Polyurethane Adhesive

Polyurethane adhesive is a remarkable and versatile bonding solution renowned for its strength and flexibility. As a vital component in various industries, from construction to manufacturing, this adhesive offers a unique combination of adhesive power and resilience, making it an invaluable choice for countless applications. With its ability to securely bond a wide range of materials while accommodating temperature, humidity, and stress fluctuations, polyurethane adhesive emerges as a cornerstone for durable and enduring connections in everyday and specialized contexts.
In this exploration, we delve into polyurethane adhesive’s diverse characteristics and applications, uncovering its pivotal role in joining materials with a strong and flexible embrace.
What Sets Polyurethane Adhesive Apart in Terms of Strength and Flexibility?
Polyurethane adhesive stands out in strength and flexibility due to its unique chemical composition and curing process. Here’s how it differs from other types of adhesives:
- Chemical Composition:Polyurethane adhesives are formulated from two main components: polyol and isocyanate. A chemical reaction occurs when these components are mixed, forming strong urethane linkages. This chemical structure contributes to the adhesive’s robust bonding capabilities.
- Strong Bonding:Polyurethane adhesives create a solid and durable bond on various substrates, including metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, and composites. The chemical reaction during curing results in a crosslinked network of molecules, enhancing adhesion and preventing the bond from weakening over time.
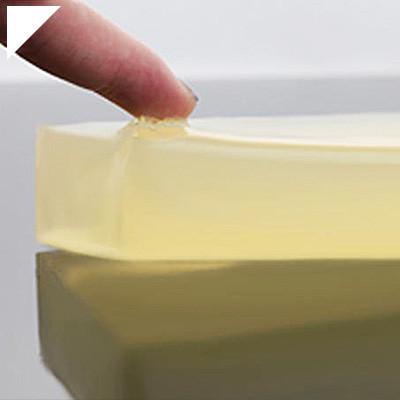
- Flexibility:One of the most significant advantages of polyurethane adhesives is their flexibility. The urethane linkages formed during curing have inherent elasticity, allowing the adhesive to absorb and distribute stress and movement without losing bond integrity. This flexibility makes polyurethane adhesives suitable for applications where materials are subjected to dynamic loads, vibrations, or thermal expansion and contraction.
- Toughness:The combination of strength and flexibility in polyurethane adhesives results in toughness. They can withstand impact and deformation without easily breaking or delaminating. This toughness is essential in applications where substrates are exposed to harsh conditions or mechanical stress.
- Resilience:Polyurethane adhesives exhibit excellent stability, meaning they can return to their original shape after deformation or stress. This property further contributes to their ability to maintain a strong bond even in dynamic environments.
- Water and Chemical Resistance:Polyurethane adhesives often possess good resistance to water, moisture, and a range of chemicals. This resistance is due to the crosslinked structure formed during curing, which helps prevent water and chemicals from penetrating the bond interface.
- Versatility:Polyurethane adhesives come in various formulations, allowing customization based on specific application requirements. Whether a high-strength bond, flexibility, or resistance to environmental factors is crucial, a polyurethane adhesive variant is likely suited to the task.
- Curing Mechanism:Unlike other adhesives that rely on solvent evaporation or moisture for curing, polyurethane adhesives cure through a chemical reaction, less affected by the surrounding environment. This enables them to be used in various conditions, including low-temperature environments.
The combination of solid bonding, flexibility, toughness, and chemical resistance makes polyurethane adhesive a preferred choice for applications ranging from automotive manufacturing and construction to electronics assembly and the marine industry, where strength and the ability to accommodate movement are essential.
How Does the Chemical Composition of Polyurethane Adhesive Contribute to its Bonding Qualities?
The bonding qualities of polyurethane adhesive are influenced by its chemical composition, which includes the types of ingredients used and their proportions. Polyurethane adhesives are versatile and can be tailored by adjusting their chemical makeup for different applications. Here’s how the chemical composition of polyurethane adhesive contributes to its bonding qualities:
- Polyol Components:Polyurethane adhesives typically consist of two main components: polyols and isocyanates. Polyols are the base materials that react with isocyanates to form the adhesive. The choice of polyols affects the adhesive’s flexibility, toughness, and viscosity. Different types of polyols can be used, such as polyester, polyether, or polycarbonate polyols, each imparting specific characteristics to the adhesive.
- Isocyanate Components:Isocyanates are reactive compounds that react with polyols to form a polyurethane network. The type of isocyanate used can influence the adhesive’s mechanical properties, adhesion strength, and curing speed. Typical isocyanates include toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). Isocyanates also contribute to the adhesive’s chemical resistance and durability.
- Crosslinking and Curing:The reaction between polyols and isocyanates leads to the formation of crosslinks, which are chemical bonds that connect the polymer chains. The degree of crosslinking affects the adhesive’s strength and resilience. Balancing the crosslink density is crucial to achieving the desired bond strength and flexibility.
- Additives:Various additives are often incorporated into polyurethane adhesives to enhance specific properties. For instance, plasticizers can be added to increase flexibility, fillers can improve viscosity and thixotropy (ability to flow under stress), and stabilizers can extend the adhesive’s shelf life. Flame retardants, UV stabilizers, and colorants are other examples of additives that might be used.
- Molecular Weight:The molecular weight of the polyol components can influence the adhesive’s viscosity and bond strength. Higher molecular weight polyols can result in more viscous adhesives with higher bond strengths, while lower molecular weight polyols may lead to more flexible adhesives.
- Ratio and Compatibility:The correct balance of polyols to isocyanates is critical for proper curing and optimal bonding. Incompatibility between the polyol and isocyanate components can result in poor bond formation or reduced adhesive performance.
- Curing Mechanisms:Polyurethane adhesives can cure through various mechanisms, such as moisture curing or two-component mixing. The curing mechanism can impact the adhesive’s adhesion to different substrates and the speed of bond formation.
- Substrate Compatibility:The chemical composition of the adhesive should be compatible with the substrates being bonded. Adhesion can be improved by tailoring the adhesive’s properties to match the substrate’s surface energy and chemical composition.
What Types of Materials Can Polyurethane Adhesive Effectively Bond Together?
Polyurethane adhesive is versatile and can effectively bond a wide range of materials together. Some of the materials that polyurethane adhesive can bond together include:
- Wood: Polyurethane adhesive is commonly used for woodworking applications, as it forms strong bonds with various types of wood, including hardwoods and softwoods.
- Metal: It can bond metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, making it useful for metalworking and construction applications.
- Plastics: Polyurethane adhesive can bond many types of plastics, such as PVC, ABS, polycarbonate, and more.
- Rubber: It can bond rubber materials, making it suitable for applications involving rubber components.
- Glass: Polyurethane adhesive can bond glass to various surfaces, although it’s important to note that the bond strength might vary depending on the specific types of glass and surfaces involved.
- Ceramics: It can be used to bond ceramics and ceramic-coated materials.
- Foam: Polyurethane adhesive can bond foam materials, useful in the upholstery and furniture manufacturing industries.
- Fabrics and Textiles: It can bond fabric and textile materials, making it useful for clothing manufacturing and upholstery applications.
- Concrete and Masonry: Polyurethane adhesive can bond to concrete and masonry surfaces, which is valuable in construction and repair projects.
- Composite Materials: It can bond various composite materials used in aerospace and automotive manufacturing industries.
- Leather: Polyurethane adhesive can bond leather materials, making it suitable for footwear and leather goods industries.
- Cork: It can bond cork materials, which is helpful for various applications, including crafts and industrial uses.
Polyurethane adhesives often provide strong and durable bonds, and they can be used in different industries for structural and non-structural applications. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of the bond can be influenced by factors such as the specific formulation of the adhesive, the surface preparation, and the application method. They follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and perform proper testing when using polyurethane adhesive for particular materials and applications.
How Does Polyurethane Adhesive Adapt to Different Environmental Conditions?
Polyurethane adhesive is known for its versatility and ability to adapt to various environmental conditions. Its adaptability is attributed to its unique chemical structure and composition, allowing it to undergo different reactions depending on the surrounding environment. Here’s how polyurethane adhesive adapts to other environmental conditions:
- Temperature Variation:Polyurethane adhesives can withstand a wide range of high and low temperatures. At lower temperatures, the adhesive may become more dense and rigid, but it doesn’t lose its adhesive properties. At higher temperatures, it remains pliable and maintains its bonding strength, although highly high temperatures might cause some degradation over time.
- Moisture and Humidity:Polyurethane adhesives are moisture-curing, which means they react with atmospheric water to undergo a curing process. This makes them well-suited for use in humid environments. The presence of moisture triggers the crosslinking of the adhesive, leading to the formation of strong bonds.
- Substrate Variability:Polyurethane adhesives can bond well to various substrates, including metals, plastics, wood, concrete, and more. The adhesive forms a strong bond by penetrating the substrate’s surface irregularities and chemically reacting with certain materials, such as hydroxyl groups, on surfaces like wood.
- Chemical Resistance:Depending on the specific formulation, polyurethane adhesives can exhibit varying resistance to chemicals, solvents, and oils. This makes them suitable for applications where exposure to different chemicals is likely.
- Flexibility and Elasticity:Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility and elasticity. They can absorb vibrations, movements, and stress without losing their adhesive properties or causing the bond to fail. This property is precious in applications where materials are subjected to dynamic forces or thermal expansion and contraction.
- UV Resistance:Some polyurethane adhesives are formulated to be UV-resistant, making them suitable for outdoor applications where sunlight is exposed. UV resistance prevents the adhesive from degrading, yellowing, or becoming brittle over time due to UV exposure.
- Outdoor and Harsh Environments:Polyurethane adhesives are commonly used in outdoor and harsh environments due to their ability to withstand weathering, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to moisture without compromising their adhesive strength.
- Curing Time:The curing time of polyurethane adhesives can be adjusted by altering their formulation. Some polyurethane adhesives cure quickly, while others have longer curing times. This adaptability allows for flexibility in application processes.
- Expansion and Contraction:Polyurethane adhesives exhibit good adhesion even when materials bond to undergo thermal expansion and contraction. This adaptability is crucial in preventing the bond from weakening or breaking due to temperature changes.
What Industries Benefit Most from the Strength and Flexibility of Polyurethane Adhesive?
Polyurethane adhesives are known for their strength, flexibility, and versatility, making them suitable for various industries and applications. Some of the sectors that benefit the most from the properties of polyurethane adhesives include:
- Automotive and Aerospace: Polyurethane adhesives bond various components within vehicles and aircraft. They provide excellent adhesion to different substrates, withstand vibrations and thermal fluctuations, and contribute to structural integrity.
- Construction and Building: Polyurethane adhesives are used for bonding materials like concrete, wood, metals, and plastics. They offer strong adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and weather conditions, making them suitable for panel bonding, flooring installation, and insulation applications.
- Footwear and Textiles: The flexibility and durability of polyurethane adhesives make them popular in the footwear industry for bonding shoe components, such as soles, uppers, and insoles. They can also be used in textiles for laminating fabrics or creating waterproof and weather-resistant garments.
- Furniture and Woodworking: Polyurethane adhesives are used for joining wood, laminates, and other materials in furniture manufacturing. Their ability to provide solid bonds and flexibility is precious for products that may experience stress and movement.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Polyurethane adhesives are water-resistant and can withstand the challenges of marine environments. They bond various materials in shipbuilding, such as fiberglass, metals, and composites.
- Electronics and Appliances: Polyurethane adhesives are used in electronics for bonding components and securing wires. Their flexibility helps absorb vibrations and shocks, protecting delicate electronics from damage.
- Packaging and Labeling: Polyurethane adhesives are used in packaging for bonding materials like plastic, paper, and metal. They provide secure seals and can also be used in labels and decals.
- Medical and Healthcare: In the medical field, polyurethane adhesives can be used for bonding medical devices, fabricating wound dressings, and even in specific surgical applications due to their biocompatibility and flexibility.
- Sports and Outdoor Equipment: The strength and flexibility of polyurethane adhesives are valuable in manufacturing sports equipment like skis, snowboards, kayaks, and other outdoor gear that require a balance of durability and performance.
- Renewable Energy: Polyurethane adhesives are used in the renewable energy sector for bonding solar panels, wind turbine blades, and other equipment components. Their resistance to environmental factors is crucial in such applications.
It’s important to note that while polyurethane adhesives offer many advantages, the choice of glue should be based on specific application requirements and compatibility with the bonded materials. Additionally, safety considerations and proper application techniques are essential to achieve the desired results in each industry.
Can Polyurethane Adhesive Be Used for Structural Bonding Applications?
Yes, polyurethane adhesive can be used for structural bonding applications in various industries. Polyurethane adhesives are known for providing strong and durable bonds between different materials, making them suitable for joining structural components that require load-bearing capabilities. Here are some reasons why polyurethane adhesives can be used for structural bonding:
- Strength and Durability: Polyurethane adhesives offer high bond strength, making them suitable for applications where structural integrity is essential. They can withstand significant stress, tension, and shear forces.
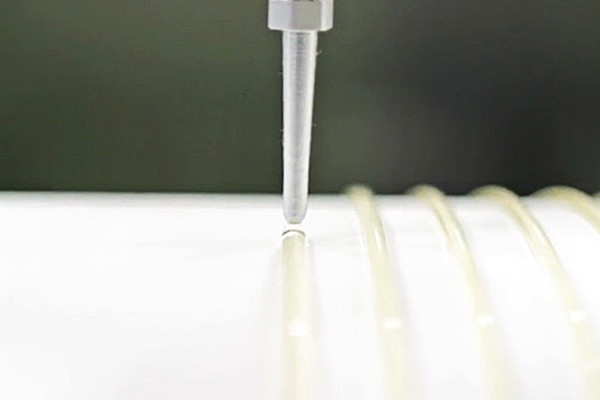

2.Flexibility: Polyurethane adhesives maintain their bond strength even in dynamic environments with movement or vibrations. This flexibility helps prevent bond failure due to material expansion, contraction, or other mechanical stresses.
3.Adhesion to Various Substrates: Polyurethane adhesives can bond with various materials, including metals, plastics, composites, wood, concrete, and more. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse structural applications.
4.Chemical Resistance: Some polyurethane adhesives resist chemicals, oils, and solvents, which can be crucial in environments where exposure to harsh substances is a concern.
5.Weather and Environmental Resistance: Polyurethane adhesives are known for their resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for outdoor and harsh environment applications.
6.Reduced Stress Concentration: Unlike mechanical fasteners, polyurethane adhesive bonds distribute stress more evenly across the bonded area, reducing stress concentrations and potential points of failure.
7.Design Flexibility: Using adhesive bonding in structural applications can allow for more complex and lightweight designs, eliminating the need for traditional fasteners like rivets or screws.
8.Vibration Dampening: The flexibility of polyurethane adhesives helps absorb vibrations, which can be advantageous in applications where vibration damping is required to enhance safety and performance.
Examples of structural bonding applications using polyurethane adhesives include:
- Automotive: Bonding car body panels, windshield installations, and vehicle structural components.
- Construction: Joining architectural features like glass panels, metal frameworks, and facade elements.
- Aerospace: Bonding aircraft components, interior panels, and structural parts in aerospace applications.
- Marine: Joining boat hulls, decks, and other structural components in shipbuilding.
- Renewable Energy: Bonding wind turbine blades, solar panels, and other renewable energy equipment components.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Assembling wooden furniture components with solid and durable bonds.
- Sports Equipment: Bonding components of sports equipment like skis, snowboards, and bicycles.
It’s essential to consider factors such as material compatibility, surface preparation, application technique, and adhesive curing time when using polyurethane adhesives for structural bonding to ensure the desired performance and reliability of the bonded joint.
What Are the Key Factors to Consider in the Application of Polyurethane Adhesive?
The successful application of polyurethane adhesive involves considering several key factors to ensure strong bonding and optimal performance. Here are the essential elements to take into account:
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation is crucial for successful adhesive bonding. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from dust, oil, grease, or other residues. Use appropriate cleaning methods, such as solvent wiping, sanding, or other treatments, depending on the substrate material.
- Substrate Compatibility:Ensure the polyurethane adhesive is compatible with your bonding materials. Different polyurethane adhesives are formulated for specific substrates like metals, plastics, wood, etc. Verify compatibility through adhesive manufacturer guidelines or compatibility testing.
- Adhesive Selection:There are various types of polyurethane adhesives available, including one-part and two-part formulations, fast-curing and slow-curing options, and different viscosity levels. Choose the bond that matches your application requirements, such as cure time, flexibility, and strength.
- Application Method:Applying the adhesive is essential for achieving consistent and reliable results. Methods include brush, roller, spray, or bead application. Choose the way that best suits the materials being bonded and the size of the bonded area.
- Temperature and Humidity:Adhesive performance can be affected by temperature and humidity. Follow the recommended temperature and humidity range the adhesive manufacturer provides during application and curing. Extremes in temperature and humidity can affect sticky cure time and bonding strength.
- Curing Time:Allow the adhesive to cure for the recommended time before exposing the bonded assembly to stress or load. Premature handling or stressing of the joint can lead to reduced bond strength.
- Joint Design:The design of the joint or bond area can significantly impact the adhesive’s effectiveness. Proper collaborative design can distribute stress evenly across the bond line, improving durability.
- Bond Line Thickness:The thickness of the adhesive layer, known as the bond line, should be consistent and within the manufacturer’s recommendations. Too much adhesive can lead to improper curing, while too little adhesive can result in inadequate bonding strength.
- Clamping or Fixturing:In some applications, attaching or fixturing may be necessary to maintain proper contact and pressure between the bonded surfaces during curing. Follow the adhesive manufacturer’s recommendations for clamping time and stress.
- Safety Precautions:Polyurethane adhesives may contain volatile components or emit fumes during curing. Follow proper safety precautions, such as using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), working in well-ventilated areas, and following the manufacturer’s safety guidelines.
- Testing and Quality Control:Perform adhesive bond testing or quality control checks to verify the strength and performance of the bonded joint. This can include lap shear tests, peel tests, or other relevant methods.
- Storage and Shelf Life:Properly store the adhesive according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain its quality and effectiveness. Adhesives can have a limited shelf life, so check the expiration date before use.
Always refer to the specific recommendations provided by the adhesive manufacturer for your particular product and application. Adhering to these guidelines will help ensure successful and durable polyurethane adhesive bonds.
How Does Polyurethane Adhesive Address Challenges of Vibration and Movement?
Polyurethane adhesive is a versatile adhesive that addresses challenges related to vibration and movement through its unique properties and characteristics. It is commonly used in various industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where bonding materials that experience dynamic stress are required. Here’s how polyurethane adhesive addresses the challenges of vibration and movement:
- Flexibility and Elasticity: Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility and elasticity. They can absorb and distribute stress caused by vibration and movement. The adhesive can stretch and compress without losing its bond integrity when materials expand, contract, or shift due to dynamic forces. This helps to prevent the adhesive joint from cracking or weakening under these conditions.
- Damping Properties: Polyurethane adhesives possess inherent damping properties, which can absorb and dissipate the energy generated by vibrations. This helps to reduce the transfer of vibrational energy from one substrate to another, minimizing the potential for structural damage or loosening of the bond.
- High Strength: Polyurethane adhesives can offer high bond strength despite their flexibility. This is important in applications where materials are subjected to movement and stress, as a strong bond helps maintain the structural integrity of the joined components.
- Thermal Expansion Compatibility: Different materials can expand and contract at different rates due to temperature fluctuations. Polyurethane adhesives can provide a degree of compatibility between materials with varying coefficients of thermal expansion. This helps to prevent bonds from weakening or breaking due to temperature-related movements.
- Excellent Adhesion to Various Substrates: Polyurethane adhesives can bond to various substrates, including metals, plastics, composites, and even dissimilar materials. This versatility ensures that materials with different expansion and contraction rates can be effectively bonded together.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors: Polyurethane adhesives are often formulated to resist moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. These formulations help maintain the adhesive’s strength and flexibility over time, even when exposed to harsh environmental conditions that could contribute to movement and vibration.
- Gap-Filling Ability: Polyurethane adhesives can fill gaps between substrates, compensating for slight misalignments and dimensional variations. This is crucial in applications where movement might cause cracks to develop over time.
- Long-Term Durability: Because of their ability to withstand dynamic stresses, polyurethane adhesives are suitable for long-term applications where constant movement and vibration are expected. They offer reliable bonding over the life of the assembly.
What Role Does Polyurethane Adhesive Play in Bonding Dissimilar Substrates?
Due to its unique properties and characteristics, polyurethane adhesive is crucial in bonding dissimilar substrates. Dissimilar substrates have different compositions, surface properties, and physical properties. Connecting these materials can be challenging because traditional adhesives might need to provide the necessary adhesion and durability. Polyurethane adhesives offer several benefits that make them suitable for bonding dissimilar substrates:
- Versatility: Polyurethane adhesives bond various dissimilar materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, and rubber. This versatility is crucial when dealing with projects that involve joining materials with vastly different properties.
- Adhesion: Polyurethane adhesives provide strong adhesion to various substrates, even those with different surface energies. They can form strong bonds on porous and non-porous surfaces, making them practical for bonding dissimilar materials.
- Flexibility: Polyurethane adhesives offer excellent flexibility and elasticity once cured. This property is fundamental when bonding materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion or when the bonded materials are subjected to movement or vibrations. The adhesive can accommodate these stresses without losing its bond.
- Chemical Resistance: Polyurethane adhesives often exhibit good resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents. This is beneficial when bonding substrates exposed to harsh environments or various chemicals.
- Durability: The bonds created by polyurethane adhesives are typically durable and resistant to factors like moisture, temperature changes, and UV radiation. This makes them suitable for outdoor applications and situations where the bonded materials will be exposed to varying conditions.
- Gap Filling: Polyurethane adhesives can fill small gaps between substrates, which is beneficial when dealing with irregular surfaces or substrates that don’t fit perfectly together. This helps ensure a uniform bond line and maximizes the contact area between dissimilar materials.
- Curing Mechanism: Polyurethane adhesives cure through a moisture-curing mechanism, which means they react with moisture in the air or on the substrate’s surface to harden. This mechanism allows them to form bonds even in areas that might be inaccessible.
- Ease of Use: Polyurethane adhesives are available in various formulations, including one-component and two-component options. One-component formulations are often ready to use and require no mixing, while two-component formulations can be tailored for specific bonding requirements.
It’s important to note that while polyurethane adhesives offer many advantages, they also have some limitations. These adhesives can have a longer curing time than other fast-curing adhesives, and their initial bond strength may be lower until they fully cure. Some polyurethane adhesives may require careful surface preparation to ensure optimal bonding.
Overall, the ability of polyurethane adhesives to provide robust, flexible, and durable bonds makes them a popular choice for bonding dissimilar substrates in various industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Is Polyurethane Adhesive Resistant to Water, Chemicals, and UV Exposure?
Polyurethane adhesives are known for their versatility and strong bonding properties, but their resistance to water, chemicals, and UV exposure can vary based on the specific formulation and intended use. Generally, polyurethane adhesives exhibit good resistance to these factors, but the degree of resistance can depend on factors such as the formulation, curing process, and application conditions.
- Water Resistance:Many polyurethane adhesives are inherently water-resistant, making them suitable for applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. They can withstand exposure to water without significantly compromising their bonding strength. However, prolonged immersion in water or exposure to excessive humidity might eventually lead to some adhesive degradation over time.
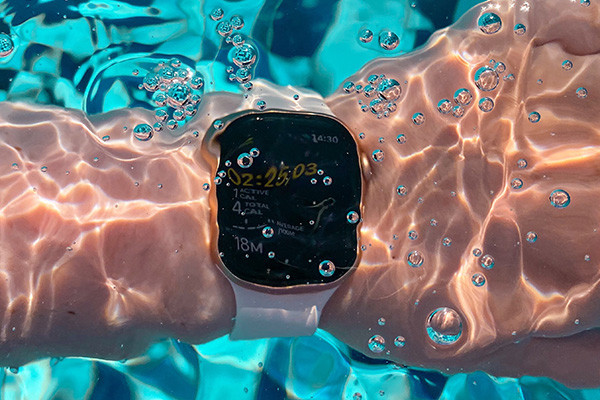

2.Chemical Resistance:Polyurethane adhesives have good chemical resistance, particularly against a wide range of mild to moderate chemicals. However, the chemical resistance can be affected by the specific chemicals involved, the concentration and duration of exposure, and the adhesive formulation. Harsh chemicals or solvents might lead to deterioration or weakening of the adhesive bond.
3.UV Exposure:The UV resistance of polyurethane adhesives can vary. While they generally have some level of UV resistance, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and UV radiation can lead to degradation of the adhesive over time. UV stabilizers and additives can be incorporated into the formulation to enhance UV resistance, but other specialized adhesives might be more suitable for applications with continuous or intense UV exposure.
It’s important to note that different types of polyurethane adhesives are available, each with its specific properties and intended applications. Some polyurethane adhesives are designed specifically for outdoor or high UV exposure applications, while others might be better suited for indoor or more controlled environments. Manufacturers often provide technical datasheets that detail the adhesive’s properties, including its resistance to water, chemicals, and UV exposure.
If you have a specific application in mind, it’s recommended to consult with adhesive manufacturers or suppliers to ensure you select the most suitable polyurethane adhesive for your needs. Additionally, conducting thorough testing or seeking expert advice can help determine the adhesive’s performance in your specific conditions.
What Techniques Are Effective for Surface Preparation Before Polyurethane Adhesive Application?
Surface preparation is crucial before applying polyurethane adhesive to ensure strong and durable bonds. Proper surface preparation enhances adhesion and minimizes the risk of bond failure. Here are some effective techniques for surface preparation before polyurethane adhesive application:
- Cleaning:
- Begin by thoroughly cleaning the surfaces to remove dirt, dust, oil, grease, moisture, and other contaminants that can hinder adhesion.
- Use solvents or cleaning agents recommended by the adhesive manufacturer to ensure proper cleaning without damaging the substrate.
- Degreasing:
- Grease and oil residues can prevent proper bonding. Use a suitable degreasing agent to remove these contaminants from the surface.
- Abrasion:
- Lightly rub the surface using methods like sanding, scuffing, or sandblasting. Abrasion enhances adhesion by creating a rougher surface, allowing the adhesive to grip better.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for the appropriate abrasion technique and grit size to avoid damaging the substrate.
- Priming:
- Some substrates require a primer to promote adhesion. Primers improve the substrate and adhesive bonding by creating a compatible interface.
- Choose a primer recommended by the adhesive manufacturer for the specific substrate.
- Chemical Etching:
- Chemical etching is suitable for specific materials like metals and plastics. It involves using an acid or chemical solution to etch the surface slightly, improving adhesion.
- Follow safety precautions and manufacturer recommendations when using chemical etching methods.
- Mechanical Keying:
- Create minor grooves or patterns on the surface to mechanically lock the adhesive into place. This technique is beneficial for thick adhesive layers.
- Surface Activation:
- Use techniques like plasma treatment or corona discharge to modify the surface properties, improving wettability and promoting adhesion.
- Drying and Curing:
- Ensure the surfaces are dehydrated and moisture-free before applying the adhesive. Moisture can interfere with adhesion and lead to bond failure.
- Follow recommended curing times for primers or surface treatments to achieve the best results.
- Testing and Validation:
- Before applying the adhesive on a larger scale, perform adhesion tests on a small sample to ensure that the surface preparation techniques are practical and that the adhesive bonds well.
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
- Always refer to the adhesive manufacturer’s guidelines for surface preparation techniques specific to the adhesive and substrate materials.
Remember that the effectiveness of surface preparation techniques can vary based on the specific adhesive, substrate, and application conditions. Following manufacturer recommendations and conducting proper testing will help ensure successful adhesive bonding.
Can Polyurethane Adhesive Be Applied Manually, or Is Automation Preferred?
Depending on the specific application and requirements, polyurethane adhesives can be applied manually or using automation. The choice between manual and automated applications depends on several factors, including the adhesive’s nature, the project’s complexity, the desired precision level, and the production volume.
- Manual Application:
- Manual application of polyurethane adhesive can be suitable for smaller-scale projects or applications that require a personal touch.
- The manual application provides more control over the adhesive placement and bonding process, which can be necessary for intricate or delicate work.
- Craftsmen and artisans often use manual applications for custom or artistic projects.
- Automated Application:
- Automation is preferred in industrial settings where high production volumes and consistent quality are crucial.
- The automated application ensures uniform adhesive distribution, which can lead to more reliable and repeatable bonding results.
- Automation can improve efficiency and reduce labor costs, especially for large-scale manufacturing operations.
- Automated systems can be integrated into production lines, dispensing adhesives with precision and speed.
In both cases, it’s essential to consider factors like adhesive viscosity, curing time, substrate materials, and the required bond strength. Some polyurethane adhesives may have specific requirements for application, such as controlled humidity or temperature, which could impact the choice between manual and automated methods.
Ultimately, the decision to use a manual or automated application depends on the project’s scope, quality requirements, budget, and available resources. It’s important to carefully evaluate these factors to determine the most suitable application method for your needs.
What Are the Key Factors to Consider in the Application of Polyurethane Adhesive?
Applying polyurethane adhesive involves several key factors that must be carefully considered to ensure adequate bonding and optimal performance. Here are some essential elements to keep in mind:
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation is critical for successful bonding. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from dust, grease, oil, and rust. Mechanical abrasion or chemical treatments might be necessary to improve adhesion.
- Substrate Compatibility:Consider the compatibility of the polyurethane adhesive with the materials you’re bonding. Different formulations of polyurethane adhesives are designed for specific substrates like metals, plastics, wood, and more. Make sure the adhesive is suitable for both substrates you’re bonding.
- Viscosity and Cure Time:The viscosity (thickness) of the adhesive affects how easily it can be applied and the bond line thickness. Also, consider the cure time, which is the time it takes for the adhesive to set and develop its maximum strength fully. Some applications may require fast-curing adhesives, while others can benefit from longer open times.
- Environmental Conditions:Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to UV light can significantly impact the performance of polyurethane adhesives. Ensure you’re using adhesives suitable for the specific conditions the bonded assembly will experience.
- Application Method:Polyurethane adhesives can be applied using various methods such as brush, roller, spray, or bead application. Choose the most suitable way for your application and consider factors like the size and geometry of the parts being bonded.
- Bond Line Thickness:The thickness of the adhesive layer, known as the bond line, can affect the strength and performance of the bond. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the ideal bond line thickness is crucial.
- Assembly Design:The design of the assembly and how the parts fit together can impact the adhesive’s performance. Ensure sufficient contact area for bonding and that stress concentrations are minimized.
- Adhesive Handling and Storage:Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for storing and handling the adhesive. Improper storage can lead to changes in adhesive properties and reduced performance.
- Safety Precautions:Polyurethane adhesives can contain chemicals that may be hazardous to health. Follow safety precautions such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and working in a well-ventilated area.
- Testing and Quality Control:Perform tests to ensure the adhesive’s compatibility with the substrate and to verify the bond’s strength and durability. Quality control measures during the application process can help catch any issues early on.
- Cure and Post-Cure Conditions:The adhesive can fully cure according to the manufacturer’s recommendations before subjecting the assembly to stress or load. Some bonds may require a post-cure process to achieve optimal properties.
Remember that the specific requirements for each application can vary, so it’s essential to consult with adhesive manufacturers or technical experts to select the most appropriate polyurethane adhesive and to get guidance on its proper application.
How Does Polyurethane Adhesive Address Challenges of Vibration and Movement?
Polyurethane adhesive is known for its excellent ability to address challenges related to vibration and movement. It offers unique properties that make it particularly well-suited for applications where these challenges are prominent. Here’s how polyurethane adhesive addresses these challenges:
- Flexibility and Elasticity:Polyurethane adhesive possesses inherent flexibility and elasticity, allowing it to withstand vibrations and movements without cracking or losing its bond. It can absorb the stress and strain that result from dynamic forces, which helps maintain the integrity of the bond over time.
- Damping Properties:Polyurethane adhesive has softening properties, absorbing and dissipating energy from vibrations. This helps reduce the magnitude of vibrations and prevents them from transferring to other parts of a structure or assembly, effectively minimizing the potential for damage or noise generation.
- Adhesion to Various Substrates:Polyurethane adhesive forms strong bonds with many substrates, including metals, plastics, composites, and even dissimilar materials. This strong bond helps distribute stresses more evenly across the joint, reducing the likelihood of localized stress concentrations that can lead to bond failure.
- Resilience:Polyurethane adhesive is resilient and can return to its original shape after deformation. This property enables it to accommodate movements and vibrations without damaging the adhesive or bonded components permanently.
- Chemical Resistance:Many polyurethane adhesives are resistant to various chemicals, oils, and environmental factors, which ensures the adhesive’s stability and effectiveness in challenging operating conditions.
- Gap-Filling Ability:Polyurethane adhesive can effectively fill gaps and irregularities between surfaces, providing a uniform load distribution across the bonded area. This property is fundamental when dealing with uneven or irregular surfaces that might experience movement or vibrations.
- Temperature Stability:Polyurethane adhesive can often withstand a wide temperature range, remaining stable and maintaining its adhesive properties even in extreme environments. This characteristic is crucial for applications where temperature fluctuations are common and can impact the bond’s integrity.
- UV and Weather Resistance:Many polyurethane adhesives are formulated to resist UV radiation and weathering, which helps maintain their performance and bond strength over extended periods of exposure to outdoor conditions.
- Longevity:The combination of flexibility, strength, and resilience in polyurethane adhesive contributes to its long-term durability. This is essential for applications with continuous vibration and movement, as the adhesive can maintain its effectiveness for an extended period.
What Role Does Polyurethane Adhesive Play in Bonding Dissimilar Substrates?
Due to its unique properties and capabilities, polyurethane adhesive is crucial in bonding dissimilar substrates. When it comes to joining materials that have different compositions, structures, or properties, such as metal to plastic or wood to plastic, polyurethane adhesives offer several advantages:
- Versatile Bonding:Polyurethane adhesives are known for their versatility in bonding various dissimilar materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and porous surfaces like wood and concrete. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across industries.
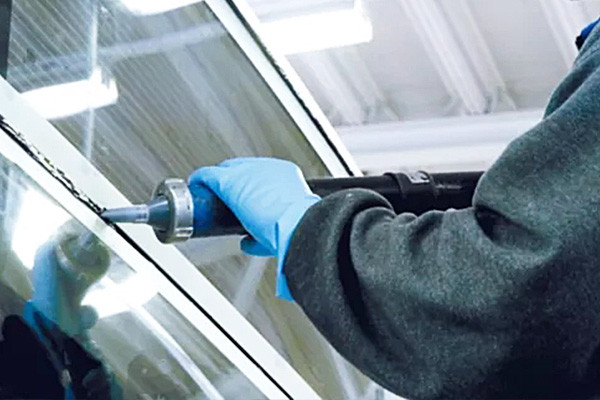

2.Adhesion to Diverse Surfaces:Polyurethane adhesives have excellent adhesion to porous and non-porous surfaces. This allows them to create strong bonds between materials with different surface energies or textures.
3.Flexibility and Elasticity:Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility and elasticity. They can accommodate differential expansion, contraction, and movement due to temperature variations or mechanical stresses. This is particularly important when bonding dissimilar materials that might have different coefficients of thermal expansion.
4.High Strength:Polyurethane adhesives can provide high bond strength, creating durable connections between dissimilar substrates. This is crucial for applications that involve load-bearing or structural components.
5.Chemical Resistance:Polyurethane adhesives often exhibit good resistance to chemicals, solvents, and environmental factors, which is beneficial when bonding materials that may be exposed to harsh conditions.
6.Dampening Vibrations:Polyurethane adhesives can act as a vibration-dampening material, helping to absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is applicable when bonding materials in applications where vibrations are a concern.
7.Gap-Filling Capability:Some polyurethane adhesives can fill gaps between substrates. This is particularly valuable when bonding irregular or uneven surfaces.
8.Excellent Durability:Polyurethane adhesives can maintain their bonding properties over time, even in challenging environments. This durability is essential for long-lasting bonds in various applications.
9.Water Resistance:Many polyurethane adhesives have good water resistance, essential for applications exposed to moisture or humidity.
10.Ease of Application:Polyurethane adhesives are available in different formulations, including one-part and two-part systems. They can be applied using various methods such as manual application, automated dispensing, or spray application, making them adaptable to different manufacturing processes.
Overall, the role of polyurethane adhesive in bonding dissimilar substrates is to provide a strong, durable, and flexible connection that can withstand various environmental and mechanical challenges. Its ability to bridge the gap between materials with differing properties makes it an essential tool in many industries, including automotive, construction, aerospace, electronics, and more.
Is Polyurethane Adhesive Resistant to Water, Chemicals, and UV Exposure?
Polyurethane adhesives are known for their versatility and wide range of applications. Their water, chemicals, and UV exposure resistance can vary based on the specific formulation and intended use. Here’s a general overview of their resistance properties:
- Water Resistance:Polyurethane adhesives are generally quite resistant to water exposure. They can maintain their bond strength and structural integrity even when exposed to moisture or submerged in water. This water resistance is precious for outdoor applications or in environments with high humidity.
- Chemical Resistance:The chemical resistance of polyurethane adhesives depends on the specific chemicals they come into contact with. Generally, polyurethanes exhibit good resistance to many common chemicals, including oils, fuels, solvents, and certain acids. However, their resistance can be compromised when exposed to certain aggressive chemicals, so it’s essential to consult the adhesive manufacturer’s technical data sheets for compatibility information.
- UV Exposure:UV resistance can be more variable with polyurethane adhesives. Some formulations are designed to withstand UV exposure better than others. Over time, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and UV radiation can cause polyurethane adhesives to degrade, leading to changes in color, brittleness, and reduced bond strength. For applications exposed to significant UV radiation, it’s advisable to choose adhesives that are specifically formulated for UV resistance or consider using additional protective coatings or measures.
It’s important to note that the performance of polyurethane adhesives can be influenced by factors such as the specific formulation, application method, substrate materials, temperature, and the specific environmental conditions they will be exposed to. Therefore, before using a polyurethane adhesive in a critical application, it’s recommended to consult the manufacturer’s technical data sheets and conduct thorough testing to ensure that the adhesive meets the required performance criteria for water, chemical, and UV resistance in your specific use case.
What Techniques Are Effective for Surface Preparation Before Polyurethane Adhesive Application?
Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving solid and durable adhesive bonds when using polyurethane adhesives. Here are some effective techniques for preparing surfaces before applying polyurethane adhesives:
- Cleaning: Start by thoroughly cleaning the surfaces to be bonded. Remove dirt, dust, oils, grease, and other contaminants using solvents appropriate for the specific materials. Isopropyl alcohol or acetone is commonly used for cleaning.
- Degreasing: Many surfaces, especially metals, might have a layer of oil or grease that can hinder adhesion. Degreasing agents can help remove these substances effectively.
- Abrasion: Lightly scuff the surfaces using sandpaper, a wire brush, or an abrasive pad. This roughens the surface slightly, creating more surface area for the adhesive to bond. Make sure not to damage the surface integrity.
- Priming: Sometimes, using a primer specifically designed for polyurethane adhesives can greatly enhance bonding performance. Primers promote adhesion by providing a chemically compatible interface between the adhesive and the substrate.
- Mechanical Anchoring: If feasible, create a mechanical anchor by introducing small features like grooves, notches, or holes into the surface. These features can improve adhesive bonding strength by creating interlocking points.
- Drying: Ensure that the surfaces are dehydrated before applying the adhesive. Moisture can negatively impact adhesive performance, so follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for moisture content.
- Surface Activation: Some materials benefit from surface activation methods such as plasma treatment or corona discharge. These techniques modify the surface’s chemical properties, enhancing its receptiveness to adhesives.
- Compatibility Testing: Before applying the adhesive, test the surfaces and the bond. Some substrates might need to be compatible with certain polyurethane adhesives, leading to poor bonding or adhesion failure.
- Dust Control: Ensure the work area is free from dust and particles that can settle onto the prepared surfaces. Dust can create barriers between the adhesive and the substrate, affecting bonding quality.
- Temperature and Humidity: Pay attention to environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity during surface preparation and adhesive application. These factors can influence the adhesion process.
- Masking: Use masking tape or other protective materials to cover areas that should not come into contact with the adhesive. This prevents unwanted spread and ensures neat application.
- Application Method: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for applying the polyurethane adhesive. Different adhesives require specific application techniques like brushing, spraying, or dispensing from a syringe.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for surface preparation and adhesive application. Adhesive performance can be significantly affected by improper surface preparation, so investing time and effort into this step will ultimately lead to better bonding results.
Can Polyurethane Adhesive Be Applied Manually, or Is Automation Preferred?
Depending on the specific application, project requirements, and production volume, polyurethane adhesives can be applied manually and through automation.
- Manual Application:Polyurethane adhesives can be applied manually using tools such as brushes, rollers, spatulas, or dispensing guns. This method is suitable for smaller-scale projects, repairs, or situations where precise control over the adhesive application is needed. The manual application allows flexibility and adaptability in applying the adhesive to various surfaces and shapes.
- Automated Application:Automation is often preferred for larger production volumes or when consistency and speed are essential. Mechanical systems can include robotic dispensing arms, conveyor-based applications, or other specialized equipment. Automation can ensure uniform adhesive coverage, precise application, and higher production rates than manual methods. This is particularly important in the automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing industries.
Key factors influencing the choice between manual and automated applications include:
- Volume:Automation is usually preferred for high-volume production to ensure efficiency and consistency.
- Precision:Applications requiring precise adhesive placement may benefit from automation, as it can offer accurate positioning and uniform coverage.
- Labor Costs:Manual application might be more labor-intensive and costly for large-scale projects, making automation a more cost-effective choice.
- Quality Control:Automation can improve quality control by minimizing human error and ensuring consistent application.
- Complexity:Some projects involve intricate designs or hard-to-reach areas, making the manual application more practical.
- Flexibility:Manual application is more adaptable to changing project requirements and irregular surfaces.
Whether to apply polyurethane adhesive manually or through automation depends on factors like project size, precision needs, production volume, labor costs, and the complexity of the application. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages, so the choice should be based on the specific needs and goals of the project.
How Does the Cure Time of Polyurethane Adhesive Impact Bond Strength?
The cure time of a polyurethane adhesive can significantly impact the bond strength it achieves. Bond strength refers to the ability of a glue to hold two substrates together under various forces and conditions. Here’s how to cure time influences bond strength in polyurethane adhesives:
- Initial Strength: As the polyurethane adhesive cures, it goes through various stages of development, including an initial stage where the adhesive starts to bond the substrates together. The bond strength might be relatively low during this early phase compared to the fully cured state.
- Chemical Reaction: Polyurethane adhesives typically cure through a chemical reaction between the polyol and isocyanate components. The curing process involves crosslinking polymer chains, forming a solid network contributing to the adhesive’s final strength. If the adhesive is not given sufficient time to cure, the crosslinking might not be complete, leading to weaker bonds.
- Complete Cure:The bond strength of polyurethane adhesives generally increases as they approach a complete cure. A longer cure time allows the chemical reaction to progress to a point where the adhesive achieves its maximum potential strength. Complete treatment might take several hours to several days, depending on the specific formulation of the adhesive and the environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.).
- Environmental Factors:The environment in which the adhesive is curing can impact the bond strength. Higher temperatures can accelerate the curing process, leading to quicker attainment of higher bond strength. However, extremely high temperatures might also cause the adhesive to cure too quickly, potentially affecting its overall performance.
- Cure Conditions: Following the manufacturer’s recommended cure conditions for the specific polyurethane adhesive is essential. Deviating from these conditions could result in incomplete curing and compromised bond strength. Factors like temperature, humidity, and substrate type can all influence how well the adhesive cures and the resulting bond strength.
- Application Specifics: The intended application and the loads or stresses the bond will experience also influence how critical the cure time is. In some cases, a rapid bond might be sufficient, while in others, it’s crucial to allow the adhesive to cure to ensure long-term durability and reliable bond strength fully.
The cure time of a polyurethane adhesive significantly affects its bond strength. Allowing the glue sufficient time to cure fully, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and under appropriate environmental conditions, is essential for achieving the highest possible bond strength. Always refer to the adhesive manufacturer’s guidelines for proper usage and curing recommendations to ensure the desired performance of the adhesive in your specific application.
Are There Special Considerations for High-Temperature Applications with Polyurethane Adhesive?
There are special considerations for using polyurethane adhesive in high-temperature applications. While polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility, durability, and strong bonding properties, elevated temperatures can affect their performance. Here are some key points to consider:
- Temperature Resistance: Polyurethane adhesives are generally less heat-resistant than other adhesive types like epoxies or silicone adhesives. They can soften or degrade at high temperatures, potentially leading to a loss of adhesive strength. The exact temperature at which this occurs depends on the specific formulation of the adhesive.
- Temperature Range: Before using polyurethane adhesive in a high-temperature application, it’s crucial to know the temperature range to which the adhesive will be exposed. This will help you choose an adhesive formulation that can withstand the expected temperature conditions.
- Formulation Selection: Some polyurethane adhesive formulations are specifically designed for high-temperature applications. These formulations might include additives or components that enhance their heat resistance. When selecting an adhesive, consult the manufacturer to ensure you choose the correct formulation.
- Pre-Curing: For high-temperature applications, pre-curing the adhesive at a lower temperature might be beneficial before exposing it to the intended high-temperature environment. This can help improve the adhesive’s resistance to heat.
- Testing: Always thoroughly test under conditions that simulate the high-temperature environment the adhesive will be exposed to. This can include mechanical testing, bond strength testing, and durability testing. Testing will help you determine the adhesive’s performance under these conditions.
- Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is critical to achieving a solid bond with polyurethane adhesive, especially in high-temperature applications. Ensure the characters to be bonded are clean, dry, and free from contaminants that could interfere with adhesion.
- Bond Strength: While polyurethane adhesives might lose some strength at high temperatures, they can still maintain a certain level of bonding. Evaluate whether this reduced bond strength is acceptable for your application or if an alternative adhesive type would be more suitable.
- Stress and Movement: Consider how the adhesive joint will be subjected to pressure and movement at high temperatures. Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility, but excessive movement could lead to premature failure.
- Application Techniques: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for application techniques, including mixing ratios, curing times, and temperature conditions. Proper application is critical to achieving the best possible bond.
- Consulting Manufacturers: If you have specific requirements for a high-temperature application, consider contacting adhesive manufacturers for guidance. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise.
What Testing Methods Ensure the Durability and Longevity of Polyurethane Bonded Assemblies?
Polyurethane-bonded assemblies are used in various applications where durability and longevity are crucial. Several testing methods are employed to ensure these assemblies’ quality and performance over time. Some of the standard testing methods include:
1.Tensile Strength and Elongation Testing:This test measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) force a bonded assembly can withstand before breaking. It also measures how much the material can stretch before breaking. These properties are important indicators of the bond’s durability and ability to withstand mechanical stress.
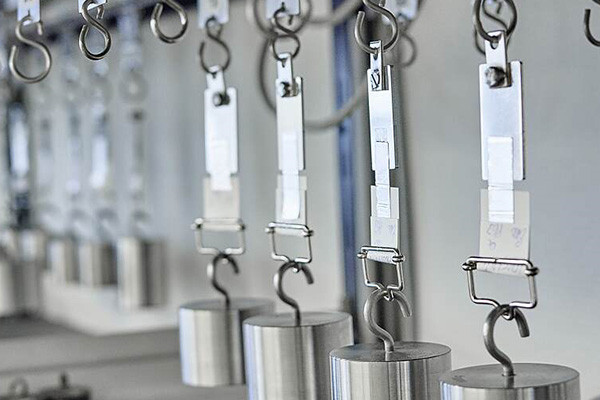

2.Shear Strength Testing:Shear strength testing evaluates the ability of the adhesive to resist forces applied parallel to the bonded surfaces. It is essential for assemblies subjected to shear loads, such as joints that experience sliding or rubbing muscles.
3.Peel Strength Testing:Peel strength testing assesses the bond’s ability to resist forces perpendicular to the bonded surfaces. This is crucial for applications where the assembly is subjected to peeling or separating forces.
4.Aging and Environmental Exposure Testing:Polyurethane bonded assemblies are often exposed to various environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and chemical exposure. Accelerated aging tests involve subjecting the masses to these conditions over an extended period to simulate real-world usage and assess how well the bond holds up.
5.Creep and Stress Relaxation Testing:Creep testing involves applying a constant load or stress to a bonded assembly over an extended period and measuring the deformation or movement occurring over time. Stress relaxation testing uses a continuous deformation and measures how the applied stress decreases over time. These tests help evaluate the assembly’s long-term stability under sustained loads.
6.Fatigue Testing:Fatigue testing simulates repetitive loading and unloading cycles to assess how well the bonded assembly can withstand cyclic stress over time. This is crucial for applications where the body is subjected to dynamic loads.
7.Impact Resistance Testing:Impact resistance testing involves subjecting the bonded assembly to controlled impacts to evaluate its ability to withstand sudden loads without failure. This is important for communities in applications where impact loads are likely, such as automotive components.
8.Chemical Resistance Testing:If the polyurethane bonded assembly is exposed to chemicals, this test evaluates how well the bond withstands chemical exposure without degradation or loss of adhesion.
9.Heat Aging Testing:Heat aging tests involve subjecting the bonded assembly to elevated temperatures for an extended period to assess the bond’s stability and strength under high-temperature conditions.
10.Microscopic Analysis:Microscopic techniques such as optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be used to examine the bond interface at a microscopic level. This helps identify defects, voids, or imperfections that could compromise the bond’s durability.
Combined, these testing methods provide a comprehensive assessment of the durability and longevity of polyurethane-bonded assemblies under various conditions. Tailoring the testing approach to the specific application and environmental factors the communities will be subjected to is essential.
What Innovations Have Enhanced the Performance of Polyurethane Adhesive in Recent Years?
Recent innovations have substantially bolstered the efficacy of polyurethane adhesive. Enhanced formulations and application techniques have propelled its performance across diverse applications.
- Nanotechnology Integration: Incorporating nanoparticles has yielded impressive enhancements. These nanofillers augment adhesive strength and improve bonding with various substrates.
- UV-Curing Advancements: Progress in ultraviolet (UV) curing mechanisms has expedited the bonding process. UV-curable polyurethane adhesives now ensure rapid and robust bonds without extended curing times.
- Bio-based Ingredients: Integration of renewable resources has diminished dependence on fossil fuels. Bio-based polyols and reactive diluents foster eco-friendliness without compromising adhesive quality.
- Microreplication Techniques: Employing microreplication methodologies on adhesive surfaces has led to superior contact and interlocking with substrates. This elevates overall adhesive strength and durability.
- Enhanced Durability through Crosslinking: Innovations in crosslinking agents have bolstered adhesive resilience against harsh conditions, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations.
- Intelligent Monitoring Systems: Implementation of real-time monitoring systems permits meticulous control over adhesive application variables. This optimizes adhesive usage and ensures consistent outcomes.
- Tailored Rheology for Automation: Adapting adhesive rheology to suit automated application processes has streamlined manufacturing. Controlled flow characteristics result in uniform bonds and reduced wastage.
- Adhesion Promoters: Advanced adhesion promoters, designed at the molecular level, have intensified adhesive-substrate interactions. This is particularly significant for challenging surfaces.
- Dual Cure Mechanisms: Dual cure mechanisms, encompassing light and moisture activation, offer versatility. This enables bonding in scenarios where access to specific curing conditions is limited.
- Non-Volatile Formulations: Innovations have led to the development of low-volatile organic compound (VOC) formulations. These align with regulatory demands while maintaining adhesive effectiveness.
Collectively, these innovations signify a transformative era for polyurethane adhesive. By capitalizing on nanotechnology, novel curing methods, sustainable ingredients, and advanced monitoring, the performance of polyurethane adhesive has been elevated across the board.
How Does Polyurethane Adhesive Contribute to Environmental Sustainability?
Polyurethane adhesive contributes significantly to environmental sustainability through a range of mechanisms and practices:
- Reduced Fossil Fuel Dependency: Many polyurethane adhesives now incorporate bio-based ingredients, such as renewable polyols derived from plant-based sources. By decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, these adhesives help mitigate the carbon footprint associated with traditional adhesive production.
- Lower Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Innovations have led to development of low-VOC and even VOC-free formulations. This reduces the emission of harmful volatile organic compounds into the atmosphere, improving indoor air quality and minimizing the environmental impact.
- Enhanced Durability and Longevity: Polyurethane adhesives are known for their durability and resilience to various environmental stresses, leading to longer-lasting bonds. This can extend the lifespan of products and structures, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Some polyurethane adhesives utilize UV or moisture-curing mechanisms requiring less energy than traditional thermal curing methods. This contributes to energy efficiency and reduces overall energy consumption during adhesive curing.
- Reduced Waste: The superior bonding properties of polyurethane adhesives often result in less material waste during production. The efficient adhesion minimizes the need for excess adhesive application and reduces material scrap, leading to resource conservation.
- Recyclability and Reprocessability: Certain polyurethane adhesives can be designed to have properties that facilitate recycling and reprocessing. This can promote circular economy practices by allowing the adhesive to be reclaimed and reused in new applications.
- Sustainable Packaging: Innovations in packaging, such as using eco-friendly materials or reducing packaging waste, can further contribute to the overall environmental sustainability of polyurethane adhesives.
- Water-Based Formulations: Water-based polyurethane adhesives have gained traction as an environmentally friendly alternative to solvent-based adhesives. They have lower VOC emissions, reduced flammability risks, and a smaller ecological footprint.
- End-of-Life Considerations: Some polyurethane adhesives are designed with considerations for their end-of-life impact. This may involve creating adhesive formulations compatible with recycling processes or breaking down more quickly in landfills.
- Green Certification and Regulations: Adhesive manufacturers increasingly adhere to green certifications and environmental regulations. This ensures that the production and use of polyurethane adhesives align with environmentally responsible practices.
Polyurethane adhesives enhance environmental sustainability through reduced fossil fuel dependency, lower VOC emissions, energy efficiency, reduced waste generation, and considerations for recycling and end-of-life impacts. These factors collectively position polyurethane adhesives as a more environmentally conscious choice in various industries and applications.
What Precautions Should Be Taken When Handling and Storing Polyurethane Adhesive?
Handling and storing polyurethane adhesive requires careful attention to safety and proper storage conditions to ensure its effectiveness and prevent potential hazards. Here are some precautions you should take:
Handling Precautions:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing, to prevent direct contact with the adhesive. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific type of PPE required.
- Ventilation:Work in a well-ventilated area or use local exhaust ventilation to minimize inhalation of fumes and vapors generated during adhesive application.
- Avoid Skin Contact:Polyurethane adhesives can be harmful to skin. In case of skin contact, wash the affected area immediately with plenty of water and soap. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Eye Protection:Use safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from accidental splashes or fumes. In case of eye contact, flush your eyes with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
- Avoid Inhalation:Avoid breathing in the fumes and vapors generated by the adhesive. If working in an enclosed space, use a respirator or mask approved for use with polyurethane adhesives.
- No Smoking:Do not smoke or bring open flames near the adhesive, as polyurethane adhesives are often flammable.
Storage Precautions:
- Temperature and Humidity:Store polyurethane adhesives in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Check the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific storage temperature recommendations.
- Sealed Containers:Always store the adhesive in its original container, tightly sealed to prevent air and moisture from entering. This helps maintain the adhesive’s quality and shelf life.
- Keep Away from Ignition Sources:Store polyurethane adhesives away from ignition sources, such as open flames, sparks, and electrical equipment.
- Separation from Incompatible Materials:Store polyurethane adhesives away from materials that could react with or contaminate the adhesive. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for proper storage practices.
- Labels and Documentation:Keep the original tags and documentation on the container intact for reference. This includes essential information such as usage instructions, safety precautions, and emergency contact details.
- Shelf Life:Polyurethane adhesives have a limited shelf life. Always use the adhesive within its recommended shelf life to ensure its effectiveness.
- Childproofing:If you store polyurethane adhesives in a household setting, keep them out of the reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
- First Aid Kit:Keep a kit nearby in case of accidental exposure or injuries.
Remember that the precautions mentioned here are general guidelines. It’s crucial to follow the specific recommendations provided by the manufacturer of the polyurethane adhesive you are using. Different formulations and brands have slightly different handling and storage requirements. Always refer to the product’s Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information on handling, storage, and emergency procedures.
Can Polyurethane Adhesive Be Painted Over or Otherwise Finished?
Yes, polyurethane adhesive can be painted over or finished, but there are a few essential considerations to keep in mind:
- Curing Time:Polyurethane adhesives typically have a curing or drying time before they are fully set. It’s essential to allow the adhesive to cure completely before attempting to paint or finish it. This time can vary based on the specific adhesive product you’re using, so follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for curing time.
- Surface Preparation:Before painting or finishing over polyurethane adhesive, ensure the adhesive is clean and free from contaminants. Sanding the adhesive surface lightly can help improve adhesion for paint or finish.
- Compatibility:Some polyurethane adhesives may not bond well with certain paints or finishes. It’s a good idea first to test a small, inconspicuous area to ensure that the color or finish adheres appropriately to the adhesive surface.
- Priming:Applying a primer before painting can help improve adhesion and create a smooth surface for the paint. Choose a primer compatible with both the adhesive and the type of paint you intend to use.
- Type of Paint:The type of paint you use matters. Water-based paints, oil-based paints, and other specialized paints have different characteristics and requirements. Ensure that the paint you choose suits the type of surface you’re working with and bonds well with the cured adhesive.
- Finishing Techniques:If you’re applying a clear finish (e.g., varnish, lacquer, polyurethane topcoat), ensure it’s compatible with the adhesive and doesn’t react negatively. Apply the finish according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Flexibility:Remember that polyurethane adhesives can have varying degrees of flexibility once cured. If the bonded area will experience movement or flexing, choose paints and finishes that can accommodate such activity without cracking or peeling.
- Aesthetics:Some polyurethane adhesives may have a textured or uneven surface after curing. Depending on the desired final appearance, you might need to sand or level the character before painting or finishing.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for your specific polyurethane adhesive product. They often provide valuable information on compatibility with paints and finishes and the proper surface preparation techniques. Additionally, testing on a small, inconspicuous area before proceeding with a more extensive project can help you ensure a successful outcome.
What Future Directions and Applications Can We Anticipate for Polyurethane Bonding Solutions?
Anticipating forthcoming paths and potential uses for polyurethane bonding solutions involves envisioning many promising prospects. In manufacturing, these adhesives are likely to find expanded roles in enhancing composite materials’ durability and structural integrity. Industries such as aerospace and automotive could adopt these solutions for assembling lightweight yet robust components, contributing to heightened fuel efficiency and overall performance.
The medical domain also holds potential, with the ongoing development of bio-compatible polyurethane adhesives that could be instrumental in creating advanced medical devices and implants. These adhesives might play a pivotal role in ensuring secure and enduring bonds between dissimilar materials within the human body, advancing medical technology’s frontiers.
Furthermore, the construction sector could witness a transformation by utilizing polyurethane adhesives for assembling prefabricated modules. The capacity of these adhesives to provide both strong adhesion and insulation could accelerate the construction process while enhancing energy efficiency in buildings.
As sustainability remains a paramount concern, the emergence of eco-friendly polyurethane bonding solutions derived from renewable resources could revolutionize multiple industries. Such explanations might replace conventional adhesives in sectors ranging from furniture manufacturing to packaging, providing a greener alternative without compromising performance.
The evolving field of electronics also beckons, where polyurethane bonding solutions could be instrumental in producing flexible and wearable devices. With their ability to adhere to diverse substrates and withstand varying environmental conditions, these adhesives could be instrumental in enabling the next generation of electronic innovations.
In sum, the trajectory of polyurethane bonding solutions appears poised for diverse and transformative applications across various industries. As research and development continue to unlock new formulations and capabilities, these adhesives’ full possibilities are yet to unfold.