreen displays. Additionally, they are used for bonding exterior features like glass panels and tail lights.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry benefits from UV adhesives for applications like bonding composite materials, attaching lightweight components, and sealing sensitive electronic systems. The quick curing time of UV adhesives is advantageous in aerospace manufacturing processes.
- Optics and Photonics: UV adhesives assemble optical lenses, fibers, and other components in photonics devices. Their ability to form clear and transparent bonds is essential for maintaining optical clarity.
- Jewelry and Watchmaking: UV adhesives create jewelry and watches to bond precious stones, crystals, and delicate components securely. The precise application and rapid curing of UV adhesives are beneficial for intricate designs.
- Consumer Electronics: UV adhesives assemble various consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. Their ability to bond different materials and cure quickly supports the production of slim and lightweight devices.
- Packaging: In the packaging industry, UV adhesives are used for sealing cartons, boxes, and other packaging materials. They provide solid bonds and help ensure product integrity during transportation and storage.
- Woodworking and Furniture: UV adhesives are used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing for bonding veneers, laminates, and decorative elements. Their quick curing time enables efficient production processes.
- Art and Crafts: UV adhesives are popular in arts and crafts for bonding various materials, such as glass, ceramics, and plastics. Their precision and speed make them suitable for intricate projects.
Overall, UV adhesives find application in industries that require fast curing, strong bonding, and the ability to work with intricate designs. Their versatility and effectiveness have made them essential in modern manufacturing processes across various sectors.
Why Choose UV Adhesive Over Other Bonding Methods?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesive is a type of adhesive that cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light. Its unique advantages have gained popularity over other bonding methods for various applications. Here’s a comparison of UV adhesive with traditional bonding methods like soldering and mechanical fastening:
Advantages of UV Adhesive:
- Rapid Curing:UV adhesive cures almost instantly when exposed to UV light. This significantly reduces production time, making it ideal for high-speed manufacturing processes. In contrast, traditional adhesive methods like epoxy or cyanoacrylate may take much longer to cure.
- Strong Bonds:UV adhesive forms solid and durable bonds on various substrates, including plastics, glass, metals, and ceramics. The adhesive’s chemical composition allows for excellent adhesion properties, resulting in robust bonds that can withstand various stresses.
- Minimal Thermal Impact:UV adhesive curing is a low-temperature process, as it doesn’t require elevated temperatures for bonding. This is particularly beneficial for sensitive components or substrates that heat could damage, unlike soldering, which involves high temperatures that can affect the materials being joined.
- Versatility:UV adhesive can be used in various applications, from electronics and medical devices to automotive and aerospace industries. Its ability to bond dissimilar materials makes it versatile for many scenarios.
- Precision and Control:UV adhesive application offers precise control over the amount of adhesive applied, minimizing waste and ensuring consistent results. The adhesive can be dispensed in small amounts with high accuracy, making it suitable for intricate designs and micro-scale bonding.
Comparison with Traditional Bonding Methods:
- Soldering:
- Soldering involves melting a filler metal to create a bond between two surfaces. It’s commonly used for electrical connections.
- Requires high temperatures, which can potentially damage sensitive components or substrates.
- Joint flexibility can be limited due to the rigid nature of solder.
- UV adhesive doesn’t require high temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal damage.
- UV adhesive can bond dissimilar materials more effectively.
- Mechanical Fastening:
- Mechanical fastening methods include screws, bolts, rivets, and other physical connectors.
- It creates a visible joint and may require post-processing to achieve the desired aesthetic.
- Mechanical fasteners can weaken the joined materials due to drilling or hole creation.
- UV adhesive creates a seamless, aesthetically pleasing bond without needing visible connectors.
- UV adhesive doesn’t compromise material integrity through drilling or hole creation.
How is UV Adhesive Applied?
UV adhesive, or ultraviolet-curing adhesive, is an adhesive that cures or hardens when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is commonly used in electronics, medical devices, optics, and automotive industries for bonding and assembly applications. Applying UV adhesive involves carefully considering dispensing techniques and ensuring precise application for the best results.
Dispensing Techniques: Manual vs. Automated
UV adhesive can be applied using both manual and automated dispensing techniques, each with its advantages and considerations:
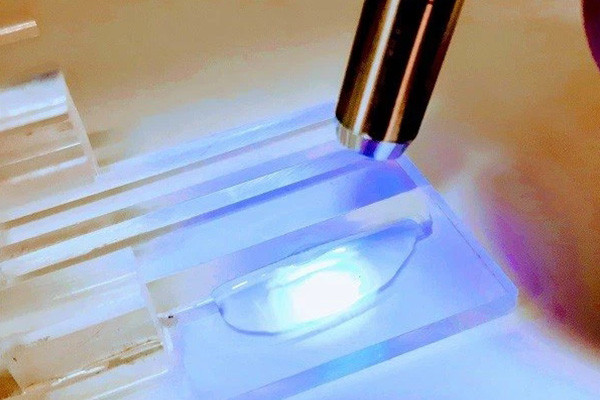
- Manual Dispensing:In manual dispensing, an operator controls the application of the adhesive using handheld dispensing tools. This technique is suitable for smaller-scale applications and projects that do not require high levels of precision or consistency. Manual dispensing provides more flexibility and is often used when the adhesive needs to be applied to irregular or complex shapes.
- However, manual dispensing can be less accurate and consistent than automated methods. It’s also more dependent on the skill and experience of the operator, which can lead to variations in adhesive thickness and coverage.
- Automated Dispensing:Automated dispensing involves using specialized equipment that precisely controls the application of UV adhesive. This technique is beneficial for large-scale production and applications requiring high accuracy, repeatability, and consistency. Automated systems can ensure uniform adhesive distribution and controlled curing conditions, leading to more reliable and consistent bonding.
- Automated dispensing systems include robotic arms, dispensing robots, and conveyor-based systems. These systems can be programmed to apply the adhesive in specific patterns, quantities, and locations, improving quality control.
Ensuring Precise Application for Optimal Results
To ensure the precise application of UV adhesive for optimal results, consider the following factors:
- Substrate Preparation:Proper cleaning and preparation of the substrates are crucial for achieving solid and durable bonds. Any contaminants, oils, or residues on the surfaces can hinder adhesive performance.
- Adhesive Viscosity:The viscosity of the UV adhesive should be chosen based on the application method and the desired bond line thickness. Different dispensing techniques require adhesives with varying viscosities to achieve consistent results.
- Dispensing Parameters:Accurate programming of dispensing parameters is essential for automated dispensing. This includes controlling dispensing speed, flow rate, path, and curing time. These parameters should be optimized for the specific adhesive and substrates being used.
- Curing Conditions:UV adhesive requires exposure to UV light to cure. Ensure that the UV light source is appropriate for the adhesive and provides uniform and sufficient curing energy. Monitoring and controlling the curing process is essential to achieve full adhesive strength and durability.
- Quality Control:Implement measures to monitor the application process and ensure consistent results. This can involve regular adhesive volume, coverage, and bond strength checks.
- Training and Maintenance:For manual and automated dispensing, proper training of operators and regular maintenance of equipment are essential to achieve reliable results over time.
What Types of Materials Can UV Adhesive Bond?
UV adhesives, or ultraviolet or light-curing adhesives, are adhesives that cure and harden when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. These adhesives are versatile and can bond a wide range of materials, including:
- Glass: UV adhesives are commonly used for bonding glass due to their transparency and ability to create strong, optically clear bonds. They are used in electronics, optics, and medical devices.
- Plastics: UV adhesives can bond various plastics, including acrylics, polycarbonates, PVC, PET, and more. These adhesives are ideal for applications where traditional solvent-based adhesives might damage or deform the plastic substrates.
- Metals: UV adhesives can bond metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and various alloys. They provide a clean and reliable bonding solution for automotive, electronics, and aerospace metal components.
- Ceramics: UV adhesives can bond ceramics, providing excellent adhesion and creating solid and durable bonds between ceramic components. This is particularly useful in industries like electronics and advanced manufacturing.
- Wood: While less common, UV adhesives can also bond wood materials. However, they might not be the primary choice for wood bonding due to the availability of other adhesive types that work better with wood.
- Composite Materials: UV adhesives can bond composite materials used in aerospace industries where lightweight and robust materials are critical.
- Rubber and Elastomers: Some UV adhesives are formulated to bond rubber and elastomeric materials, allowing for flexible yet strong bonds.
- Fabric and Textiles: UV adhesives can also bond materials and textiles in applications such as textiles for medical devices or apparel.
- Paper and Cardboard: UV adhesives can be used for bonding paper and cardboard in packaging applications where fast curing and strong bonds are required.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of UV adhesive bonding can depend on various factors, including the specific formulation of the adhesive, the properties of the substrates, surface preparation, and the intensity of the UV light source. For optimal results, choosing a UV adhesive formulation tailored to the specific material interaction you’re working with is recommended. This might involve selecting an adhesive with the proper viscosity, flexibility, and compatibility for your application.
How Strong are UV Adhesive Bonds?
The strength of UV adhesive bonds depends on several factors, including the type of adhesive, the materials being bonded, the surface preparation, curing conditions, and the application-specific requirements. UV adhesives, or ultraviolet-curing adhesives, are adhesive that cure or harden when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. They commonly bond various materials, including glass, plastics, metals, and ceramics. UV adhesive bonds can exhibit good strength, but it’s essential to consider the specific conditions and testing methods when evaluating their strength.
- Tensile Strength:Tensile strength refers to the resistance of a material to being pulled apart along its length. UV adhesive bonds can have reasonably high tensile strength, but the exact value varies based on factors like the adhesive’s formulation, the bonding surfaces’ preparation, and the curing conditions. Tensile testing involves applying a force in opposite directions to the bonded materials until the bond breaks. The maximum force applied during this test measures the tensile strength of the bond.
- Shear Strength:Shear strength refers to the resistance of a material to being cut or sliced along a plane parallel to the bonded surfaces. Shear testing involves applying a force parallel to the adhesive bond, causing one material to slide against the other until the bond fails. UV adhesive bonds can also exhibit good shear strength, and similar to tensile strength, it depends on the same factors.
Real-world stress and durability tests involve subjecting bonded assemblies to conditions that simulate the intended use or environment. Some standard tests include:
- Aging and Environmental Tests:UV adhesive bonds can be tested under different environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity variations, chemical exposure, and UV radiation. These tests evaluate how well the adhesive bond maintains its strength and integrity over time.
- Impact and Shock Tests:Adhesive bonds are often subjected to impact and shock during use. Testing involves dropping or impacting the bonded materials to simulate real-world scenarios. The strength of the bond is assessed based on how well it withstands these forces without failing.
- Fatigue Tests:Real-world applications often involve repeated loading and unloading cycles. Fatigue tests involve subjecting adhesive bonds to cyclic loading to determine how well they endure repetitive stress without deteriorating.
- Peel Tests:For flexible materials or those bonded at an angle, peel tests measure the force required to peel the related materials apart. This is particularly important for applications where the materials experience bending or flexing.
- Adhesion Tests:These tests assess the bond between the adhesive and the substrate by trying to separate them. Adhesion tests help determine whether the bond failure occurs within the adhesive itself or at the adhesive-substrate interface.
It’s important to note that the strength of UV adhesive bonds can vary widely depending on the specific adhesive formulation, the bonded substrates, and the testing conditions. When using UV adhesive in practical applications, following the manufacturer’s guidelines for surface preparation, curing conditions, and any recommended testing procedures is recommended to ensure optimal bond strength and durability.
When are UV Adhesive Bonds Preferred?
UV adhesive bonds are preferred due to their unique properties and advantages. Some of the specific scenarios where UV adhesive bonds are favored include:
- Fast Curing Time: UV adhesives cure rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light. This quick curing time is especially beneficial for high-volume production processes where efficiency and speed are crucial.
- Delicate Substrates: UV adhesives are often used for bonding delicate or sensitive substrates that might be damaged by the heat generated during traditional curing methods. Since UV curing is a relatively low-temperature process, it is well-suited for heat-exposure materials.
- Small Bonding Areas: UV adhesives work well for applications involving small bonding areas or intricate designs, as the adhesive can be precisely applied and cured with UV light. This level of precision is often challenging to achieve with other adhesive methods.
- Flexibility and Vibration Resistance: As you mentioned, UV adhesive bonds are preferred when flexibility and vibration resistance are crucial. These adhesives can maintain their bond strength even in environments with dynamic movement or vibrations, making them suitable for applications like bonding components in electronic devices or automotive parts.
- Clear Bonds: UV adhesives can create transparent and optically clear bonds, making them ideal for applications with essential aesthetics or visibility. This includes bonding glass, plastic, and other fine materials.
- Chemical Resistance: UV adhesives can be formulated to offer resistance to various chemicals, which is essential in industries where exposure to corrosive substances is every day.
- Environmental Friendliness: UV adhesives often have low or no volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and produce minimal waste. This aligns with the growing emphasis on environmentally friendly adhesive options.
- Consistency and Reliability: UV curing provides consistent and reliable results since the curing process is initiated and completed rapidly, reducing the chances of variations in bond strength.
- Stringent Regulatory Requirements: UV adhesives are suitable for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as the medical and pharmaceutical sectors. They can be formulated to meet specific standards and offer biocompatibility and sterilization resistance.
- Delicate Electronics: UV adhesives are commonly used in electronics manufacturing for bonding small components and ensuring excellent electrical insulation properties.
- Low Heat Generation: UV curing generates minimal heat, making it suitable for heat-sensitive substrates like certain plastics or electronic components.
- Low Volatile Emissions: UV adhesives typically have lower emissions of volatile compounds than other adhesive types, contributing to a healthier work environment.
What Are the Challenges of Working with UV Adhesive?
Working with UV adhesive presents several challenges that must be carefully managed to ensure successful bonding and curing. Some of the challenges include:
- Sensitivity to Ambient Conditions:UV adhesives typically use ultraviolet light to cure and harden. However, they can be sensitive to variations in ambient conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and UV light intensity. Too much moisture can interfere with curing, and high temperatures might cause premature curing before proper alignment or positioning is achieved.
- UV Light Intensity and Penetration:UV adhesives require sufficient UV light intensity to cure correctly. The power of UV light decreases with distance, which can be challenging when bonding intricate or deep assemblies where light might only reach some areas uniformly. This can result in incomplete curing and weaker bonds.
- Substrate Compatibility:UV adhesives might not bond well with all substrates. Some materials, like certain plastics or metals, might not transmit UV light effectively or exhibit poor adhesion properties. Surface preparation and selection of appropriate adhesive formulations are crucial to ensure good bonding.
- Bonding Complex Shapes and Uneven Surfaces:Achieving a consistent bond line thickness can be challenging when dealing with complex shapes or uneven surfaces. Inadequate bond line thickness can lead to weak bonds, as UV light might not penetrate sufficiently through thicker areas.
- Alignment and Positioning:Since UV adhesives cure rapidly under UV light exposure, it’s essential to achieve accurate alignment and positioning of the components before fixing them. This can be incredibly challenging when bonding intricate or delicate parts.
- Shelf Life and Storage:UV adhesives can have a limited shelf life due to their sensitivity to UV light and other environmental factors. Proper storage conditions, such as calm and dark environments, are essential to maintain the adhesive’s performance over time.
- Health and Safety:UV adhesives emit UV light during curing, posing health risks to operators if not correctly managed. Adequate protective equipment, such as UV-blocking eyewear and appropriate clothing, must be worn when working with UV adhesives to prevent potential skin and eye damage.
- Curing Depth and Speed:UV light might not penetrate deeply into certain materials, limiting the adhesive’s ability to bond thick substrates or materials with opaque properties. Additionally, the rapid curing speed of UV adhesives can be both an advantage and a challenge, as it leaves little time for adjustments.
- Cost:UV adhesive technology and equipment can initially be more expensive to set up compared to traditional adhesive methods. UV light sources, curing equipment, and process controls all add to the cost of implementation.
- Quality Control:Monitoring and ensuring consistent curing across all bonded parts can be challenging. Variations in adhesive thickness, part positioning, and UV light intensity can lead to inconsistencies in the cured adhesive’s mechanical properties.
Despite these challenges, UV adhesives offer many advantages, such as rapid curing, minimal or no volatile emissions, and high bond strength. Successful implementation involves understanding these challenges and taking appropriate measures to address them during bonding.
How Does UV Adhesive Impact Manufacturing Processes?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesive is a type of adhesive that cures or hardens when exposed to ultraviolet light. Its impact on manufacturing processes can be significant, particularly in streamlining production lines and reducing the need for specialized equipment and curing times. Here’s how UV adhesive can impact manufacturing processes:
- Rapid Curing: One of the critical benefits of UV adhesive is its immediate curing process. When UV light is applied to the adhesive, it triggers a photochemical reaction that causes it to harden almost instantly. This quick curing time can significantly accelerate production processes, as components can bond and move to the next production stage without lengthy waiting times for the adhesive to set.
- Streamlined Production Lines: Because UV adhesive cures rapidly, it allows for faster assembly and bonding of components. This can lead to a more streamlined production line, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall efficiency. Manufacturers can produce more units quickly, increasing output and lowering production costs.
- Minimal Post-Processing: To ensure proper bonding and curing, traditional adhesives often require post-processing steps such as clamping, heat curing, or solvent evaporation. UV adhesive, on the other hand, eliminates or significantly reduces the need for these post-processing steps. This can simplify manufacturing processes and reduce the time and resources required for finishing, resulting in faster turnaround times.
- Reduced Equipment Needs: UV adhesive curing often requires specialized equipment, such as UV light sources, to emit the necessary wavelengths for curing. However, UV curing equipment can be more compact and versatile compared to traditional methods involving ovens, autoclaves, or other curing setups. This can save valuable floor space in the manufacturing facility and potentially reduce the need for large, energy-consuming curing equipment.
- Energy Efficiency: UV adhesive curing is energy-efficient compared to traditional curing methods requiring elevated temperatures. While UV curing systems consume electricity, the overall energy usage can still be lower than heating entire curing chambers. This can contribute to cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Reduced Work-in-Progress Inventory: Traditional adhesives require longer curing times, resulting in large amounts of work-in-progress inventory as components wait for the adhesive to set. With UV adhesive’s rapid curing, manufacturers can minimize the amount of work-in-progress inventory, leading to better inventory management and potentially lower storage costs.
- Enhanced Quality Control: UV adhesive’s quick curing allows for faster inspection and quality control of bonded components. Manufacturers can identify defects or issues earlier in the production process, enabling them to take corrective actions promptly. This can lead to higher-quality finished products and fewer defects.
When Does UV Adhesive Enhance Product Design?
UV adhesive, or ultraviolet-cured adhesive, is a type of adhesive that cures rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light. It has several properties that make it valuable for enhancing product design, particularly in the contexts you mentioned:
- Seamless, Borderless Displays in Consumer Electronics:UV adhesive can enhance product design in consumer electronics by enabling seamless and borderless displays. Traditional bonds may leave visible seams or borders between display components, which can detract from the device’s visual appeal and immersive experience. On the other hand, UV adhesive can create nearly invisible bonds between members, resulting in a sleek and continuous display surface. This enhances the aesthetics and functionality of smartphones, tablets, TVs, and monitors, providing users with a more visually pleasing and immersive viewing experience.
- Design Freedom and Aesthetics in Product Development:UV adhesive offers design engineers greater flexibility and creative freedom when designing products. This adhesive can bond various materials, including glass, plastic, metal, and ceramics. Its rapid curing process allows for precise assembly and bonding of intricate designs without clamps or fixtures. Designers can explore innovative shapes, sizes, and configurations, knowing UV adhesive can securely and seamlessly bond various materials. This leads to products with improved aesthetics, unique shapes, and enhanced visual appeal.
- Durability and Reliability:UV adhesive often provides excellent durability and reliability. Once cured, it forms a strong bond that can withstand various environmental factors such as temperature changes, moisture, and vibration. This durability is crucial for products exposed to everyday wear and tear, ensuring the design integrity is maintained over time.
- Reduced Visual Disturbances:UV adhesive can minimize visual disturbances in products by eliminating the need for visible mechanical fasteners like screws or clips. This contributes to a cleaner and more streamlined appearance. In applications such as automotive interiors, electronic displays, and glass structures, the absence of protruding fasteners enhances the overall visual experience.
- Optical Clarity:UV adhesive can offer exceptional optical clarity, making it ideal for applications that involve transparent materials, such as glass or plastic. This property is particularly relevant in products like touchscreens, optical lenses, and displays where maintaining high visual quality is essential for user interaction and viewing.
What Innovations Have UV Adhesives Enabled in Electronics?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesives, also known as UV-curing adhesives or UV-curable adhesives, have played a significant role in enabling various innovations in electronics. Here are a couple of key innovations that UV adhesives have helped:
- Thin and Flexible Wearable Devices:UV adhesives have been instrumental in developing thin, flexible, and lightweight wearable electronic devices. These adhesives can bond delicate electronic components, sensors, and flexible circuits onto various substrates such as fabrics, polymers, and elastomers. Their fast-curing properties and ability to connect dissimilar materials while maintaining flexibility make them ideal for assembling wearable devices without compromising their form factor or functionality.
- Bonding Sensitive Components without Heat Damage:Traditional adhesive bonding methods often involve the application of heat, which can be detrimental to sensitive electronic components. UV adhesives offer a cold bonding process, as they cure rapidly under UV light without needing elevated temperatures. This feature is particularly beneficial for bonding heat-sensitive components like microprocessors, sensors, and displays. By using UV adhesives, manufacturers can avoid heat-related damage and ensure the proper functioning of these components.
- Miniaturization of Electronics:UV adhesives enable precise and controlled bonding at a microscopic scale, making them essential for the miniaturization of electronic devices. As electronics shrink in size while maintaining or improving performance, UV adhesives can bond tiny components securely and interconnect within a confined space. This contributes to the development of smaller and more efficient electronic devices.
- Optical Bonding in Displays:UV adhesives are commonly used to assemble displays, such as LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) and OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes). These adhesives help bond various layers of the display stack, such as cover glass, touch sensors, and display panels. The ability of UV adhesives to cure quickly and create optically clear bonds is crucial for maintaining high-quality displays with minimal distortion or visual artifacts.
- Water and Moisture Resistance:Many UV adhesives resist water, moisture, and environmental factors. This makes them suitable for electronic devices that may be exposed to outdoor conditions or require protection against liquids. For instance, UV adhesives can seal and protect the internal components of outdoor sensors or ruggedized electronic devices.
How is UV Adhesive Utilized in Medicine?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesive is a type of adhesive that cures or solidifies when exposed to ultraviolet light. This adhesive has various applications in the medical field due to its unique properties and advantages. Here’s how UV adhesive is utilized in medicine:
- Medical Device Assembly:UV adhesive is used to assemble medical devices. These devices range from small, intricate components to larger, more complex systems. The adhesive binds different parts, creating a strong and durable connection. The advantage of UV adhesive is that it cures quickly when exposed to UV light, allowing for efficient production processes.
- Biocompatibility:One of the most crucial aspects of using any material in medical applications is its biocompatibility, which means the material does not cause harmful reactions or side effects when in contact with living tissue. UV adhesives can be formulated to be biocompatible, making them safe for use in medical devices that come into direct or indirect contact with the human body.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:UV adhesive is handy in minimally invasive procedures. These medical procedures are performed through small incisions or natural body openings, reducing the need for large surgical incisions. UV adhesive can secure and seal incisions or wounds, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection.
- Faster Healing:UV adhesive can contribute to shorter healing times because it sometimes eliminates the need for traditional sutures or staples. Sutures and nails can cause tissue trauma and leave scars. UV adhesive provides a non-invasive alternative that securely holds tissues together while minimizing tissue damage, improving healing outcomes.
- Reduced Infection Risk:UV adhesive can help reduce the risk of infection. Traditional sutures and staples create openings in the skin that can serve as potential entry points for bacteria. UV adhesive forms a tight, sealed bond without leaving gaps, reducing the likelihood of infection.
- Enhanced Aesthetics:UV adhesive can improve aesthetic outcomes, especially in visible body areas. Because it forms a thin, evident bond, it is less noticeable than sutures or staples. This can be particularly important for cosmetic or plastic surgery procedures.
- Flexibility and Strength:UV adhesive offers a balance between flexibility and strength. It can be formulated to have suitable properties to suit different medical applications. For instance, it can be used in applications requiring flexibility and resistance to movement or tension.
- Customizable Formulations:UV adhesive can be formulated to meet specific medical requirements, such as sterilization methods, temperature resistance, and long-term stability. This flexibility allows medical professionals to select the adhesive that best suits their needs.
UV adhesive has found its place in the medical field by providing a reliable, efficient, and biocompatible solution for various applications, including medical device assembly, wound closure, and minimally invasive procedures. Its ability to promote faster healing, reduce infection risks, and enhance overall patient comfort makes it a valuable tool in modern medical practice.
When Does UV Adhesive Prove Valuable in Automotive Applications?
UV or ultraviolet adhesive proves valuable in various automotive applications due to its unique properties and advantages. It is particularly beneficial in bonding lightweight materials for fuel efficiency and improving vehicle aesthetics and safety. Here’s how UV adhesive is valuable in these specific automotive applications:
- Bonding Lightweight Materials for Fuel Efficiency:In the automotive industry, there is a constant drive to reduce vehicle weight to improve fuel efficiency and meet environmental standards. UV adhesive is significant in bonding lightweight materials such as composites, plastics, and metals. The adhesive cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, creating a solid and durable bond. This rapid curing process minimizes assembly time and allows for streamlined production processes.
- Lightweight materials are often used to construct vehicle components like interior panels, trims, and even structural components. Manufacturers can maintain structural integrity by using UV adhesive to bond these materials while reducing overall vehicle weight. This leads to improved fuel efficiency, as lighter vehicles require less energy. Moreover, UV adhesives’ ability to bond dissimilar materials can lead to innovative design options that enhance fuel efficiency.
- Improving Vehicle Aesthetics and Safety:UV adhesive is also valuable for enhancing the aesthetics and safety of vehicles. In terms of aesthetics, UV adhesive offers an evident, transparent bond that is practically invisible after curing. This makes it ideal for bonding glass, transparent plastics, and other materials used in windows, sunroofs, and interior displays. The seamless and discreet bonding enhances the overall visual appeal of the vehicle.
- From a safety standpoint, UV adhesive can bond components related to airbags, sensors, and other critical safety systems. The adhesive’s fast curing time ensures that these components are securely bonded, contributing to the vehicle’s overall structural integrity. Additionally, UV adhesive can be resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals, which are crucial for maintaining the safety and performance of various automotive components.
In both cases, UV adhesive offers advantages such as rapid curing, strong bonds, and compatibility with various materials. However, it’s important to note that UV adhesives may have limitations in terms of temperature resistance and load-bearing capabilities compared to traditional mechanical fastening methods or other types of bonds. Therefore, its use should be carefully considered based on the specific requirements of each automotive application.
What Role Does UV Adhesive Play in Aerospace Engineering?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesive plays a significant role in aerospace engineering, particularly in bonding critical components in aircraft and satellites and withstanding extreme conditions in outer space. Here’s how:
- Bonding Critical Components:Aerospace engineering involves assembling various components and materials to create complex structures such as aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft. UV adhesive is used as a bonding agent to join these components together. It offers a robust and reliable bond between materials like metals, composites, plastics, and glass, ensuring that different parts of an aerospace vehicle remain securely connected.
- Lightweight Bonding:Aerospace vehicles must be as light as possible to achieve optimal fuel efficiency and performance. UV adhesive is valued for its lightweight properties compared to traditional mechanical fastening methods, such as bolts and rivets. This adhesive minimizes the need for additional hardware, reducing the vehicle’s overall weight.
- Vibration Damping:Aerospace vehicles experience vibrations during takeoff, flight, and landing. UV adhesive helps dampen these vibrations by forming a flexible bond that can absorb and distribute the mechanical stresses generated during operation. This contributes to the structural integrity and longevity of the vehicle.
- Uniform Stress Distribution:UV adhesive can be applied in a thin, even layer across irregular or contoured surfaces. This uniform stress distribution helps to reduce stress concentrations, which can lead to material fatigue and failure over time. This is particularly important in aerospace engineering, where components are subjected to various loads and stressors.
- Hermetic Sealing:In outer space, aerospace components are exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations, vacuum conditions, and cosmic radiation. UV adhesive can create airtight seals, preventing the intrusion of moisture, gases, or contaminants that could compromise the functionality of sensitive electronic components.
- Resistance to Harsh Environments:UV adhesive formulations can be tailored to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, including high levels of UV radiation, thermal cycling, and chemical exposure. This resilience is crucial in aerospace applications where vehicles can encounter extreme heat from atmospheric reentry and cold temperatures in the vacuum of space.
- Rapid Curing:UV adhesive cures rapidly when exposed to UV light, allowing for efficient assembly processes in aerospace manufacturing. The quick curing time can lead to increased production rates and reduced downtime.
- Minimal Outgassing:Outgassing releases volatile compounds from materials when exposed to vacuum conditions. Some traditional adhesives can release gases that could interfere with sensitive equipment or optics. UV adhesive formulations can be chosen or designed to minimize outgassing and avoid potential contamination issues.
- Optical Clarity:UV adhesives can be transparent, making them suitable for applications involving optical components such as sensors, cameras, and lenses in aerospace vehicles. The adhesive’s optical clarity ensures that these components function effectively without distortion.
How Sustainable are UV Adhesives?
UV (Ultraviolet) adhesives are a type of adhesive that cures and bonds rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light. When evaluating the sustainability of UV adhesives, it’s essential to consider their environmental impacts throughout their lifecycle, including production, usage, and disposal. Here’s an overview of these considerations:

- Environmental Impacts:
- Raw Materials:The sustainability of UV adhesives largely depends on the raw materials used in their formulation. Some UV adhesives can be formulated with bio-based or renewable materials, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and potentially lowering their carbon footprint.
- Energy Consumption:The curing process of UV adhesives requires energy to generate UV light. However, compared to traditional adhesive curing methods that involve heat or chemical reactions, UV curing often consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases.
- Hazardous Substances:UV adhesives generally have low levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous chemicals. However, it’s crucial to review the specific formulation of the adhesive to ensure that it doesn’t contain any harmful or toxic substances that could be released during the curing process or over time.
- Disposal Considerations:
UV adhesives can offer benefits in terms of disposal:
- Reduced Waste:UV adhesives often result in less waste during curing compared to solvent-based adhesives. Since UV curing is a rapid process, there is less excess adhesive to clean up, reducing waste generation.
- No Solvent Emissions:Unlike solvent-based adhesives, UV adhesives don’t require solvents for curing. This eliminates releasing harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the environment.
- Recyclability:Some UV adhesives can be designed to be easily removable or reversible, making it easier to disassemble products for recycling at the end of their life cycle.
- Transitioning to Greener Formulations:
- Bio-Based and Renewable Ingredients:Manufacturers can focus on using bio-based and renewable materials in their adhesive formulations. These materials can help reduce the carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Eco-Friendly Curing Sources:Researchers are exploring using more sustainable curing sources, such as LED curing systems, which require less energy and have a longer lifespan than traditional mercury lamps.
- Life Cycle Assessment:Conducting a life cycle assessment (LCA) can help adhesive manufacturers identify environmental hotspots in their products’ lifecycle and make informed decisions for improvement.
When Might UV Adhesive Revolutionize Construction?
UV (ultraviolet) adhesive has the potential to revolutionize construction in several ways:
- Bonding Transparent Architectural Elements:UV adhesive is often used in connecting glass panels and other transparent architectural elements like skylights, glass facades, and windows. Traditional adhesives can leave visible marks or interfere with the aesthetics of these elements. UV adhesive, conversely, cures quickly and forms an evident, strong bond that is practically invisible. This enables architects and designers to create seamless and visually appealing structures emphasizing transparency and allowing natural light to flow freely.
- Enhancing Structural Integrity in Unconventional Designs:Unconventional or innovative architectural designs often require unconventional construction methods. UV adhesive can offer enhanced structural integrity in these cases. It can bond various materials like glass, metal, plastic, and some composites, allowing designers to experiment with new shapes, forms, and materials. This opens the door to unique and daring architectural designs that might have been challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional construction methods.
- Efficiency in Construction:UV adhesive cures rapidly when exposed to UV light. This fast curing time accelerates the construction process, reducing labor and construction time. When time is of the essence, such as urgent repairs or projects with tight deadlines, UV adhesive can be crucial in expediting construction without compromising quality.
- Reduced Need for Mechanical Fasteners:Traditional construction often relies on mechanical fasteners like screws, nails, and bolts. While these are effective, they can weaken the materials they penetrate and lead to potential points of failure. UV adhesive can eliminate the need for many mechanical fasteners, distributing stress more evenly across the bonded surfaces and potentially increasing overall structural integrity.
- Improved Energy Efficiency:UV adhesive can create airtight seals in windows and doors, enhancing energy efficiency by preventing drafts and heat loss. This can contribute to sustainable construction practices by reducing the energy consumption of buildings.
- Reduced Maintenance:Strong and durable UV adhesive bonds can contribute to lower maintenance requirements over time. When securely bonded with UV adhesive, materials are less likely to shift, separate, or develop vulnerabilities that require repair or replacement.
However, it’s important to note that while UV adhesive has significant potential benefits, its application in construction also comes with challenges. Proper surface preparation, UV light penetration, and long-term durability must be considered. Additionally, UV adhesive may not be suitable for all construction scenarios, and traditional methods will still have their place. As technology evolves, its adoption and impact on construction will become more apparent.
What Lies Ahead for UV Adhesive Technology?
UV adhesive technology has rapidly evolved, driven by technological advancements and the need for more efficient and versatile solutions. Several trends and developments are anticipated shortly:
- Formulation Advancements:
- Customization:UV adhesives will likely become more customizable to meet specific application requirements, including varying substrate materials, environmental conditions, and bonding strengths.
- High-Performance:The industry will likely focus on developing UV adhesives with improved mechanical properties, such as higher flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals, heat, and UV degradation.
- Sustainability:With increasing emphasis on eco-friendly solutions, UV adhesives may see developments in bio-based or biodegradable formulations, reducing their environmental impact.
- Curing Techniques:
- Faster Curing:Efforts will continue to improve the speed of curing processes. Advancements in UV LED technology and more efficient photoinitiators will contribute to shorter curing times, enhancing production efficiency.
- Depth of Cure:Innovations may address the challenge of achieving consistent curing depths, especially for thicker adhesive layers, enabling more reliable bonding across various applications.
- Applications:
- Electronics and Optoelectronics:UV adhesives will continue to play a crucial role in electronics manufacturing, particularly in assembling delicate components and devices such as microchips, displays, and sensors.
- Medical Devices:The medical industry will likely benefit from UV adhesives’ ability to bond dissimilar materials with minimal heat generation, making them suitable for applications like disposable medical devices and wound closure.
- Automotive:UV adhesives can be used for bonding glass, plastic, and metals in automotive assembly, promoting lightweight design and structural integrity.
- Packaging:UV-curable adhesives are well-suited for high-speed packaging applications, offering rapid cure times and strong bonds, potentially reducing production cycle times.
- Cross-Industry Collaborations:
- Material Suppliers:Collaboration between UV adhesive manufacturers and material suppliers (e.g., manufacturers of substrates, coatings, and additives) can lead to synergistic developments that optimize compatibility and performance.
- Equipment Manufacturers:Close partnerships with equipment manufacturers will drive the design of UV curing systems that accommodate emerging adhesive formulations and curing requirements.
- Research Institutions:Collaboration with research institutions can facilitate the exploration of novel photoinitiators, polymers, and curing techniques, fostering innovation in the field.
How Can Users Optimize UV Adhesive Bonding?
Optimizing UV adhesive bonding involves careful attention to surface preparation and UV light exposure. Here are some tips to help users achieve dependable bonds:
- Surface Preparation:
- Cleanliness:Ensure that the surfaces to be bonded are thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants like dust, grease, oils, and residues. Even small amounts of contaminants can hinder bonding.
- Degreasing:Use appropriate solvents to degrease surfaces. Isopropyl alcohol is commonly used for this purpose. Make sure the solvent is evaporated entirely before applying the adhesive.
- Surface Activation:Some substrates may benefit from surface activation methods like plasma treatment or corona discharge. These techniques improve adhesion by modifying the surface chemistry to promote better bonding.
- Surface Roughness:In some cases, slightly roughening the surface using techniques like sanding or abrasion can enhance adhesion by providing more surface area for the adhesive to grip onto.
- UV Light Exposure:
- Use the Right UV Source:Ensure you’re using a high-quality UV light source that emits the appropriate wavelength for curing your specific adhesive. Different adhesives require different UV wavelengths for adequate curing.
- Intensity and Duration:Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended intensity (measured in milliwatts per square centimeter) and duration of UV exposure. Excessive exposure may cause issues like over-curing, while insufficient exposure can lead to inadequate bonding.
- Uniform Exposure:Ensure UV light reaches all parts of the bonded area uniformly. Angles and shadows can cause uneven curing. Consider using reflective surfaces or rotating the assembly during curing to achieve uniform exposure.
- Adhesive Thickness:UV light penetration is limited, so consider the adhesive’s recommended maximum thickness. If the adhesive layer is too thick, the UV light might not reach the bottom layers effectively, leading to incomplete curing.
- Multiple Bonds:If you’re bonding multiple parts simultaneously, ensure enough space between them for the UV light to reach all the adhesive areas properly.
- Monitoring and Testing:
- Quality Control:Implement a quality control process to verify that bonds are adequately cured and meet the desired strength requirements. This can involve performing peel tests, shear tests, or other appropriate tests.
- Adhesive Compatibility:Ensure the UV adhesive is compatible with the materials you’re bonding. Some adhesives may not adhere to certain plastics, metals, or substrates.
- Adhesive Storage:Store the adhesive properly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Heat, humidity, or light exposure can degrade the adhesive’s performance.
By paying close attention to these factors and following the manufacturer’s guidelines, users can optimize UV adhesive bonding for dependable and robust bonds. Remember that different adhesives and materials might have specific requirements, so always refer to the adhesive manufacturer’s instructions for the best results.