Industrial Bonding Adhesives: An In-Depth Guide
Industrial Bonding Adhesives: An In-Depth Guide
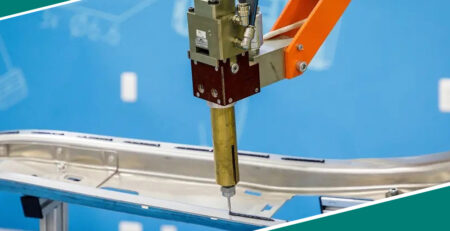
Industrial bonding adhesives are critical in manufacturing, providing a versatile, robust, and reliable solution for joining materials. They are widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction, and many more industries. The advent of new bonding technologies has revolutionized how materials are joined, offering an alternative to traditional mechanical fastening methods like welding, riveting, and screwing. This article explores industrial bonding adhesives, their types, applications, and benefits.
1. Introduction to Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Bonding adhesives in industrial settings are specialized formulations that adhere to various materials, creating solid bonds. These adhesives are designed to hold different surfaces, whether similar or dissimilar, such as metal, plastic, glass, rubber, and composites. Their effectiveness stems from their ability to distribute stress evenly across the bond line, unlike mechanical fasteners, which concentrate stress at specific points.
Key Characteristics
Industrial adhesives offer distinct characteristics:
- High strength: Capable of handling extreme loads and environmental stresses.
- Flexibility: Able to absorb shocks and vibrations without breaking.
- Temperature resistance: Capable of withstanding both high and low-temperature extremes.
- Durability: Long-lasting, offering sustained performance over time.
Advantages Over Traditional Fasteners
- Lightweight: Adhesives eliminate the need for screws, bolts, or rivets, reducing the weight of assemblies.
- Enhanced aesthetics: They provide a clean and smooth surface without visible fasteners.
- Stress distribution: Adhesives spread stress across the joint, reducing the likelihood of failure at specific points.
- Multi-material bonding: Adhesives allow bonding of dissimilar materials that are difficult to join mechanically.
These properties make bonding adhesives an essential tool for modern manufacturing, where efficiency, performance, and material compatibility are prioritized.
2. Types of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Several types of adhesives are used in industrial applications, each designed for specific materials, conditions, and requirements. These can be broadly categorized into five primary types: epoxy, polyurethane, acrylic, cyanoacrylate, and silicone.
2.1 Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are among the most commonly used in industries. They are known for their exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. They consist of two components: a resin and a hardener, which, when mixed, undergo a chemical reaction to form a robust and stable bond.
- Key Features: High tensile strength, excellent temperature, and chemical resistance.
- Applications: The aerospace, automotive, and marine industries use epoxy adhesives for structural bonding, coating, and sealing. They are ideal for bonding metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
2.2 Polyurethane Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives are flexible, making them ideal for applications requiring bonding materials that experience frequent movement or vibration. They provide strong bonds while maintaining elasticity, which is crucial in dynamic environments.
- Key Features: Elasticity, impact resistance, and good performance at low temperatures.
- Applications: Widely used in the construction industry for bonding insulation panels, wood, and glass, as well as in the automotive industry for interior and exterior assembly.
2.3 Acrylic Adhesives
Acrylic adhesives are fast-setting and exhibit excellent adhesion to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and composites. They can bond well even under less-than-ideal surface conditions, making them versatile in industrial applications.
- Key Features: Fast curing, high bond strength, and resistance to oils and chemicals.
- Applications: They are commonly used in the automotive industry, electronics, and signage manufacturing due to their versatility and quick curing time.
2.4 Cyanoacrylate Adhesives
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, often called “super glue,” are single-component adhesives known for their rapid bonding and high strength. They polymerize quickly in moisture, forming a solid bond within seconds.
- Key Features: Fast bonding, high strength, and ease of use.
- Applications: It is ideal for small-scale bonding rubber, plastics, and metals in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive.
2.5 Silicone Adhesives
Silicone adhesives offer high flexibility and resistance to extreme hot and cold temperatures. They are commonly used for sealing applications where flexibility is critical, and materials must maintain their integrity over time.
- Key Features: Flexibility, resistance to extreme temperatures, and UV stability.
- Applications: Used in the electronics industry for sealing components, in construction for glazing and sealing windows, and the automotive industry for gaskets and weatherproofing.
 3. Applications of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
3. Applications of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
The applications of industrial bonding adhesives are vast, spanning many industries requiring solid and durable bonds. Some key sectors include:
3.1 Automotive and Transportation
The automotive industry relies heavily on adhesives for structural and non-structural applications—adhesives bond components such as body panels, windshields, and interior parts. The shift towards lightweight materials like composites and aluminum to improve fuel efficiency has increased the demand for high-performance bonding solutions.
- Adhesives in electric vehicles (EVs): Adhesives play a vital role in EV battery assembly, helping secure and protect battery cells from environmental hazards.
3.2 Aerospace
Adhesives have replaced traditional fasteners, mainly in aerospace, where performance, weight reduction, and durability are critical. High-performance adhesives, such as epoxy and acrylic, bond aircraft structures, wings, and the cabin’s interior components.
- Key benefitsinclude a reduction in weight, improved aerodynamic design, and the ability to bond advanced materials like carbon fiber composites.
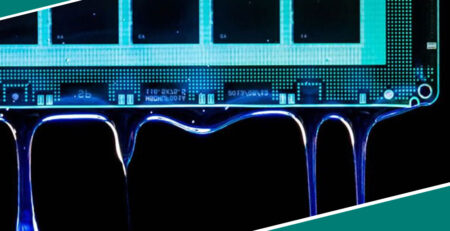
3.3 Electronics and Electrical
The electronics industry utilizes adhesives for various applications, including bonding and sealing components in smartphones, computers, and circuit boards. Adhesives are also used for potting, encapsulating sensitive components, and protecting them from moisture and environmental contaminants.
- Thermal management: Adhesives are also formulated to have thermal conductivity, helping heat dissipation for electronic components.
3.4 Construction and Building Materials
Adhesives bond various materials such as wood, glass, metal, and concrete in the construction sector. They are also applied in projects such as façade installation, flooring, roofing, and even prefabricated building components.
- Green building: Adhesives contribute to sustainable building practices by enabling advanced materials like composite panels and insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings.
3.5 Medical Devices
Medical device manufacturing requires adhesives that meet stringent biocompatibility standards. Adhesives bond materials like plastics, metals, and ceramics in devices such as catheters, syringes, and diagnostic equipment.
- Essential requirements: Adhesives used in this field must be sterilizable, non-toxic, and able to bond with diverse materials used in medical devices.
4. Choosing the Right Industrial Adhesive
Selecting the suitable adhesive for an industrial application involves considering several factors, including the materials to be bonded, the environment in which the adhesive will be used, and the type of load the bond will experience. Below are vital factors to consider when selecting industrial bonding adhesives.
4.1 Substrate Compatibility
Different adhesives are optimized for other materials. For example, epoxy adhesives are ideal for metals and composites, while silicone adhesives are often used for plastics and rubber. Understanding the substrates involved is crucial for achieving a durable bond.
4.2 Environmental Conditions
Adhesives are exposed to various environmental factors, such as moisture, temperature extremes, chemicals, and UV light. The chosen adhesive must be able to withstand these conditions without degrading. Epoxy adhesives are highly resistant to chemicals and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for harsh environments.
4.3 Load and Stress
The type of load (tensile, shear, peel, or cleavage) that the bond will experience dictates the choice of adhesive. Structural adhesives, such as epoxies and polyurethanes, are best for high-load-bearing applications, while silicone adhesives may be more suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
4.4 Application Method
Another critical factor is the application process. Some adhesives are applied manually, while others require automated dispensing systems. The viscosity and curing time of the adhesive adhesive will influence the application method, especially in large-scale industrial settings.
5. The Future of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
The future of industrial bonding adhesives looks promising, with ongoing advancements in material science. A significant innovation is the rise of smart adhesives that change properties in response to environmental factors, such as temperature or pressure. Moreover, sustainability is becoming a key focus, with bio-based adhesives emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional synthetic adhesives.
- Lightweight materials: The growing use of lightweight materials like composites in industries like automotive and aerospace is driving the demand for advanced adhesives capable of bonding dissimilar and lightweight substrates.
- Nanotechnology: Innovations in nanotechnology enhance adhesive performance, providing stronger bonds and faster curing times.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Industrial bonding adhesives have transformed the way materials are joined in manufacturing. Offering advantages such as weight reduction, multi-material bonding, and enhanced durability, adhesives have become an integral part of modern industrial processes. With innovations continuously improving their performance, the role of adhesives in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction is set to expand further. As industries continue to evolve, so will the capabilities of industrial bonding adhesives, ensuring they remain a cornerstone of manufacturing technologies.
For more about a complete guide to Industrial Bonding Adhesives: An In-Depth Guide, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.