The Power of Industrial Bonding Adhesives: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Beyond
The Power of Industrial Bonding Adhesives: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Beyond
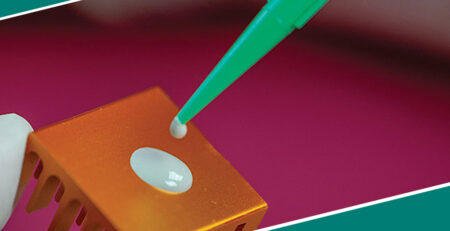
Industrial bonding adhesives are pivotal in modern manufacturing, offering solutions far beyond traditional mechanical fastening methods. From automotive assembly lines to aerospace engineering, these adhesives enhance strength, durability, and efficiency in various applications. The evolution of adhesive technology has opened doors to innovations that have transformed industries, creating more robust, lighter, and durable products.
This comprehensive guide explores the world of industrial bonding adhesives, delving into their types, applications, benefits, and the future trends shaping the industry. Whether you’re in the manufacturing sector or simply curious about the science behind these adhesives, this post will provide in-depth insights into their significance.
Types of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Industrial bonding adhesives come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and material requirements. Understanding the different types of adhesives can help you select the right one for a particular project. Below are the key types of industrial bonding adhesives:
Epoxy Adhesives
- Two-Part Epoxies:Comprise resin and hardeners offer high strength and durability.
- Heat-Resistant Epoxies:Ideal for applications requiring resistance to extreme temperatures.
- Chemical-Resistant Epoxies:These are used in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals occurs every day.
Acrylic Adhesives
- Fast-Curing Acrylics:Provide quick bonding times, essential for high-speed production environments.
- Structural Acrylics: Known for their high shear and impact strength, they are suitable for load-bearing applications.
- UV-Curing Acrylics:These adhesives quickly cure when exposed to ultraviolet light, offering a clear and durable finish.
Polyurethane Adhesives
- Flexible Polyurethanes:Ideal for bonding materials that experience movement or flexing, such as in automotive and construction applications.
- Moisture-Curing Polyurethanes:React with moisture to form strong bonds, often used in wood and plastic bonding.
- Foaming Polyurethanes:Expand during curing to fill gaps, providing additional sealing properties.
Silicone Adhesives
- High-Temperature Silicones:Withstanding extreme heat makes them suitable for electronics and automotive uses.
- Electrical-Grade Silicones:Used in applications requiring insulation and protection from electrical currents.
- Waterproof silicones:Provide excellent water resistance and are commonly used in marine and outdoor applications.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glues)
- Instant Bonding:Known for their ability to bond quickly with various materials.
- Medical-Grade Cyanoacrylates:Used in medical device assembly and skin closure applications.
- High-Viscosity Cyanoacrylates: Designed to bond porous surfaces like wood and leather.
Hot Melt Adhesives
- Low-Temperature Hot Melts:Suitable for delicate materials like fabrics and foams.
- Pressure-Sensitive Hot Melts:Remain tacky after application, allowing bonded parts to be repositioned.
- High-Strength Hot Melts:High-strength hot melts are used in packaging, woodworking, and other industrial applications where a strong bond is required.
 Critical Applications of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Critical Applications of Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Automotive Industry
- Body Assembly: Adhesives bond different parts of the vehicle’s body, replacing traditional welding methods. This results in lighter vehicles with improved fuel efficiency.
- Interior Components:Adhesives attach interior panels, trim, and electronic components, enhancing aesthetics and functionality.
Aerospace Industry
- Composite Bonding:Adhesives are essential in bonding composite materials used in aircraft, contributing to weight reduction and fuel efficiency.
- Structural Bonding:They play a crucial role in the structural integrity of aircraft, ensuring safety and durability under extreme conditions.
Construction Industry
- Facade Bonding:Adhesives bond facade panels, offering an aesthetic finish and enhanced weather resistance.
- Flooring and Tiling:Specialized adhesives are used in flooring and tiling applications, providing solid bonds and long-lasting durability.
Electronics Industry
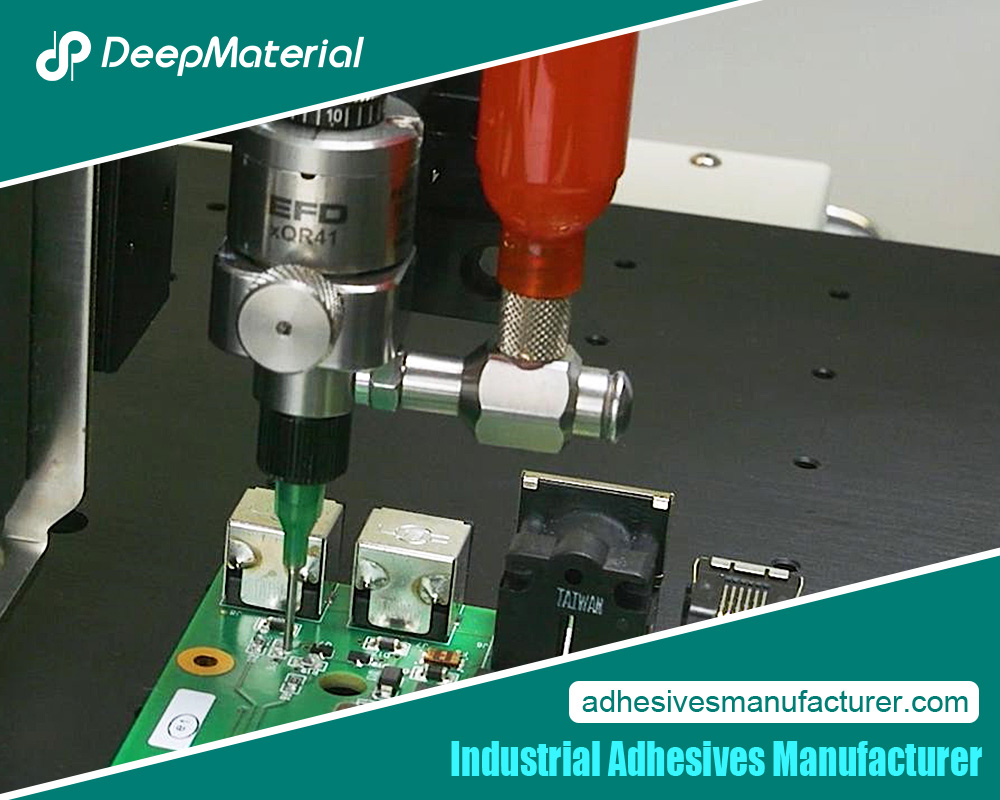
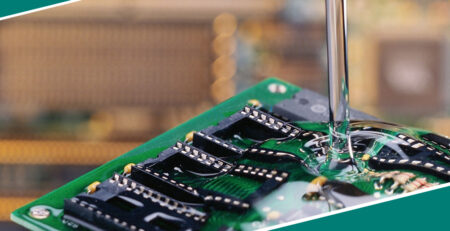
- Component Assembly:Adhesives bond small components on circuit boards, providing solid connections without soldering.
- Encapsulation: They are also used to encapsulate electronic components, protecting them from environmental factors such as moisture and dust.
Medical Devices
- Device Assembly:Adhesives are used in assembling medical devices, offering biocompatibility and strong bonds essential for patient safety.
- Wound Care:Special adhesives are used in wound care products, providing secure and painless adhesion to the skin.
Advantages of Using Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Enhanced Strength and Durability
- Industrial adhesives provide strong bonds that withstand extreme conditions, including high stress, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure.
Lightweight Solutions
- Replacing traditional fasteners with adhesives reduces the final product’s weight, leading to energy efficiency and cost savings, particularly in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Versatility in Material Bonding
- Adhesives can bond various materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and composites, offering flexibility in design and manufacturing processes.
Improved Aesthetics
- Adhesives eliminate the need for visible fasteners, resulting in cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing finishes in products ranging from vehicles to consumer electronics.
Cost Efficiency
- Adhesives can reduce manufacturing costs by streamlining assembly processes and eliminating the need for complex tooling and labor-intensive fastening methods.
Environmental Benefits
- Many modern adhesives are formulated to be environmentally friendly, with low VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions and reduced energy consumption during the curing process.
Challenges and Considerations in Using Industrial Bonding Adhesives
Surface Preparation
- Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving a solid bond. Oil, dust, and moisture contaminants can significantly reduce adhesive performance.
Curing Time
- Some adhesives require extended curing times, which can slow down production processes. Choosing a suitable adhesive with an appropriate curing time is essential for efficiency.
Temperature Sensitivity
- While many adhesives offer excellent temperature resistance, some may degrade under extreme heat or cold. Therefore, selecting a suitable adhesive for specific environmental conditions is critical.
Material Compatibility
- Not all adhesives are suitable for all materials. Ensuring compatibility between the adhesive and the bonded materials is crucial for achieving the desired performance.
Safety Considerations
- Handling and applying adhesives require proper safety precautions, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adequate ventilation to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
Future Trends in Industrial Bonding Adhesives
As technology advances, the industrial bonding adhesives market is poised for significant growth and innovation. Below are some key trends expected to shape the future of this industry:
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Adhesives
- Bio-based Adhesives:Development of adhesives derived from renewable resources, reducing the environmental impact.
- Low VOC Emissions:Adhesives with reduced volatile organic compounds (VOC) to meet stricter environmental regulations.
- Recyclability:Adhesives that allow for easier disassembly of bonded materials, facilitating recycling.
Smart Adhesives
- Self-Healing Adhesives:Materials that can repair themselves after damage, extending the lifespan of bonded products.
- Responsive Adhesives:These change properties in response to external stimuli, such as temperature or moisture, offering versatility in various applications.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
- 3D Printing with Adhesives:Integrating adhesives in additive manufacturing processes enables the production of complex bonded structures through 3D printing.
- Nano-Technology: Nano-technology involves the incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance adhesive properties such as strength, conductivity, and durability.
Industry 4.0 Integration
- IoT-Enabled Adhesives:Development of adhesives with embedded sensors to monitor the bonding process and performance over time.
- Automated Application Systems:Advancements in robotics and AI are improving the precision and efficiency of adhesive applications in manufacturing through automated application systems.
Performance Enhancements
- High-Temperature Adhesives:Developing adhesives that can withstand extreme temperatures, expanding their use in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Ultra-Strong Bonds:Innovations lead to superior bonding strength adhesives, capable of replacing traditional mechanical fasteners in more demanding applications.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Industrial bonding adhesives have become indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled strength, durability, and versatility. From automotive assembly to aerospace engineering, these adhesives have transformed how products are designed and manufactured. As technology continues to evolve, the future of industrial adhesives promises even more significant innovations, driving industries towards more sustainable, efficient, and advanced bonding solutions.
For more about the power of industrial bonding adhesives: revolutionizing manufacturing and beyond, you can pay a visit to Deepmaterial at https://www.adhesivesmanufacturer.com/ for more info.